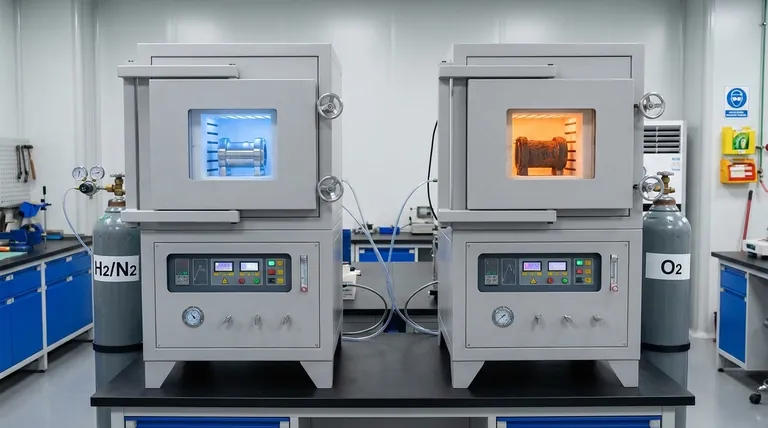
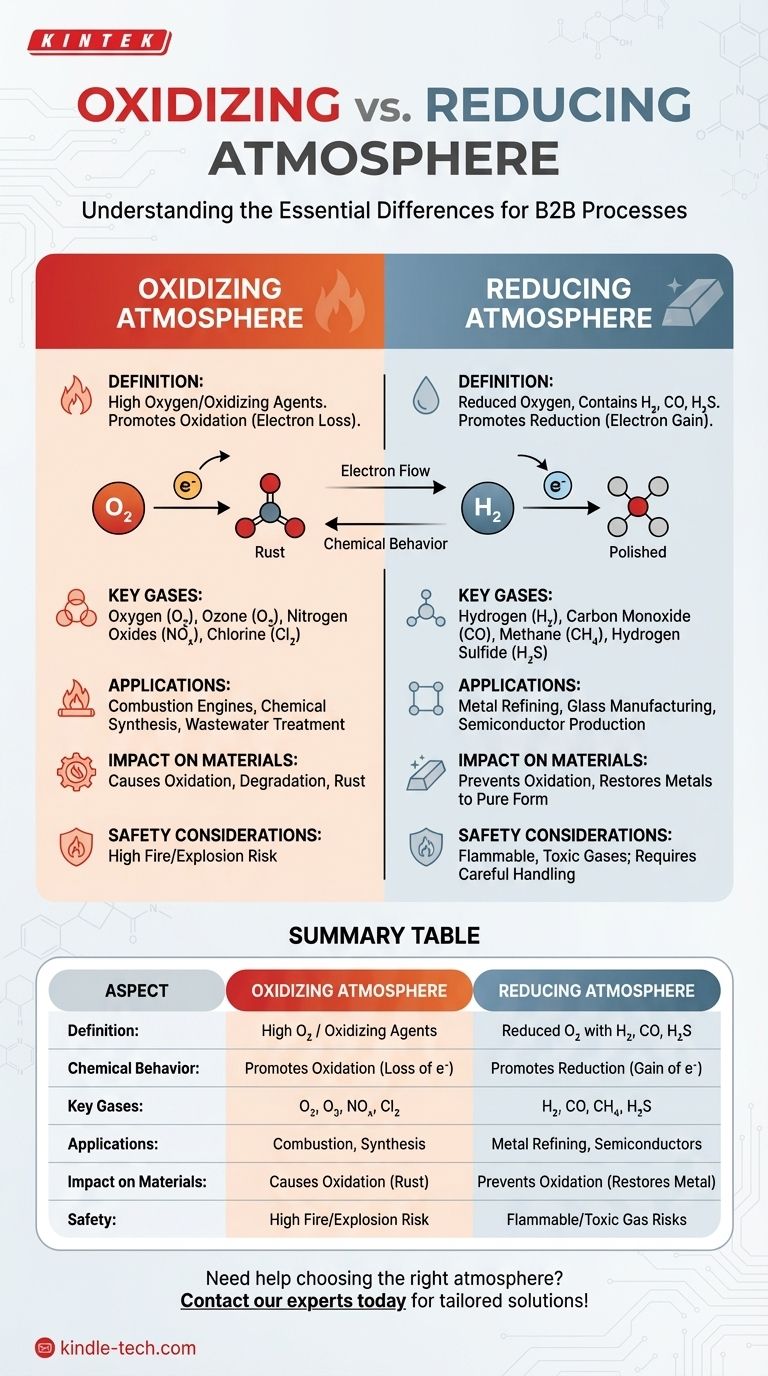
An oxidizing atmosphere contains a high concentration of oxygen or other oxidizing agents, promoting oxidation reactions, while a reducing atmosphere has a reduced amount of oxygen and may contain gases like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, or hydrogen sulfide, which prevent oxidation and encourage reduction reactions. The key difference lies in the chemical behavior of the environment: oxidizing atmospheres facilitate the loss of electrons (oxidation), whereas reducing atmospheres promote the gain of electrons (reduction). These differences are critical in applications like metallurgy, chemical manufacturing, and materials processing, where controlling the atmosphere can significantly impact the outcome of reactions.

