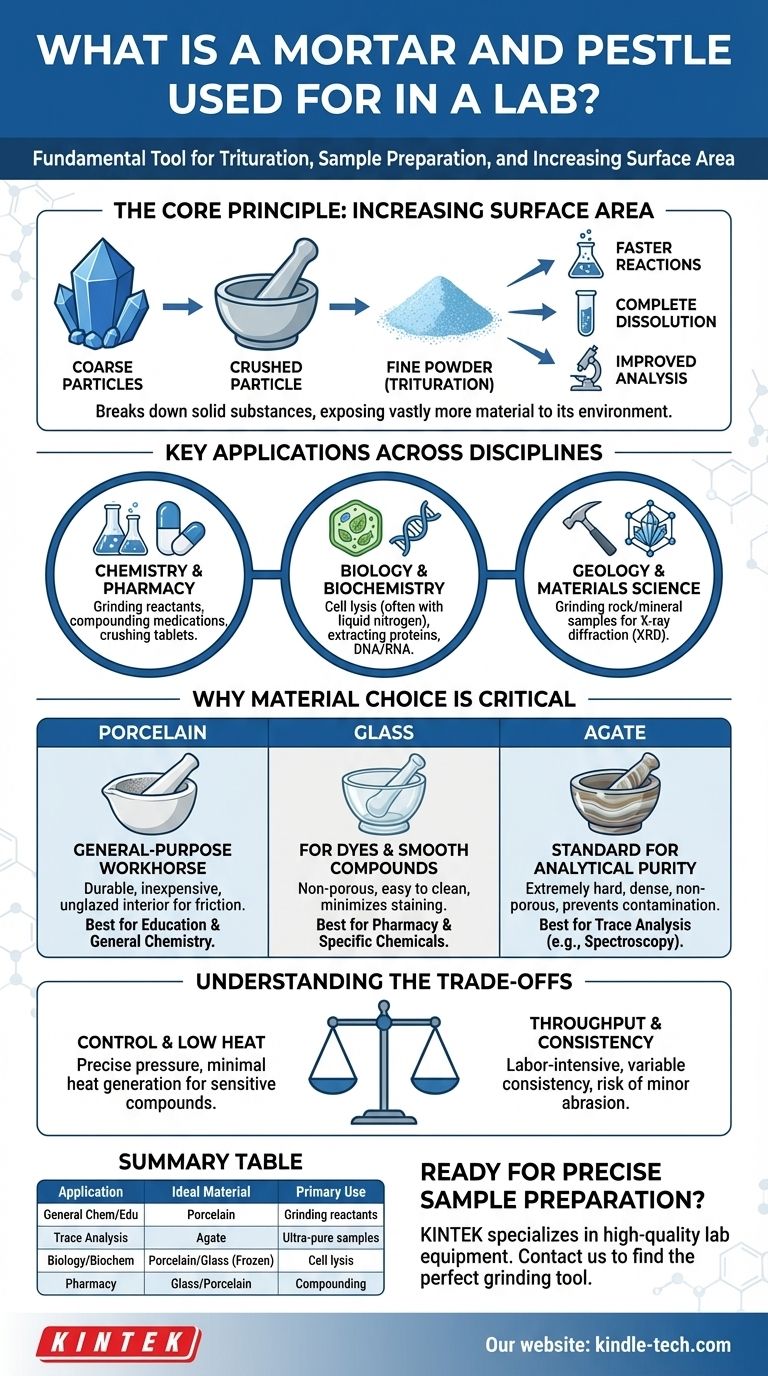
In a laboratory, a mortar and pestle is a fundamental tool used to crush, grind, and mix solid substances. This process, known as trituration, breaks down coarse particles into a fine, uniform powder, dramatically increasing the material's surface area for subsequent steps like chemical reactions, dissolution, or analysis.
The true value of this ancient tool in a modern lab lies not in its simplicity, but in the precise control it offers over particle size, its ability to process samples without generating excessive heat, and the critical role its material plays in preventing sample contamination.

The Core Principle: Increasing Surface Area
The primary function of a mortar and pestle is to perform mechanical size reduction on a solid sample. This is essential for a wide range of scientific procedures.
What is Trituration?
Trituration is the technical term for reducing a substance to fine particles by grinding. The pestle (the club-shaped tool) is used to apply pressure and shear force against the sample in the mortar (the bowl).
This is achieved through a combination of crushing with a downward force and grinding with a circular motion, ensuring the particles are broken down efficiently.
Why Surface Area Matters
Grinding a solid from a large crystal or chunk into a fine powder exposes vastly more of the substance to its environment.
This is critical for accelerating chemical reactions, ensuring a substance dissolves completely and quickly, and creating a homogenous mixture of two or more solids.
