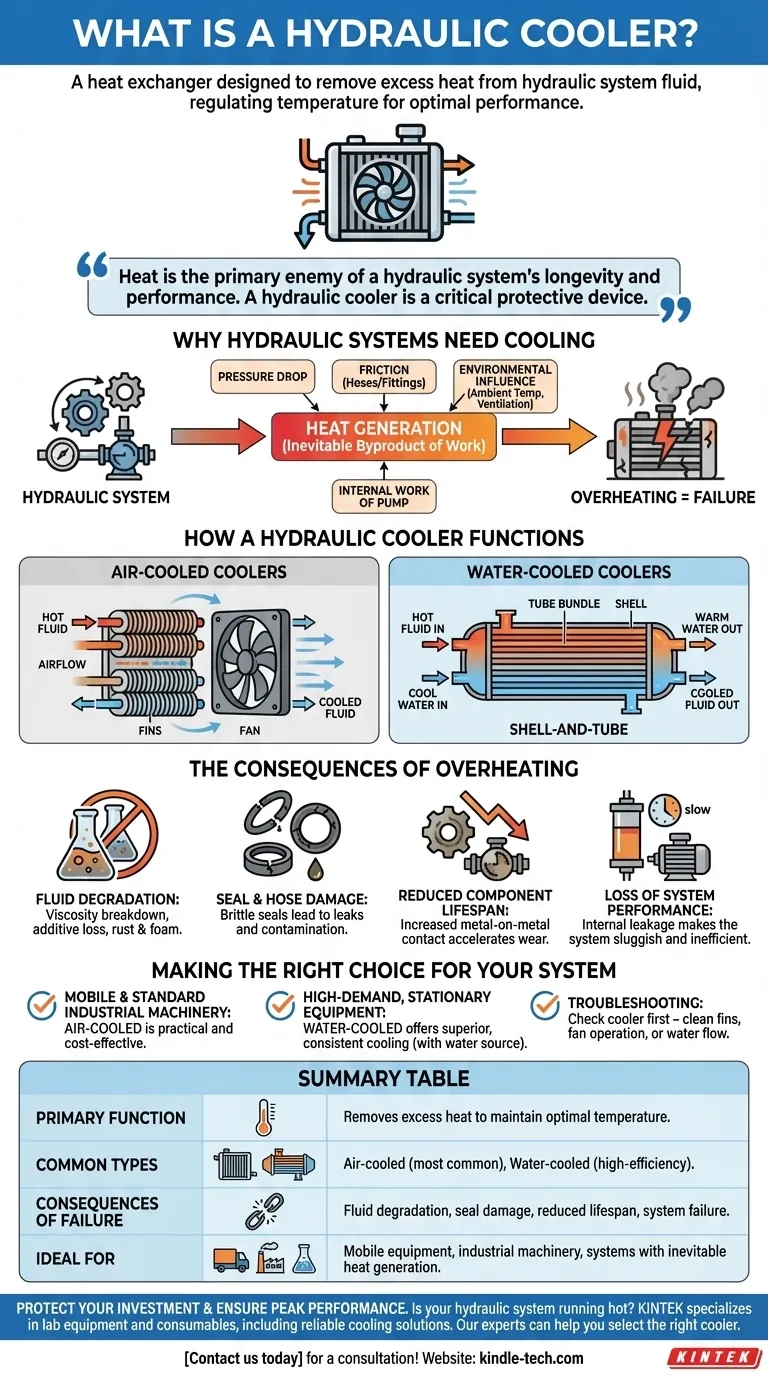
In simple terms, a hydraulic cooler is a heat exchanger designed specifically to remove excess heat from the fluid in a hydraulic system. Its sole purpose is to regulate the fluid's temperature, keeping it within the optimal operating range recommended by the equipment manufacturer. Without this crucial component, the system would quickly overheat, leading to component damage and operational failure.
Heat is the primary enemy of a hydraulic system's longevity and performance. A hydraulic cooler is not merely an accessory; it is a critical protective device that safeguards the fluid, seals, and mechanical components from the destructive effects of excessive temperature.
Why Hydraulic Systems Need Cooling
Understanding why a cooler is necessary begins with understanding how hydraulic systems generate heat in the first place. This heat is an unavoidable byproduct of energy conversion.
The Inevitable Byproduct of Work
No machine is 100% efficient. As the hydraulic pump forces fluid through the system to do work (like lifting a load or clamping a part), some energy is always lost. This lost energy is converted directly into heat.
