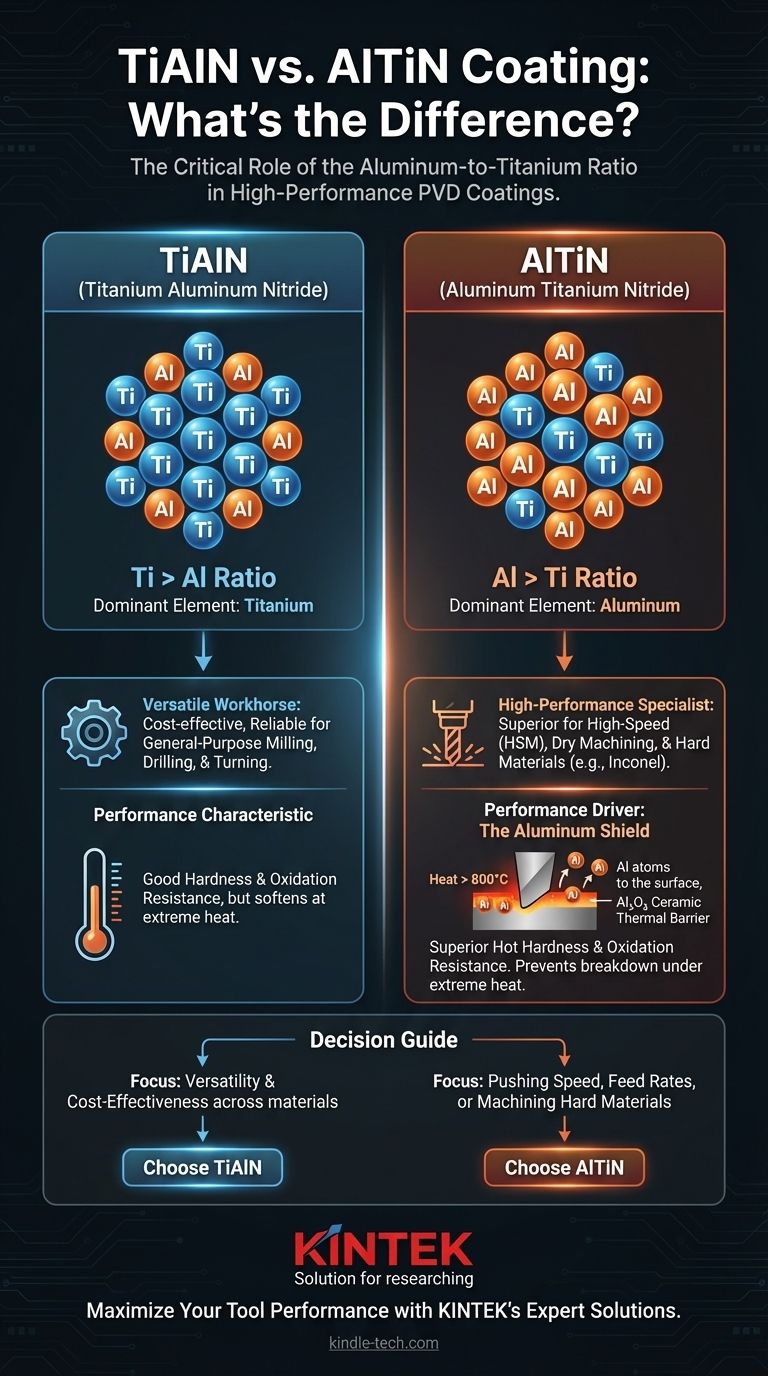
At its core, the difference between TiAlN and AlTiN is the ratio of aluminum to titanium. While both are high-performance PVD coatings, AlTiN contains a higher concentration of aluminum than titanium (Al > Ti), whereas TiAlN contains more titanium than aluminum (Ti > Al). This seemingly minor chemical distinction has a significant impact on performance, particularly under high-heat conditions.
The choice between TiAlN and AlTiN is a strategic decision based on your machining parameters. AlTiN's higher aluminum content gives it superior hot hardness and oxidation resistance, making it the preferred coating for aggressive, high-speed, and dry machining applications where extreme heat is generated.

The Foundation: A Tale of Two Ratios
Both TiAlN (Titanium Aluminum Nitride) and AlTiN (Aluminum Titanium Nitride) are advanced coatings applied via Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). They belong to a family of coatings that build upon the success of the original Titanium Nitride (TiN) by incorporating aluminum to dramatically improve performance.
The Critical Difference: Atomic Composition
The order of the elements in the name is a convention used to signify the dominant metallic element in the coating's matrix.
