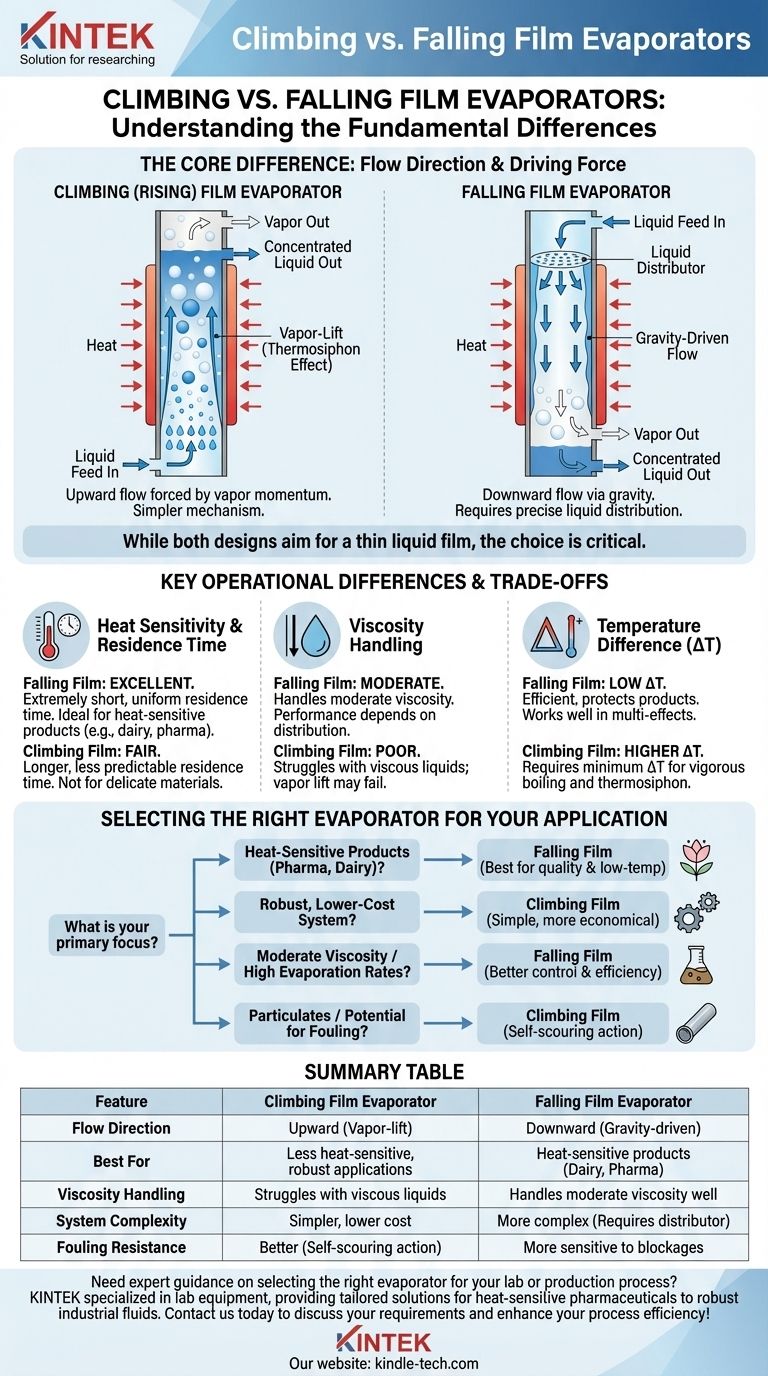
The fundamental difference between a climbing and falling film evaporator is the direction of fluid flow and the force that drives it. In a climbing (or rising) film evaporator, the liquid enters from the bottom and is forced upward by the momentum of the vapor bubbles created during boiling. Conversely, in a falling film evaporator, the liquid is introduced at the top and flows downward along the tube walls purely by gravity.
While both designs aim to create a thin liquid film for efficient heat transfer, the choice between them is a critical engineering decision. Falling film evaporators offer precise control for delicate, heat-sensitive products, whereas climbing film evaporators provide a simpler, more robust solution for less demanding applications.

The Core Mechanism: How Each Evaporator Works
Both climbing and falling film evaporators are typically shell-and-tube heat exchangers. The core difference lies in how the liquid feed is introduced and transported through the heated tubes.
