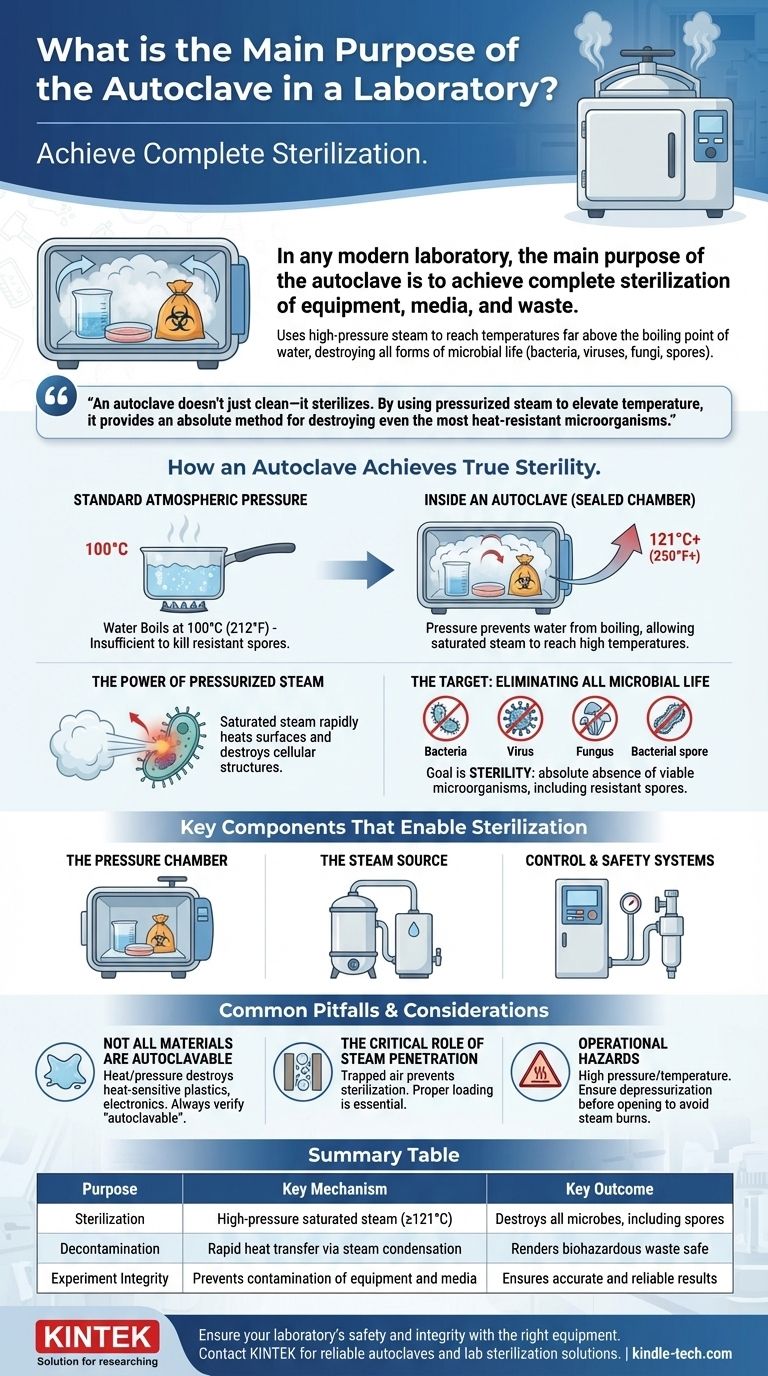
In any modern laboratory, the main purpose of the autoclave is to achieve complete sterilization of equipment, media, and waste. It uses high-pressure steam to reach temperatures far above the boiling point of water, a condition required to destroy all forms of microbial life, including resilient bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores. This process ensures that experiments are not contaminated and that hazardous biological materials are rendered safe for disposal.
An autoclave doesn't just clean—it sterilizes. By using pressurized steam to elevate temperature, it provides an absolute method for destroying even the most heat-resistant microorganisms, a level of certainty that simple washing or boiling cannot achieve.

How an Autoclave Achieves True Sterility
To understand the autoclave's purpose, it's essential to understand its mechanism. It is fundamentally different from a simple oven or dishwasher because it leverages the physical properties of steam under pressure.