Key Applications Across Scientific Disciplines
While the action is simple, the applications of the mortar and pestle are diverse and vital across many fields of study.
In Chemistry and Pharmacy
Chemists use this tool to grind reactants together, sometimes initiating a solid-state reaction or ensuring a mixture is perfectly uniform before being dissolved in a solvent.
In pharmacy, it's the classic tool for compounding—crushing tablets or mixing powdered ingredients to formulate personalized medications.
In Biology and Biochemistry
To analyze the contents of a cell, you first have to break it open. A mortar and pestle is a common method for cell lysis, especially for plant and animal tissues.
Often, the tissue sample and the mortar are first frozen with liquid nitrogen. This makes the tissue brittle and easy to fracture, and the low temperature protects sensitive molecules like DNA, RNA, and proteins from degradation.
In Geology and Materials Science
Geologists grind rock and mineral samples into a fine powder for analytical techniques like X-ray diffraction (XRD). This preparation ensures the analysis is representative of the entire sample, not just its surface.
Why Material Choice is Critical
The material of the mortar and pestle is not an afterthought; it is a critical variable that determines its proper use and prevents contamination.
Porcelain: The General-Purpose Workhorse
Porcelain sets are common, durable, and relatively inexpensive. The interior grinding surface is typically left unglazed to provide the necessary friction for efficient grinding. They are excellent for most educational and general chemistry applications.
Glass: For Dyes and Smooth Compounds
Glass mortars and pestles have a smooth, non-porous surface, which makes them easy to clean and minimizes staining. They are ideal for working with chemicals that might absorb into or react with porcelain.
Agate: The Standard for Analytical Purity
Agate is an extremely hard, dense, and non-porous material. Mortars and pestles made from it are the standard for preparing samples for highly sensitive analysis (like spectroscopy).
Their hardness ensures that the sample is ground down without the mortar and pestle itself shedding particles, which would contaminate the sample and compromise analytical results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
In an age of high-tech equipment, the manual mortar and pestle holds its place because of its unique advantages and disadvantages compared to electric grinders or mills.
The Advantage of Control and Low Heat
The primary benefit of a manual mortar and pestle is control. The user can carefully adjust the pressure and motion to achieve the desired particle size without generating significant heat, which is crucial for temperature-sensitive compounds.
The Limitations of Throughput and Consistency
Manual grinding is labor-intensive and not suitable for large quantities of material. Achieving perfectly consistent particle size between different batches can also be challenging, as it depends on operator technique.
The Inescapable Risk of Contamination
No matter how hard the material, a minuscule amount of the mortar and pestle can be abraded into the sample. While negligible for many applications, this is why choosing the right material (like agate for trace analysis) is paramount.
Selecting the Right Mortar and Pestle for Your Task
Choosing the correct tool requires understanding the goal of your sample preparation.
- If your primary focus is general chemistry or educational use: A porcelain set offers the best balance of durability, effectiveness, and cost.
- If your primary focus is preventing all sample contamination for sensitive analysis: An agate mortar and pestle is the necessary professional investment.
- If your primary focus is grinding biological tissue for molecular extraction: A porcelain or glass set, pre-chilled with liquid nitrogen, is a standard and effective method.
Ultimately, understanding these principles transforms the mortar and pestle from a simple crushing tool into a precision instrument for reliable scientific work.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Use | Ideal Material |
|---|---|---|
| General Chemistry/Education | Grinding chemical reactants, mixing powders | Porcelain |
| Trace Analysis (e.g., Spectroscopy) | Preparing ultra-pure samples to prevent contamination | Agate |
| Biology/Biochemistry | Grinding frozen tissues for cell lysis (with liquid nitrogen) | Porcelain or Glass |
| Pharmacy | Compounding medications, crushing tablets | Glass or Porcelain |
Ready to achieve precise and contamination-free sample preparation?
The right mortar and pestle is crucial for reliable results in chemistry, biology, and materials science. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including durable porcelain, non-porous agate, and easy-to-clean glass mortars and pestles, to meet your specific application needs.
Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to find the perfect grinding tool for your laboratory. Let our experts help you enhance your sample preparation workflow and ensure analytical accuracy.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
People Also Ask
- What is the function of an Agate Mortar and Pestle in sodium battery preparation? Ensure Contaminant-Free Mixing
- Why is an alumina mortar used for grinding dried Yttrium Oxide precursor materials? Ensure Maximum Purity and Quality
- Why is an agate mortar and pestle preferred for grinding MAX phase? Ensure Sample Purity & Zero Contamination
- What are the different types of laboratory mills? Choose the Right Grinder for Your Sample Material
- What is the function of using an agate mortar during the precursor mixing stage of sulfide solid electrolyte synthesis?



















