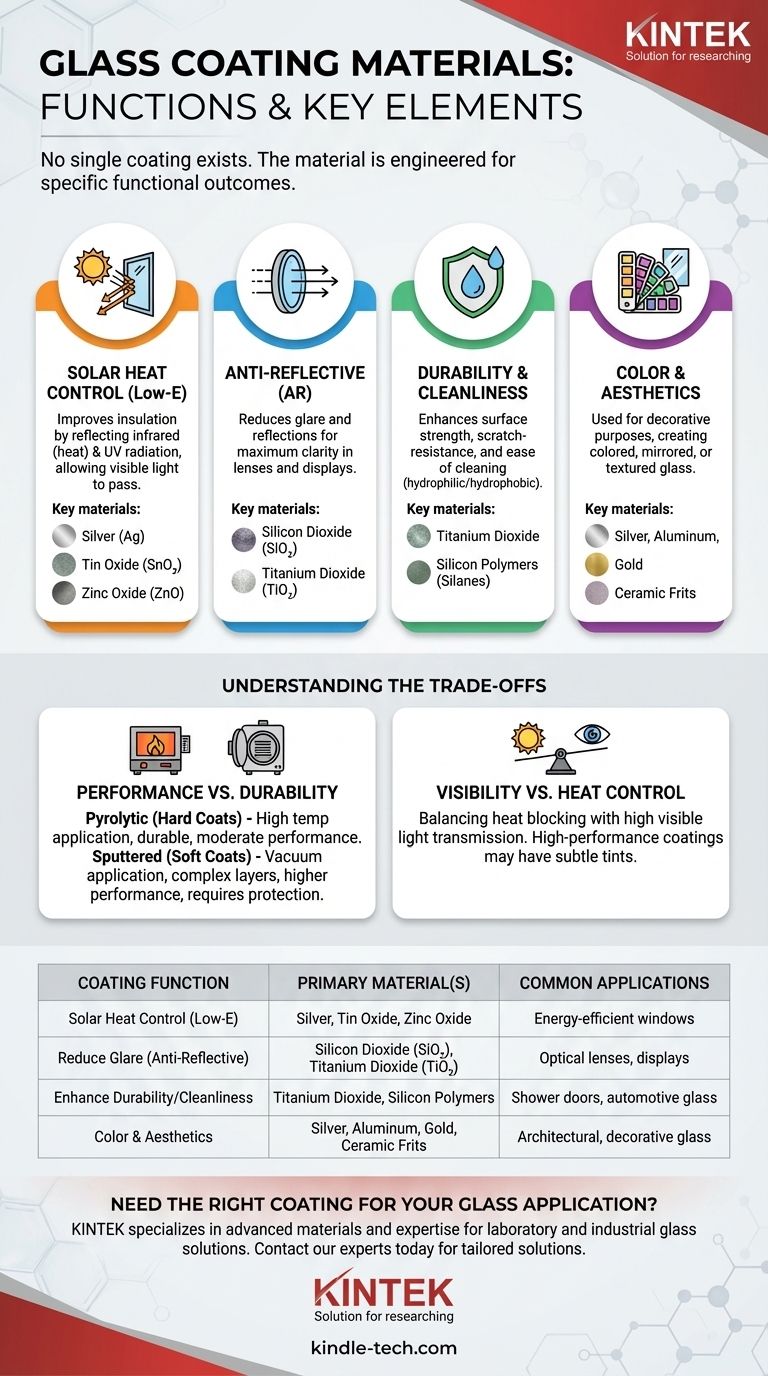
To put it simply, there is no single coating material for glass. The specific material used is entirely dependent on the desired outcome, whether that's controlling heat, reducing glare, improving durability, or simply adding color. These coatings are typically microscopic layers of metals, metal oxides, or polymers engineered to manipulate the properties of the glass surface.
The core principle to understand is that glass coatings are not just a protective layer; they are functional, microscopic films designed to selectively filter, reflect, or repel energy and matter, transforming standard glass into a high-performance material.

The Functional Goals of Glass Coatings
Glass in its natural state is highly transparent but offers little control over energy transfer or reflection. Coatings are applied to fundamentally change these properties. The choice of material is always dictated by the function it needs to perform.
