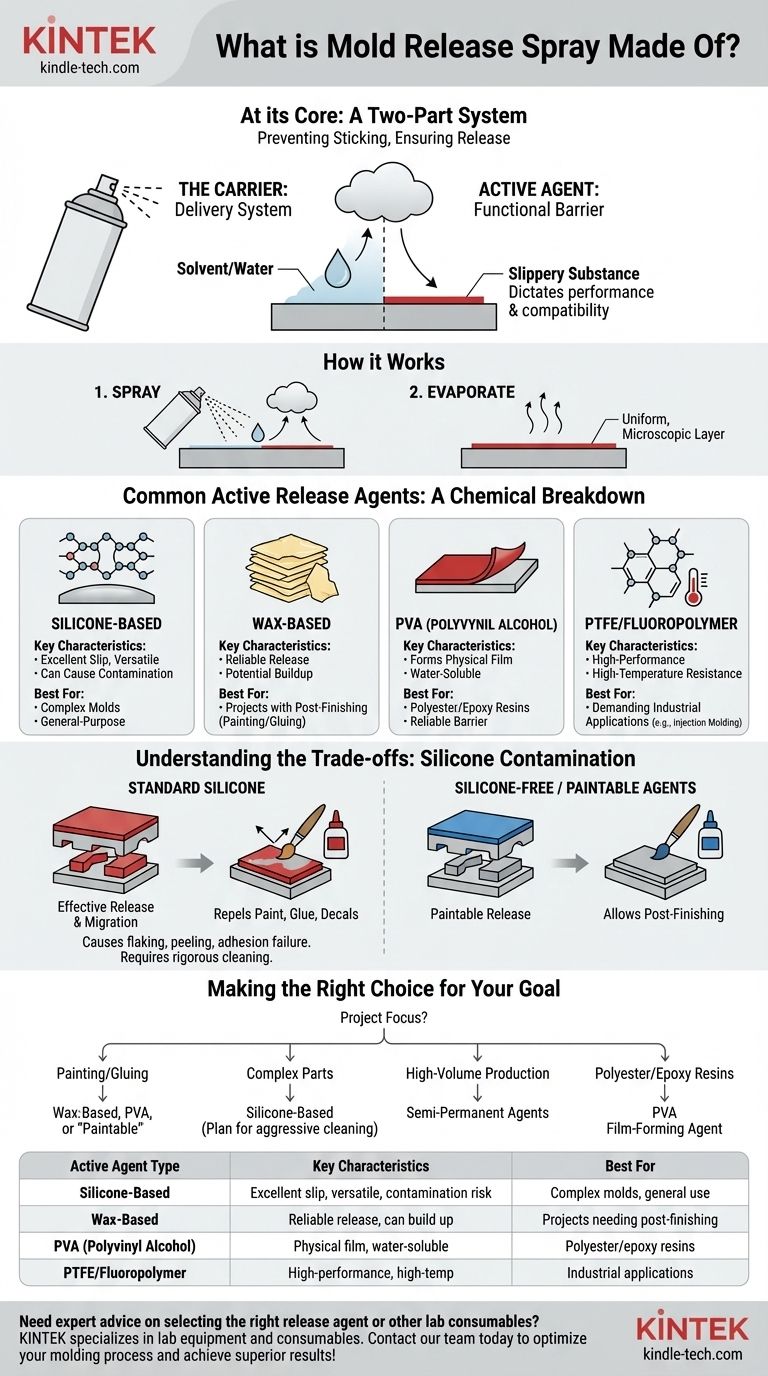
At its core, mold release spray is a two-part system designed for one purpose: to prevent a cast object from sticking to its mold. It combines an active release agent with a carrier liquid that evaporates after application, leaving behind a micro-thin film that acts as a barrier.
The specific chemical used as the active release agent is the most critical factor. This ingredient dictates the spray's performance, its compatibility with your materials, and whether it will interfere with post-production steps like painting or gluing.

How Mold Release Works: The Two Key Components
A release spray's function is simple but elegant. It delivers a non-stick coating evenly across a mold surface. This is achieved through the interaction of its two main components.
The Carrier: A Delivery System
The bulk of the liquid in an aerosol can is the carrier, often a solvent or, in some cases, water. Its only job is to dissolve the active agent and transport it out of the can in a fine mist.
