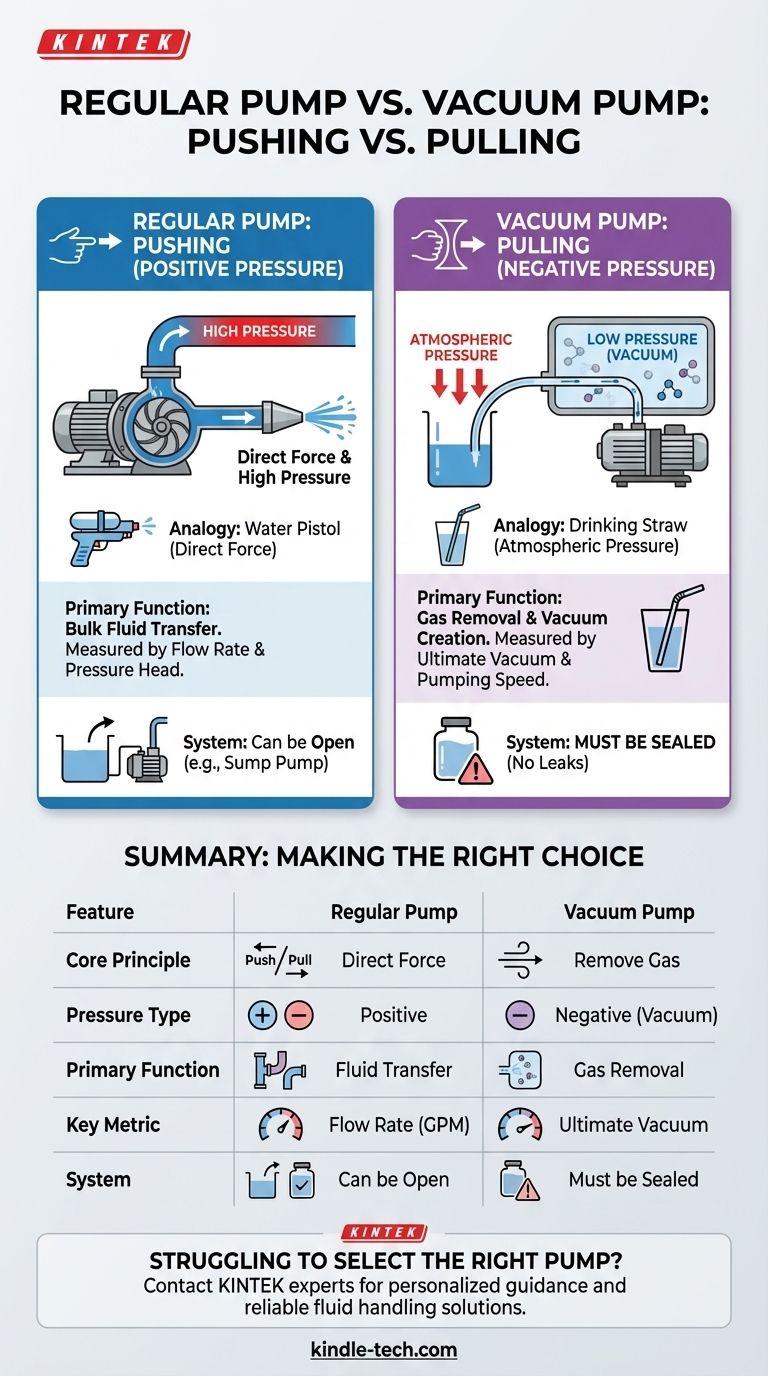
The fundamental difference lies in their core mechanism: a regular pump works by actively pushing a fluid, while a vacuum pump works by removing gas from a sealed area to pull a fluid using a pressure differential. Regular pumps create positive pressure, and vacuum pumps create negative pressure.
While both can be used to move fluids, their principles are opposite. A regular pump applies force directly to a fluid to displace it. A vacuum pump removes air to create a low-pressure zone, allowing the higher external atmospheric pressure to push the fluid into that space.
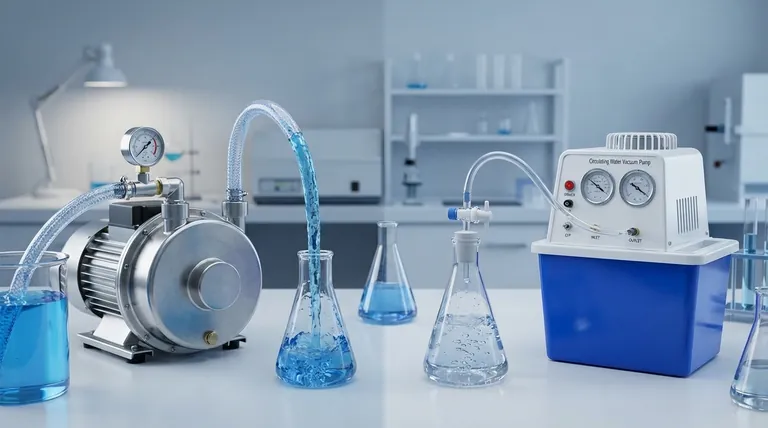

How a Regular Pump Works: The Principle of Positive Pressure
A standard pump is designed to add energy directly to a fluid, typically a liquid, to move it from one place to another.
