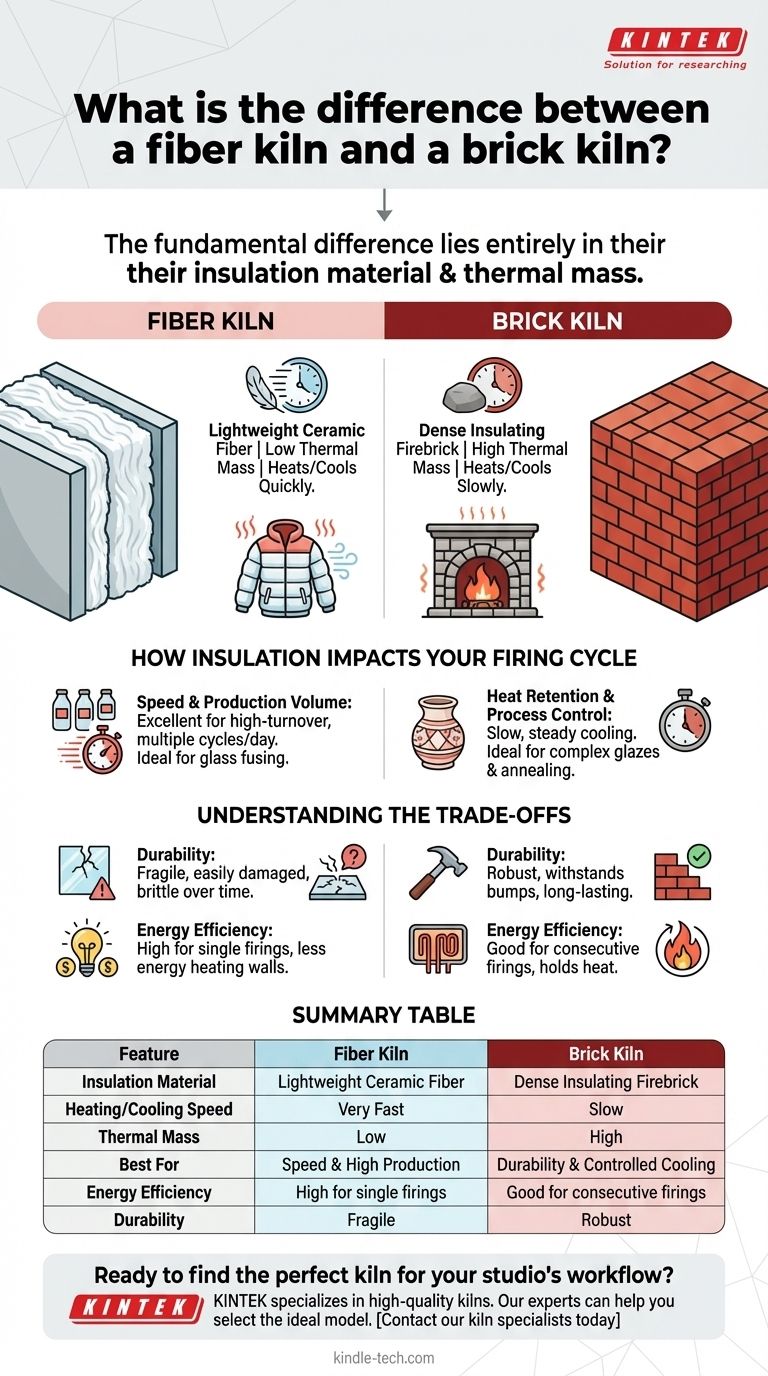
The fundamental difference between a fiber kiln and a brick kiln lies entirely in their insulation material, which dictates how they handle heat. A fiber kiln uses lightweight ceramic fiber, allowing it to heat and cool very quickly, while a brick kiln uses dense insulating firebrick that heats and cools much more slowly. This single distinction has significant consequences for firing speed, energy efficiency, and durability.
The choice between a fiber and a brick kiln is a strategic one. Fiber kilns prioritize speed and energy efficiency for rapid production, while brick kilns offer thermal stability and physical durability for long-term, heavy-duty use.