- TiAlN: The ratio of Titanium to Aluminum is greater than one (Ti:Al > 1:1).
- AlTiN: The ratio of Aluminum to Titanium is greater than one (Al:Ti > 1:1).
This difference in atomic percentage is the primary driver of their distinct functional properties.
How the Ratio Dictates Performance
The key to understanding these coatings lies in what happens at the cutting edge when temperatures soar. The aluminum content is the critical performance-enhancing element.
The Role of Aluminum: A Self-Forming Shield
At the high temperatures generated during aggressive machining (typically above 800°C or 1475°F), the aluminum in the coating migrates to the surface. It then reacts with oxygen in the air to form a nano-thin, highly stable, and lubricious layer of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃).
This ceramic layer acts as a thermal barrier, insulating the tool from heat and preventing the coating itself from oxidizing and breaking down.
Hot Hardness and Temperature Resistance
Because AlTiN has a higher concentration of aluminum, it can form a more robust and stable aluminum oxide layer.
This gives AlTiN significantly higher "hot hardness"—the ability to retain its hardness at elevated temperatures. While both coatings perform well, AlTiN will maintain its integrity at temperatures where TiAlN begins to soften and wear more rapidly.
Application Sweet Spots
TiAlN is a highly versatile and reliable workhorse coating. It offers a substantial upgrade over basic TiN and is effective across a wide range of materials and general-purpose milling, drilling, and turning operations.
AlTiN is the high-performance specialist. It excels in demanding applications such as:
- High-speed machining (HSM)
- Dry or minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) cutting
- Machining difficult materials like hardened steels, titanium alloys, and nickel-based superalloys (Inconel).
In these scenarios, the extreme heat generated makes AlTiN's superior thermal stability a decisive advantage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While AlTiN offers superior high-temperature performance, it is not always the default choice. The optimal selection depends on a clear understanding of the entire operational context.
Cost vs. Performance
AlTiN coatings are typically more expensive than TiAlN due to the more complex deposition process required to achieve the high aluminum content. For general-purpose machining where extreme heat is not a factor, the performance gains of AlTiN may not justify the additional cost.
Coating Brittleness
Increasing the aluminum content can sometimes lead to a slight increase in the coating's internal stress and brittleness. In applications with heavy interruption or chatter, a tougher, more ductile coating might be required, though modern AlTiN formulations have largely mitigated this concern.
The Importance of Application Quality
The performance difference between a well-applied TiAlN and a poorly-applied AlTiN can be negligible. The quality of the PVD process—including substrate preparation, deposition temperature, and process controls—is as critical as the coating's chemical formula. Always partner with a reputable coating provider.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct coating is not about choosing the "best" one in a vacuum, but the most appropriate one for the specific task, material, and machine capability.
- If your primary focus is versatility and cost-effective performance across many materials: TiAlN is a superb, reliable choice that provides a significant upgrade over older coating technologies.
- If your primary focus is pushing speed, feed rates, or machining hard materials: AlTiN is the clear winner, as its superior hot hardness and thermal barrier formation will lead to longer tool life and better performance.
- If you are experiencing rapid tool wear due to extreme heat at the cutting edge: Switching from TiAlN to AlTiN is one of the most effective solutions to investigate.
Ultimately, understanding the role of aluminum allows you to match the coating's chemistry directly to the physics of your machining operation.
Summary Table:
| Coating | Dominant Element | Key Characteristic | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiAlN | Titanium (Ti > Al) | Versatile, cost-effective | General-purpose milling, drilling, and turning |
| AlTiN | Aluminum (Al > Ti) | Superior hot hardness & oxidation resistance | High-speed, dry, or hard material machining (e.g., Inconel) |
Maximize Your Tool Performance with the Right Coating
Choosing between TiAlN and AlTiN is critical for optimizing tool life and machining efficiency. The expert team at KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including advanced coating solutions for the manufacturing industry.
We can help you select the ideal PVD coating for your specific application, materials, and machining parameters.
Contact us today to discuss your needs and discover how our expertise can enhance your operations. Get in touch via our contact form for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Corrosion Resistant Cleaning Rack Flower Basket
People Also Ask
- What is titanium disadvantages and advantages? Weighing Performance vs. Cost for Your Project
- How does hardness change with temperature? Understand the Inverse Relationship to Prevent Failure
- How can you improve corrosion resistance? Extend Equipment Life with Proven Strategies
- What are the disadvantages of using metal? Understanding Corrosion, Weight, and Cost Challenges
- What is titanium used for in manufacturing? Leveraging High-Performance Properties for Critical Applications



