Applying Direct Force
Most common pumps, like centrifugal or piston pumps, use an impeller or a plunger to physically push the fluid. This action directly imparts velocity and pressure onto the fluid itself.
Creating High Pressure
This direct force creates a high-pressure zone at the pump's outlet. The fluid then naturally flows away from this high-pressure area towards a lower-pressure destination, such as the open end of a hose.
Analogy: A Water Pistol
Think of a simple water pistol. When you pull the trigger, a piston applies direct force to the water inside, creating positive pressure and forcing it out of the nozzle. The work is done directly on the water.
How a Vacuum Pump Works: The Principle of Negative Pressure
A vacuum pump's primary function is not to move fluid, but to remove gas molecules from a sealed volume to create a vacuum. Moving fluid is a secondary application of the resulting pressure difference.
Removing Air and Gas
The pump's mechanism expels air or gas from a sealed chamber or line. This lowers the density of molecules within that space, which is the definition of a partial vacuum.
Leveraging Atmospheric Pressure
By creating this low-pressure zone, the pump allows the constant, higher atmospheric pressure outside the system to do the work. The external air pressure pushes on the surface of the fluid, forcing it into the empty space the pump created.
Analogy: Drinking Through a Straw
This is the perfect real-world example. You don't actually "suck" the liquid up the straw. You use your mouth to remove the air inside the straw (creating a vacuum), and the atmospheric pressure on the surface of your drink pushes the liquid up to fill that void. The vacuum pump is your mouth in this scenario.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these pumps depends entirely on the objective, as their designs are optimized for fundamentally different tasks.
Primary Function
A regular pump's goal is bulk fluid transfer. Its efficiency is measured in flow rate and pressure head (e.g., gallons per minute).
A vacuum pump's goal is to create a vacuum. Its efficiency is measured by how low a pressure it can achieve (its "ultimate vacuum") and how quickly it can remove gas.
The Medium Being Moved
A regular pump acts directly on the liquid or gas it is intended to move.
A vacuum pump acts on the gas within a system. Its ability to then move a liquid is an indirect result of the pressure differential it creates.
System Requirements
Systems using regular pumps can often be open to the atmosphere. A sump pump, for example, sits in an open pit.
Systems using vacuum pumps must be sealed from the outside atmosphere. Any leak will allow air to rush in, destroying the vacuum and preventing the pump from functioning correctly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application dictates the correct tool. The distinction is not subtle; it is a fundamental choice between pushing and pulling.
- If your primary focus is transferring a liquid from a tank to a truck: A regular pump, such as a centrifugal pump, is the direct and efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is removing all the air from a chamber for a scientific experiment: A vacuum pump is the only tool designed for this purpose.
- If your primary focus is using suction cups to lift a heavy object: You need a vacuum pump to evacuate the air from under the cups, allowing atmospheric pressure to create the holding force.
Ultimately, understanding whether your task requires generating force or creating an absence of it is the key to solving your engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Regular Pump | Vacuum Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Pushes fluid by applying direct force | Pulls fluid by removing gas to create a pressure differential |
| Pressure Type | Creates Positive Pressure | Creates Negative Pressure (Vacuum) |
| Primary Function | Bulk fluid transfer | Gas removal and vacuum creation |
| Key Metric | Flow rate (e.g., GPM) | Ultimate vacuum level and pumping speed |
| System Requirement | Can be open | Must be sealed |
| Common Analogy | Water Pistol | Drinking Straw |
Struggling to select the right pump for your laboratory application? The choice between a vacuum pump and a regular pump is critical for efficiency and results. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance and reliable solutions for all your fluid handling and vacuum needs.
Let our experts help you optimize your process. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover the perfect pump for your specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Variable Speed Peristaltic Pump
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What types of gases can a water circulating vacuum pump handle? Safely Manage Flammable, Condensable & Dirty Gases
- What can I use a vacuum pump for? Powering Industrial Processes from Packaging to Automation
- How is a circulating water vacuum pump utilized for hydrogen production residues? Optimize Your Solid-Liquid Separation
- What are the advantages of a water circulating vacuum pump? Superior Durability for Demanding Lab Environments
- Why is a water circulating vacuum pump suitable for handling flammable or explosive gases? Inherent Safety Through Isothermal Compression



