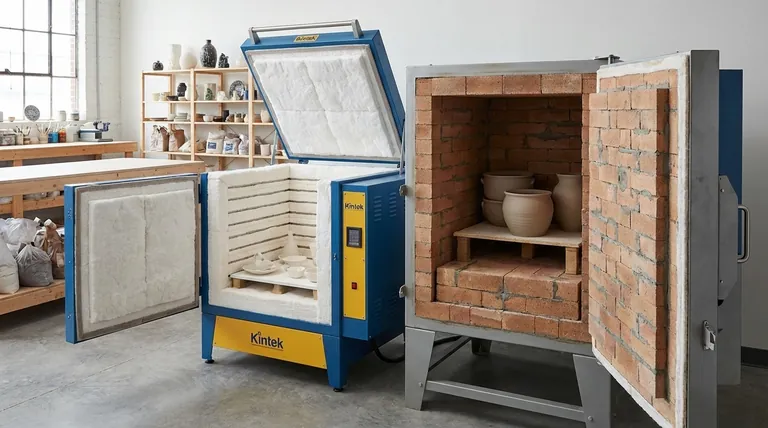

The Core Distinction: Insulation and Thermal Mass
The material a kiln is made from determines its thermal mass—its ability to absorb and store heat. This is the central concept that separates these two kiln types.
Understanding Fiber Kilns
Fiber kilns are constructed from rigidized ceramic fiber boards. This material is an excellent insulator but has a very low thermal mass.
Think of it like a modern, lightweight puffy jacket. It keeps you warm by trapping air, but the material itself doesn't hold much heat. This means nearly all the energy from the heating elements goes directly to heating the kiln chamber and your work.
Understanding Brick Kilns
Brick kilns are built with insulating firebrick, a material with a high thermal mass.
This is more like a traditional stone fireplace. The stones themselves absorb a tremendous amount of heat. A significant portion of the energy is spent heating the bricks before the chamber reaches its target temperature.
How Insulation Impacts Your Firing Cycle
The difference in thermal mass directly translates to practical differences in how you use the kiln.
Speed and Production Volume
Fiber kilns excel at speed. Because the walls don't store much heat, they can reach peak temperature and cool down rapidly.
This is ideal for high-turnover work, such as glass fusing or a studio firing many bisque loads a day. You can complete multiple firing cycles in the time it takes a brick kiln to complete one.
Heat Retention and Process Control
Brick kilns are slow and steady. Their high thermal mass means they cool down very slowly and evenly.
While this means longer wait times between firings, it can be a significant advantage for certain processes. Some complex glaze effects and the critical annealing stage for glass benefit from a slow, naturally controlled cooling period that a brick kiln provides.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither kiln type is universally superior. The right choice involves balancing speed, durability, and your specific artistic needs.
Durability and Lifespan
Brick is the clear winner in terms of durability. Insulating firebrick is hard and resilient, capable of withstanding accidental bumps during loading and unloading.
Ceramic fiber, by contrast, is soft and fragile. It can be easily damaged, gouged, or dented. Over time, it can also become brittle and may require recoating or repair.
Energy Efficiency
For a single firing, a fiber kiln is generally more energy-efficient. Less energy is "wasted" heating the dense mass of the kiln walls, so more of it goes directly to the artwork.
However, a brick kiln's heat retention can be an advantage in cold climates or when firing consecutive loads, as it doesn't have to start from a completely cold state.
A Note on Fuel Source
It's important to recognize that the insulation material (fiber vs. brick) is separate from the fuel source. Both fiber and brick kilns can be powered by electricity, gas, or other methods. The choice of fuel affects the firing atmosphere, while the insulation material dictates the kiln's thermal performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right kiln, align its characteristics with the primary demands of your work.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and speed: A fiber kiln is the superior choice, allowing for more firing cycles per day.
- If your primary focus is long-term durability and heavy use: A brick kiln's robust construction will better withstand the rigors of a busy studio.
- If your primary focus is controlled, slow cooling for specific results: A brick kiln offers unmatched thermal stability that is difficult to replicate in a fiber kiln.
Ultimately, understanding this key difference in thermal properties empowers you to choose a kiln that will serve as a true partner in your creative process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Fiber Kiln | Brick Kiln |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation Material | Lightweight Ceramic Fiber | Dense Insulating Firebrick |
| Heating/Cooling Speed | Very Fast | Slow |
| Thermal Mass | Low | High |
| Best For | Speed & High Production Volume | Durability & Controlled Cooling |
| Energy Efficiency | High for single firings | Good for consecutive firings |
| Durability | Fragile, can be damaged | Robust, long-lasting |
Ready to find the perfect kiln for your studio's workflow?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab and studio equipment, including a full range of kilns for ceramics, glass, and other materials. Our experts understand the critical differences between fiber and brick kilns and can help you select the ideal model to match your production goals, energy requirements, and budget.
We offer solutions that enhance your creative process, ensuring reliability and performance. Don't leave your equipment choice to chance—let us guide you to the right investment.
Contact our kiln specialists today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals



















