In metal casting, a mold is the essential tool that defines an object's final shape. It is a specially prepared container with a hollow cavity that receives molten metal. As the metal cools and solidifies, it conforms to the shape of this cavity, creating a finished or semi-finished part.
The mold is best understood as the "negative space" of the part you intend to create. Its internal cavity is a precise, inverse replica of the final object, making it the single most critical element in the entire casting process.

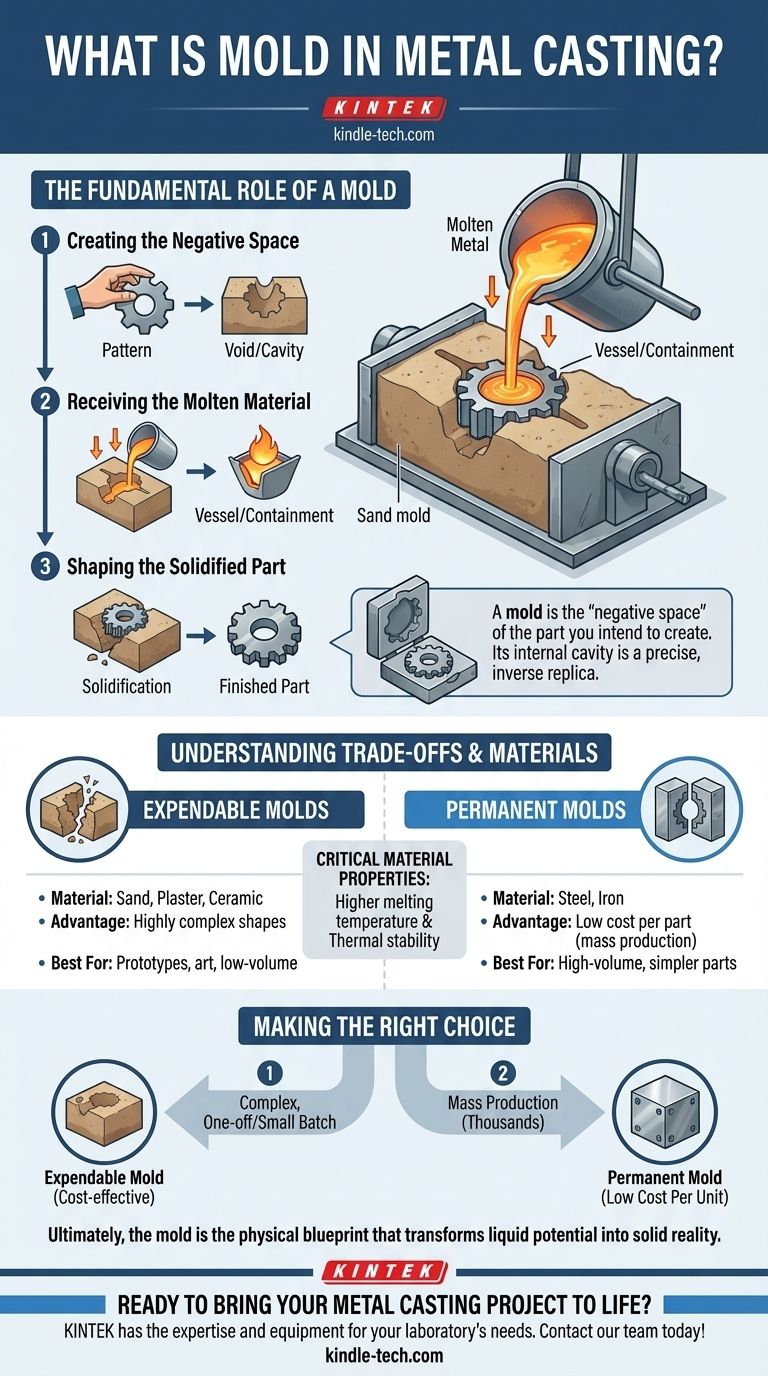
The Fundamental Role of a Mold in Casting
To truly grasp the concept, it's useful to think of the mold's function as a three-step sequence. It is designed to create a void, contain a liquid, and then release a solid.
Creating the Negative Space
The core of any mold is its cavity. This is not just a random hole; it is a meticulously designed void that is the inverse of the desired part.
For more complex geometries, this cavity is often created using a pattern—a full-size model of the part itself. The mold material is then formed around this pattern, which is later removed to leave the correct negative impression.
Receiving the Molten Material
The mold's second job is to act as a vessel. It must be able to withstand the extreme temperatures of liquid metal without deforming, cracking, or reacting chemically with the alloy.
This containment ensures the molten metal completely fills every feature of the cavity, from large surfaces to fine details.
Shaping the Solidified Part
Finally, as the liquid metal loses heat to the surrounding mold, it solidifies. The mold holds the metal in its precise shape during this transition from liquid to solid.
Once cooled, the mold is opened or broken away, revealing the newly formed metal object, which is now a positive replica of the mold's cavity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Materials
The choice of mold type and material is one of the most significant decisions in casting, directly impacting cost, production speed, and part quality. The primary distinction is between expendable and permanent molds.
Expendable Molds
These molds are destroyed in the process of removing the casting. They are typically made from materials like sand, plaster, or ceramic.
Their main advantage is the ability to produce highly complex shapes, as the mold can be broken away from intricate features. This makes them ideal for low-volume production, prototypes, and art.
Permanent Molds
These molds are machined from metal (like steel or iron) and are designed to be used thousands of times. Processes like die casting use permanent molds.
While the initial cost of creating a permanent mold is very high, the cost per part becomes extremely low in mass production. They are best suited for simpler, high-volume parts.
Critical Material Properties
The material used for the mold itself is crucial. It must have a higher melting temperature than the metal being cast and possess thermal stability to resist cracking from the shock of the hot liquid metal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the mold is the first step in selecting the right manufacturing process. Your project's goal will determine the type of mold you need.
- If your primary focus is a complex, one-off part or a small batch: An expendable mold, such as one made from sand, is the most logical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing thousands of identical parts: Investing in a durable, permanent metal mold will yield the lowest cost per unit over the long term.
Ultimately, the mold is not just a container; it is the physical blueprint that transforms liquid potential into solid reality.
Summary Table:
| Mold Type | Material | Key Advantage | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Expendable | Sand, Plaster, Ceramic | Creates highly complex shapes | Prototypes, art, low-volume production |
| Permanent | Steel, Iron | Low cost per part in mass production | High-volume, simpler parts |
Ready to bring your metal casting project to life? The right mold is critical to your success. Whether you need a durable, high-volume solution or a flexible mold for a complex prototype, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your laboratory's needs. Contact our team today to discuss the best mold solution for your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold
- Ball Press Mold for Lab
- Square Bidirectional Pressure Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using PEEK molds for sulfide all-solid-state batteries? High Performance and Insulation
- Why are custom pressure molds used during the hot pressing process for solid polymer electrolytes?
- How do custom graphite molds contribute to Al-20% Si/graphite flake composites? Optimize Microstructure & Conductivity
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- What are the primary functions of graphite molds in NiCr powder metallurgy? Optimize Your Composite Material Density

