Climbing Film (Rising Film): The Power of Vapor Lift
In a climbing film design, the liquid feed enters the bottom of long, vertical tubes, which are heated on the outside (usually by steam).
As the liquid heats up and begins to boil, bubbles form. These vapor bubbles rise rapidly, coalescing and expanding to create a core of vapor that drags the remaining liquid up the tube walls as a thin film.
This process is known as the thermosiphon effect. The upward movement is entirely dependent on the generation of sufficient vapor to lift the liquid.
Falling Film: The Precision of Gravity
In a falling film design, the process is inverted. The liquid feed is carefully pumped to the top of the evaporator.
Here, a specialized liquid distributor ensures the feed is metered evenly to each of the vertical tubes. The liquid then flows down the inner walls of the heated tubes as a continuous, thin film, driven solely by gravity.
The vapor generated also flows downward, co-currently with the liquid film, and is separated at the bottom. The performance of this system is highly dependent on the quality of the initial liquid distribution.
Key Operational Differences
The mechanical distinction between vapor-lift and gravity-driven flow creates significant differences in performance, making each type suitable for very different applications.
Heat Sensitivity and Residence Time
A falling film evaporator offers an extremely short and uniform residence time. The liquid passes through the heated zone in a matter of seconds, minimizing its exposure to high temperatures. This makes it the ideal choice for highly heat-sensitive products like dairy, fruit juices, and pharmaceuticals.
A climbing film evaporator has a slightly longer and less predictable residence time, as the flow is dependent on the rate of boiling. This makes it less suitable for extremely delicate materials.
Viscosity Handling
Falling film evaporators can effectively handle fluids with moderate viscosity. As long as the liquid can be distributed evenly and flow down the walls, the system works well.
Climbing film evaporators struggle with viscous liquids. The vapor lift may not be powerful enough to overcome the fluid's resistance to flow, leading to poor performance or operational failure.
Required Temperature Difference (ΔT)
Falling film evaporators can operate with a very low temperature difference (ΔT) between the heating medium and the process liquid. This further protects heat-sensitive products and improves thermal efficiency, especially in multi-effect systems.
Climbing film evaporators require a higher minimum ΔT to initiate the vigorous boiling needed to drive the thermosiphon effect.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an evaporator is not just about performance; it also involves considering complexity, cost, and operational robustness.
System Complexity and Cost
The liquid distributor at the top of a falling film evaporator is a critical and complex component that adds to the system's overall cost and design requirements.
Climbing film evaporators are mechanically simpler. They lack this complex distribution system, making them less expensive to manufacture and install.
Susceptibility to Fouling
A falling film evaporator is highly sensitive to blockages. If the feed contains particulates or the distributor fails, dry spots can form on the tube walls. This halts evaporation in that area and can lead to fouling or product degradation.
The high upward velocity of the vapor in a climbing film evaporator can create a "scouring" effect. This can help reduce the buildup of certain types of fouling, making the system more robust for some applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Product
The selection process must be guided by the specific properties of your liquid feed and your desired operational outcomes.
- If your primary focus is processing highly heat-sensitive products (like pharmaceuticals or dairy): A falling film evaporator is the superior choice due to its minimal residence time and low-temperature operation.
- If your primary focus is a robust, lower-cost system for non-sensitive liquids: A climbing film evaporator offers a simpler and more economical solution.
- If you are working with moderately viscous liquids or require very high evaporation rates: The falling film design typically provides better control and higher heat transfer coefficients.
- If your feed liquid may contain small particulates or has a tendency to foul: The self-cleaning action of a climbing film evaporator might be a more durable option.
Ultimately, selecting the correct evaporator hinges on a clear understanding of your product's sensitivity and your process's operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Climbing Film Evaporator | Falling Film Evaporator |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Direction | Upward (vapor-lift) | Downward (gravity-driven) |
| Best For | Less heat-sensitive, robust applications | Heat-sensitive products (dairy, pharma) |
| Viscosity Handling | Struggles with viscous liquids | Handles moderate viscosity well |
| System Complexity | Simpler, lower cost | More complex (requires liquid distributor) |
| Fouling Resistance | Better (self-scouring action) | More sensitive to blockages |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right evaporator for your lab or production process? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing tailored solutions for laboratory needs. Our team can help you choose the optimal system for your specific application, whether you're working with heat-sensitive pharmaceuticals or robust industrial fluids. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and enhance your process efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings



















