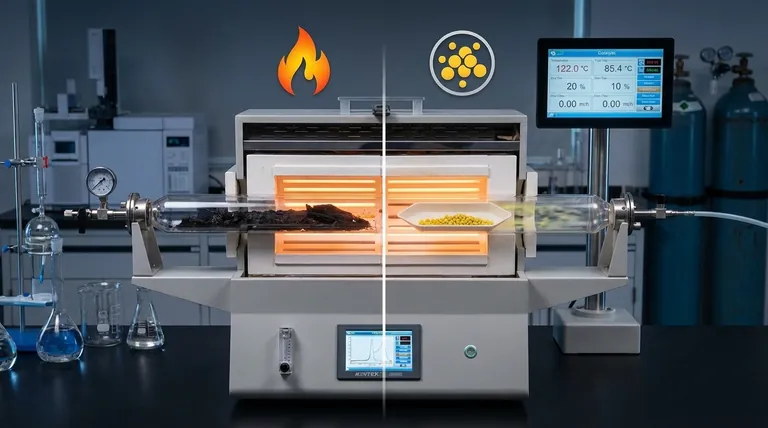
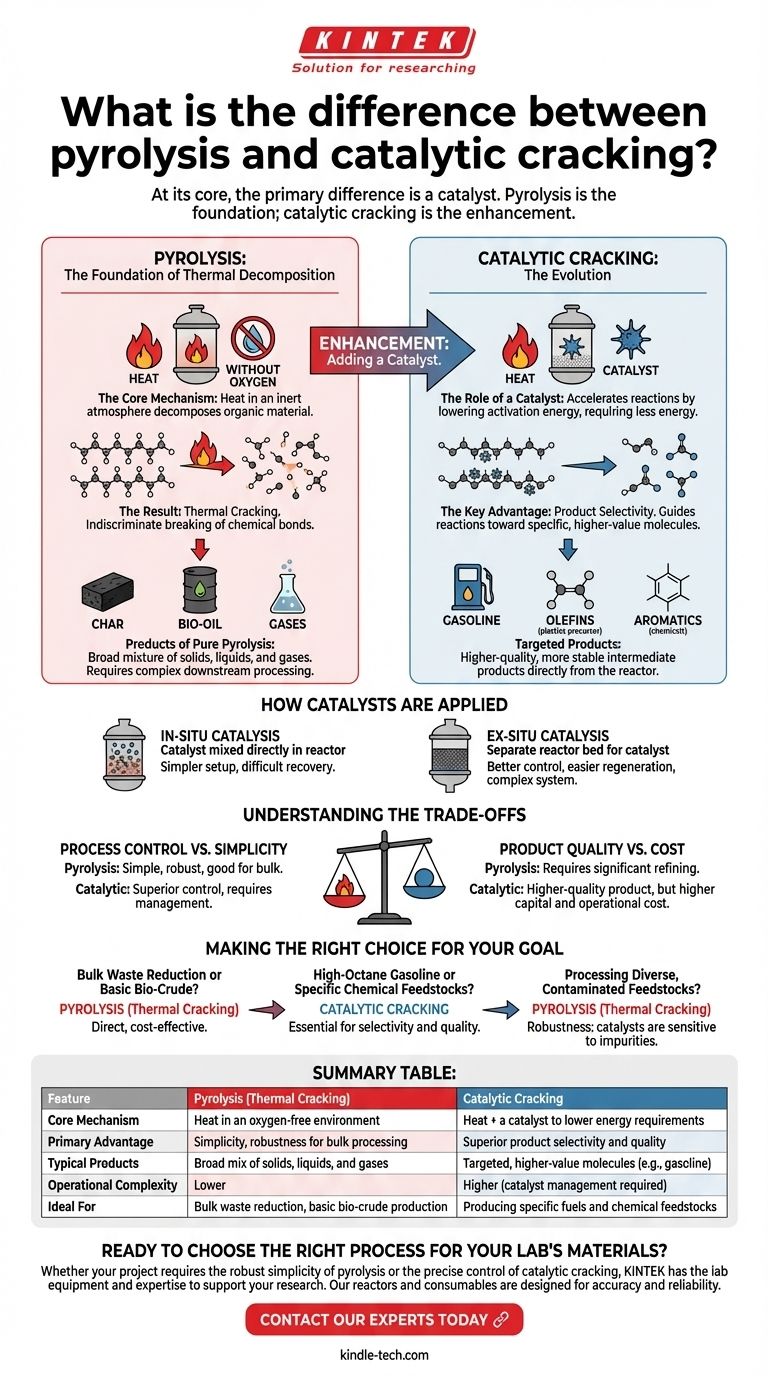
At its core, the primary difference is a catalyst. Pyrolysis is the foundational process of breaking down materials with heat in an oxygen-free environment, which results in thermal cracking. Catalytic cracking is a more advanced form of this process that introduces a catalyst to accelerate reactions and selectively control the final products.