Once sprayed onto the mold, the carrier quickly evaporates. This leaves behind a perfectly uniform, microscopic layer of the active release agent.
The Active Agent: The Functional Barrier
This is the component that does the real work. The active agent is the slippery substance left on the mold surface. Its chemical makeup determines how well it works, how durable it is, and for what applications it is best suited.
There are several common families of active agents.
Common Types of Active Release Agents
While many formulations exist, most fall into one of a few key chemical categories. The simple term "wax" only describes one type of a much broader field.
Silicone-Based Agents
Silicone is arguably the most common and versatile release agent. It is extremely effective, provides excellent slip, and works well for intricate or complex molds. It is the go-to for general-purpose molding.
Wax-Based Agents
This category includes natural waxes (like carnauba) and synthetic waxes. They provide a reliable release but can sometimes build up in the mold over many uses, potentially obscuring fine details. They are often preferred when post-finishing is required.
PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol) Agents
PVA is a water-soluble plastic that is applied to a mold and allowed to dry, forming a physical film. It is an excellent barrier, especially for polyester or epoxy resins, but it is a distinct layer that must be washed off the final part.
PTFE and Fluoropolymer Agents
Often known by the trade name Teflon, these are high-performance agents that offer exceptional release properties and high-temperature resistance. They are common in demanding industrial applications like injection molding.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Silicone Contamination
The single most important factor to consider when choosing a release agent is its potential impact on your final part.
The Problem with Silicone
Standard silicone release agents are incredibly effective because they migrate and transfer very easily. A tiny amount will transfer from the mold to your cast part.
While this ensures a clean release, that same microscopic layer of silicone will repel almost anything you try to apply to the part later. This is known as silicone contamination.
Impact on Post-Finishing
If you plan to paint, glue, or apply decals to your cast part, using a standard silicone release spray will cause these finishes to flake, peel, or fail to adhere. The paint simply cannot bond to the silicone-contaminated surface.
You must either use a silicone-free release agent or undertake a rigorous cleaning and preparation process on the part before attempting any finishing work. Some manufacturers offer "paintable" release agents designed to avoid this issue.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your release agent based on your project's final requirements, not just the casting process itself.
- If your primary focus is painting or gluing the final part: Use a wax-based, PVA, or a specifically labeled "paintable" or "silicone-free" release agent.
- If your primary focus is the easiest possible release for a complex part: A silicone-based agent provides the best slip, but you must plan for aggressive surface cleaning if you intend to finish the part.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: Investigate semi-permanent release agents that bond to the mold and last for many cycles, reducing buildup and reapplication time.
- If your primary focus is casting with polyester or epoxy resins: A PVA film-forming release agent is often the most reliable choice for a flawless surface.
Understanding the chemistry of your release agent empowers you to prevent problems before they start.
Summary Table:
| Active Agent Type | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Silicone-Based | Excellent slip, versatile, can cause contamination | Complex molds, general-purpose use |
| Wax-Based | Reliable release, can build up on mold | Projects requiring post-finishing (painting/gluing) |
| PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol) | Forms a physical film, water-soluble | Polyester/epoxy resins, reliable barrier |
| PTFE/Fluoropolymer | High-performance, high-temperature resistance | Demanding industrial applications (e.g., injection molding) |
Need expert advice on selecting the right release agent or other lab consumables for your specific materials and finishing requirements?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you choose the perfect products to ensure flawless casts and successful post-processing. Contact our team today to optimize your molding process and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
People Also Ask
- What is the technical significance of selecting hardened stainless steel grinding balls? Optimize Energy and Purity
- Why is an industrial-grade ultrasonic cleaner required for LDH conversion? Ensure Pure Crystal Growth & Adhesion
- What monitoring function do graphite rams perform during vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Eu:Y2O3 Ceramic Densification
- What is the use of a vacuum evaporator? Transform Waste into Value and Achieve ZLD
- What are the primary functions of a high-purity quartz tube? Ensure Peak Microwave Plasma Reactor Performance
- How does an electric magnetic stirrer facilitate potassium methoxide catalysts? Boost Corn Oil Transesterification
- Why are pressure switches important? Essential for Automation, Safety & Efficiency
- Why are zirconia (ZrO2) grinding balls and jars preferred for Ni-Co-Al milling? Ensure Pure Alloy Performance