To Control Solar Heat (Low-E Coatings)
The most common high-performance coatings are Low-Emissivity (Low-E) coatings, designed to improve insulation. They reflect invisible infrared (heat) and UV radiation while allowing visible light to pass through.
The primary material for this function is an incredibly thin layer of silver. Because silver is delicate, it is typically sandwiched between protective layers of transparent metal oxides like tin oxide or zinc oxide.
To Reduce Glare and Reflections (Anti-Reflective Coatings)
Anti-reflective (AR) coatings are essential for optical lenses, electronic displays, and museum glass where maximum clarity is critical. They work by using multiple layers to cause destructive interference for reflected light waves.
These coatings are almost always made from transparent metal oxides. Common materials include silicon dioxide (SiO₂) and titanium dioxide (TiO₂), applied in precise, alternating layers of high and low refractive indices.
To Enhance Durability and Cleanliness
Coatings can make glass surfaces stronger, scratch-resistant, and easier to clean. These are often used for shower doors, building exteriors, and automotive windshields.
For self-cleaning and "easy-clean" applications, hydrophilic (water-attracting) coatings like titanium dioxide or hydrophobic (water-repelling) coatings made of silicon-based polymers (silanes) are used. These cause water to either sheet off uniformly or bead up and roll away, carrying dirt with it.
To Create Color and Aesthetics
Coatings are also used for purely decorative purposes, such as creating colored or mirrored glass for architecture and interior design.
Mirrored coatings are typically made from metals like silver, aluminum, or gold. Colored glass is often produced using ceramic frits—finely ground glass mixed with inorganic pigments—that are fused to the glass surface at high temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a coating involves balancing performance, durability, and cost. The application method plays a significant role in this balance.
Performance vs. Durability
There are two primary methods of application. Pyrolytic coatings (hard coats) are applied during the glass manufacturing process at high temperatures. They are extremely durable but offer moderate performance.
Sputtered coatings (soft coats) are applied after manufacturing in a vacuum chamber. This method allows for more complex and higher-performing layers (like Low-E with multiple silver layers) but results in a more delicate surface that must be protected inside a double-glazed window unit.
Visibility vs. Heat Control
A common trade-off, especially with Low-E coatings, is between blocking solar heat and maintaining high visible light transmission.
Extremely high-performance heat-blocking coatings can sometimes have a subtle, faint color tint or appear slightly more reflective than uncoated glass. The goal of coating engineers is to minimize this effect while maximizing energy efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on the primary problem you are trying to solve with the glass.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency in a home or office: You need a Low-Emissivity (Low-E) coating, which uses layers of silver and metal oxides to reflect heat.
- If your primary focus is maximum clarity for a display, camera lens, or picture frame: You need an anti-reflective (AR) coating made from multiple layers of metal oxides like silicon dioxide.
- If your primary focus is low maintenance for a shower door or building exterior: You need a hydrophilic or hydrophobic coating, often based on titanium dioxide or silicon polymers.
Ultimately, the material itself is just a tool to achieve a specific functional goal for the glass.
Summary Table:
| Coating Function | Primary Material(s) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Heat Control (Low-E) | Silver, Tin Oxide, Zinc Oxide | Energy-efficient windows |
| Reduce Glare (Anti-Reflective) | Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂), Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂) | Optical lenses, displays |
| Enhance Durability/Cleanliness | Titanium Dioxide, Silicon Polymers | Shower doors, automotive glass |
| Color & Aesthetics | Silver, Aluminum, Gold, Ceramic Frits | Architectural, decorative glass |
Need the Right Coating for Your Glass Application?
Whether you're developing energy-efficient windows, optical components, or durable lab equipment, the correct glass coating is critical to performance. KINTEK specializes in providing advanced materials and expertise for laboratory and industrial glass solutions.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our tailored coating solutions can enhance your project's efficiency, clarity, and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
- Aluminum-Plastic Flexible Packaging Film for Lithium Battery Packaging
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- How long does diamond coating last? Maximize Lifespan with the Right Coating for Your Application
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance
- How thick is CVD diamond coating? Balancing Durability and Stress for Optimal Performance
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose

