The essential distinction is not one of opposition, but of enhancement. Pyrolysis is the engine that drives thermal decomposition; adding a catalyst fine-tunes that engine for lower energy consumption and the precision manufacturing of higher-value molecules.

What is Pyrolysis? The Foundation of Thermal Decomposition
The Core Mechanism: Heat Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that decomposes organic material at elevated temperatures in an inert atmosphere.
By eliminating oxygen, the process avoids combustion (burning). Instead of burning, the intense heat provides the energy needed to break the long-chain chemical bonds within the material.
The Result: Thermal Cracking
When pyrolysis is applied to hydrocarbon feedstocks (like biomass, plastics, or crude oil), the result is thermal cracking.
The "cracking" refers to the literal breaking, or fragmenting, of large, complex hydrocarbon molecules into smaller, often more useful ones. This happens purely due to the thermal energy applied.
Products of Pure Pyrolysis
The output of thermal cracking is typically a broad mixture of solids, liquids, and gases. This can include solid char, a liquid fraction often called bio-oil or pyrolysis oil, and various non-condensable gases. This mixture is often complex and requires significant downstream processing to become a finished product.
Introducing the Catalyst: The Evolution to Catalytic Cracking
The Role of a Catalyst
A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by it. In cracking, it works by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy.
This means the molecular bonds can be broken more easily, requiring less energy input—specifically, lower temperatures—than thermal cracking alone.
The Key Advantage: Product Selectivity
This is the most critical function of catalytic cracking. While thermal cracking breaks molecules somewhat indiscriminately, a catalyst can be chosen to guide the reaction toward producing specific types of molecules.
By controlling the catalyst type, temperature, and pressure, operators can selectively produce high-demand products like gasoline-range hydrocarbons, olefins (for plastics), or aromatics (for chemicals).
How Catalysts are Applied
As a practical matter, the catalyst can be introduced in two primary ways.
In-situ catalysis involves mixing the catalyst directly with the feedstock before or during pyrolysis. This is a simpler setup but can make catalyst recovery more difficult.
Ex-situ catalysis uses a separate reactor bed for the catalyst. The vapors produced during pyrolysis are passed through this second bed for upgrading. This offers better control and easier catalyst regeneration but adds system complexity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Control vs. Simplicity
Thermal cracking is a relatively simple, robust process that is highly effective for bulk material processing or breaking down very heavy hydrocarbons.
Catalytic cracking offers far superior control over the end product but requires managing catalyst selection, coking (deactivation), regeneration, and potential poisoning from feedstock contaminants.
Product Quality vs. Cost
The products from thermal cracking often require significant hydrotreating and other refining steps to become stable, usable fuels.
Catalytic cracking produces a higher-quality, more stable intermediate product directly from the reactor, reducing the need for extensive downstream processing. However, the catalysts themselves and the more complex reactor systems represent a significant capital and operational cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is bulk waste reduction or producing a basic bio-crude: Simple pyrolysis leading to thermal cracking is often the most direct and cost-effective method.
- If your primary focus is producing high-octane gasoline or specific chemical feedstocks: Catalytic cracking is essential for achieving the required product selectivity and quality.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse, potentially contaminated feedstocks: The robustness of thermal cracking may be advantageous, as catalysts can be sensitive to impurities.
Ultimately, choosing the right path depends entirely on whether your goal is simple decomposition or precise molecular engineering.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Pyrolysis (Thermal Cracking) | Catalytic Cracking |
|---|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Heat in an oxygen-free environment | Heat + a catalyst to lower energy requirements |
| Primary Advantage | Simplicity, robustness for bulk processing | Superior product selectivity and quality |
| Typical Products | Broad mix of solids, liquids, and gases | Targeted, higher-value molecules (e.g., gasoline) |
| Operational Complexity | Lower | Higher (catalyst management required) |
| Ideal For | Bulk waste reduction, basic bio-crude production | Producing specific fuels and chemical feedstocks |
Ready to choose the right process for your lab's materials?
Whether your project requires the robust simplicity of pyrolysis or the precise control of catalytic cracking, KINTEK has the lab equipment and expertise to support your research. Our reactors and consumables are designed for accuracy and reliability, helping you achieve your goals in waste valorization, biofuel production, or chemical synthesis.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a quartz tube facilitate fractional condensation in a horizontal tube vacuum gasification furnace? Expert Guide
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control



