Sources of System Heat
The main sources of heat include the pressure drop across valves, friction from fluid moving through hoses and fittings, and the internal work of the pump itself. Every restriction and every change in direction adds a small amount of heat to the fluid.
Environmental Influence
The ambient temperature of the operating environment also plays a significant role. A system operating in a hot climate or a confined, poorly ventilated space will absorb heat from its surroundings, compounding the internal heat generation.
How a Hydraulic Cooler Functions
A hydraulic cooler works on the fundamental principle of heat transfer: moving thermal energy from the hot hydraulic fluid to a cooler medium, which is typically either air or water.
Air-Cooled Coolers
This is the most common type, analogous to a car's radiator. Hot hydraulic fluid is pumped through a series of tubes that are covered in thin metal fins. A fan, which can be electric, hydraulic, or engine-driven, blows ambient air across these fins. The heat transfers from the fluid, through the tubes and fins, and is carried away by the airflow.
Water-Cooled Coolers
Often used in industrial or marine settings where a consistent source of cool water is available, these are generally more efficient. A common design is the shell-and-tube cooler. The hydraulic fluid flows through a bundle of small tubes, while cooler water flows through the outer shell surrounding them, absorbing the heat.
The Consequences of Overheating
Operating a hydraulic system without proper cooling is a direct path to premature and costly failure. The damage caused by excessive heat is progressive and affects the entire system.
Fluid Degradation
Heat is the number one enemy of hydraulic oil. It breaks down the fluid's viscosity (its thickness), causing it to become too thin to lubricate properly. It also degrades the essential additives that prevent rust, corrosion, and foaming.
Seal and Hose Damage
Excessive temperatures cause rubber seals, O-rings, and hoses to become hard and brittle. This leads to leaks, which can cause fluid loss, introduce contaminants, and result in catastrophic component failure.
Reduced Component Lifespan
Pumps, motors, and valves all rely on the hydraulic fluid for lubrication and cooling. When the fluid is too hot and thin, metal-on-metal contact increases, accelerating wear and drastically shortening the life of these expensive components.
Loss of System Performance
As fluid becomes thinner, internal leakage within pumps, motors, and cylinders increases. This means the system becomes sluggish, less responsive, and less efficient, wasting energy and reducing its ability to perform work.
Making the Right Choice for Your System
Selecting and maintaining the right cooling solution is essential for reliability. Your decision should be based on the system's application and environment.
- If your primary focus is mobile equipment or standard industrial machinery: An air-cooled heat exchanger is almost always the most practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is high-demand, stationary equipment in a plant setting: A water-cooled system may provide superior and more consistent cooling performance, provided a water source is available.
- If you are troubleshooting an overheating system: The cooler should be one of the first things you check. Ensure air-cooler fins are clean and the fan is operating correctly, or that water is flowing properly through a water-cooled unit.
Ultimately, viewing a hydraulic cooler as a vital investment in system longevity is the key to reliable and efficient operation.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Removes excess heat from hydraulic fluid to maintain optimal temperature. |
| Common Types | Air-cooled (most common, like a radiator) and Water-cooled (high-efficiency). |
| Consequences of Failure | Fluid degradation, seal damage, reduced component lifespan, and system failure. |
| Ideal For | Mobile equipment, industrial machinery, and any system where heat generation is inevitable. |
Protect your investment and ensure peak performance. Is your hydraulic system running hot? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including reliable cooling solutions for your laboratory's hydraulic needs. Our experts can help you select the right cooler to safeguard your equipment from costly downtime and damage.
Contact us today for a consultation and keep your systems running cool and efficiently!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Hydraulic Diaphragm Lab Filter Press for Laboratory Filtration
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the technical advantages of using a manual hydraulic press with carbide dies? Achieve High-Density Green Bodies
- What is the significance of XRF in forensic science? Achieve Rapid, Non-Destructive Elemental Analysis
- What function does a laboratory hydraulic press serve in the preparation of LLZTO ceramic electrolyte pellets?
- What is the function of a laboratory hydraulic press in C/C-SiC preparation? Achieve Precision CFRP Green Body Densification
- How are biomass pellets formed? A Step-by-Step Guide to Engineered Biomass Energy
- How is high temperature controlled in the hydraulic system? Prevent Damage and Boost Efficiency
- How many pounds of force does a hydraulic press have? Find Your Ideal Tonnage for Any Application
- What is the maximum psi for a hydraulic press? Understand Tonnage, Not Just Pressure

