Key Points Explained:
-
Definition of Oxidizing Atmosphere:
- An oxidizing atmosphere is characterized by a high concentration of oxygen or other oxidizing agents.
- It promotes oxidation reactions, where substances lose electrons.
- Common examples include air (which contains ~21% oxygen) and environments with ozone or nitrogen oxides.
- Applications include combustion processes, rusting of metals, and certain chemical syntheses.
-
Definition of Reducing Atmosphere:
- A reducing atmosphere contains a reduced amount of oxygen and may include gases like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, or hydrogen sulfide.
- It prevents oxidation and encourages reduction reactions, where substances gain electrons.
- Common examples include environments used in metallurgical processes (e.g., smelting) or food preservation (e.g., vacuum packaging).
- Applications include metal refining, glass manufacturing, and semiconductor production.
-
Chemical Behavior:
- Oxidizing Atmosphere: Facilitates the loss of electrons from substances, leading to oxidation. For example, iron reacts with oxygen to form iron oxide (rust).
- Reducing Atmosphere: Promotes the gain of electrons, leading to reduction. For example, hydrogen gas can reduce iron oxide back to metallic iron.
-
Key Gases Involved:
- Oxidizing Atmosphere: Oxygen (O₂), ozone (O₃), nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), and chlorine (Cl₂).
- Reducing Atmosphere: Hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), methane (CH₄), and hydrogen sulfide (H₂S).
-
Applications and Implications:
-
Oxidizing Atmosphere:
- Used in combustion engines, chemical synthesis (e.g., production of sulfuric acid), and wastewater treatment.
- Can cause corrosion or degradation of materials over time.
-
Reducing Atmosphere:
- Used in metal extraction (e.g., reduction of iron ore to iron), glass manufacturing (to remove impurities), and food packaging (to prevent spoilage).
- Prevents oxidation, preserving the integrity of materials or products.
-
Oxidizing Atmosphere:
-
Examples in Industry:
- Oxidizing Atmosphere: In steel production, oxygen is blown into molten iron to remove impurities (e.g., carbon) through oxidation.
- Reducing Atmosphere: In the production of silicon wafers for semiconductors, a reducing atmosphere is used to prevent oxidation of the silicon surface.
-
Impact on Materials:
- Oxidizing Atmosphere: Can lead to the formation of oxides, which may degrade materials (e.g., rust on metals).
- Reducing Atmosphere: Can restore metals to their pure form by removing oxides (e.g., reducing iron oxide to iron).
-
Environmental and Safety Considerations:
- Oxidizing Atmosphere: High oxygen levels can increase the risk of fire or explosions.
- Reducing Atmosphere: Gases like hydrogen or carbon monoxide are flammable and toxic, requiring careful handling.
By understanding these differences, equipment and consumable purchasers can make informed decisions about the type of atmosphere required for specific processes, ensuring optimal results and safety.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Oxidizing Atmosphere | Reducing Atmosphere |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | High concentration of oxygen or oxidizing agents. | Reduced oxygen levels with gases like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, or hydrogen sulfide. |
| Chemical Behavior | Promotes oxidation (loss of electrons). | Promotes reduction (gain of electrons). |
| Key Gases | Oxygen (O₂), ozone (O₃), nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), chlorine (Cl₂). | Hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), methane (CH₄), hydrogen sulfide (H₂S). |
| Applications | Combustion engines, chemical synthesis, wastewater treatment. | Metal refining, glass manufacturing, semiconductor production. |
| Impact on Materials | Causes oxidation (e.g., rust). | Prevents oxidation, restores metals to pure form. |
| Safety Considerations | High oxygen levels increase fire/explosion risks. | Flammable and toxic gases require careful handling. |
Need help choosing the right atmosphere for your process? Contact our experts today for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments
- What is the purpose of inert atmosphere? A Guide to Protecting Your Materials and Processes
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained



