The Principle: Beyond Boiling Water
At standard atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). While this temperature can kill many microbes, it is insufficient to eliminate highly resistant bacterial spores.
An autoclave is a sealed pressure chamber. By increasing the pressure inside, it prevents water from boiling at its normal temperature, allowing the saturated steam to reach 121°C or higher.
The Power of Pressurized Steam
Steam is the active agent in an autoclave. Saturated steam is an exceptionally efficient medium for transferring thermal energy to the items being sterilized.
It condenses on cooler surfaces, rapidly heating them while simultaneously destroying the cellular structures of any microorganisms present. This direct contact ensures a complete and rapid kill.
The Target: Eliminating All Microbial Life
The goal of autoclaving is sterility, which is the absolute absence of viable microorganisms.
This includes bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Critically, it also includes bacterial spores, which are dormant, tough structures that can survive extreme conditions, including boiling, for extended periods.
Key Components That Enable Sterilization
Several core components work in concert to create the precise conditions needed for effective steam sterilization.
The Pressure Chamber
This is the core of the machine—a robust vessel, often with an outer jacket, designed to safely withstand high pressure and temperature. The items to be sterilized are placed inside this chamber.
The Steam Source
Some autoclaves are plumbed into a central steam supply, while others have a built-in steam generator. This component boils water to produce the required saturated steam.
Control and Safety Systems
Modern autoclaves are managed by a control panel that allows users to select specific cycles for different loads (e.g., glassware, liquids, or waste).
Crucial safety features like a safety valve and a thermostatic trap prevent dangerous over-pressurization and ensure air is properly evacuated so that steam can effectively penetrate the entire load.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While highly effective, an autoclave's success depends on correct operation. Misunderstanding its principles can lead to failed sterilization or safety hazards.
Not All Materials are Autoclavable
The high heat and pressure will destroy or melt many materials. Heat-sensitive plastics, certain electronics, and corrosive chemicals like bleach must never be placed inside.
Always verify that an item is marked as "autoclavable" before processing it.
The Critical Role of Steam Penetration
The most common cause of sterilization failure is trapped air. If items are packed too densely, air pockets can form, preventing steam from contacting and sterilizing the surfaces within that pocket.
Proper loading, leaving space between items, is essential for ensuring the cycle's success.
Operational Hazards
An autoclave operates at high pressure and temperature, making it a potential workplace hazard. Users must be trained to ensure the chamber is fully depressurized before attempting to open the door to avoid severe steam burns.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to using an autoclave should be guided by your primary objective for that specific cycle.
- If your primary focus is ensuring complete sterilization of instruments: Prioritize proper loading techniques to eliminate air pockets and ensure steam reaches every surface.
- If your primary focus is decontaminating biohazardous waste: Use a dedicated waste cycle with a longer exposure time to guarantee full penetration and kill within a dense, complex load.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Always verify the chamber pressure has returned to zero before unlatching the door and stand back when opening it to avoid residual steam.
Ultimately, understanding the autoclave as a precision instrument for achieving absolute sterility is key to maintaining the integrity and safety of your work.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Key Mechanism | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Sterilization | High-pressure saturated steam (≥121°C) | Destroys all microbes, including spores |
| Decontamination | Rapid heat transfer via steam condensation | Renders biohazardous waste safe |
| Experiment Integrity | Prevents contamination of equipment and media | Ensures accurate and reliable results |
Ensure your laboratory's safety and integrity with the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable, high-performance autoclaves and lab sterilization solutions tailored to your specific needs. From research labs to clinical settings, our equipment guarantees complete sterilization for instruments, media, and waste. Contact us today to find the perfect autoclave solution for your laboratory and achieve absolute confidence in your sterilization processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Why is proper maintenance and cleaning of the autoclave important? Ensure Sterilization Efficacy and Safety
- What are the disadvantages of autoclave in microbiology? Key Limitations for Lab Safety
- What should be autoclaved in a lab? A Guide to Safe and Effective Sterilization
- How do you autoclave lab equipment? A Step-by-Step Guide to Sterile Results
- What are the uses of autoclave in laboratory equipment? Ensure Sterile Conditions for Your Research



















