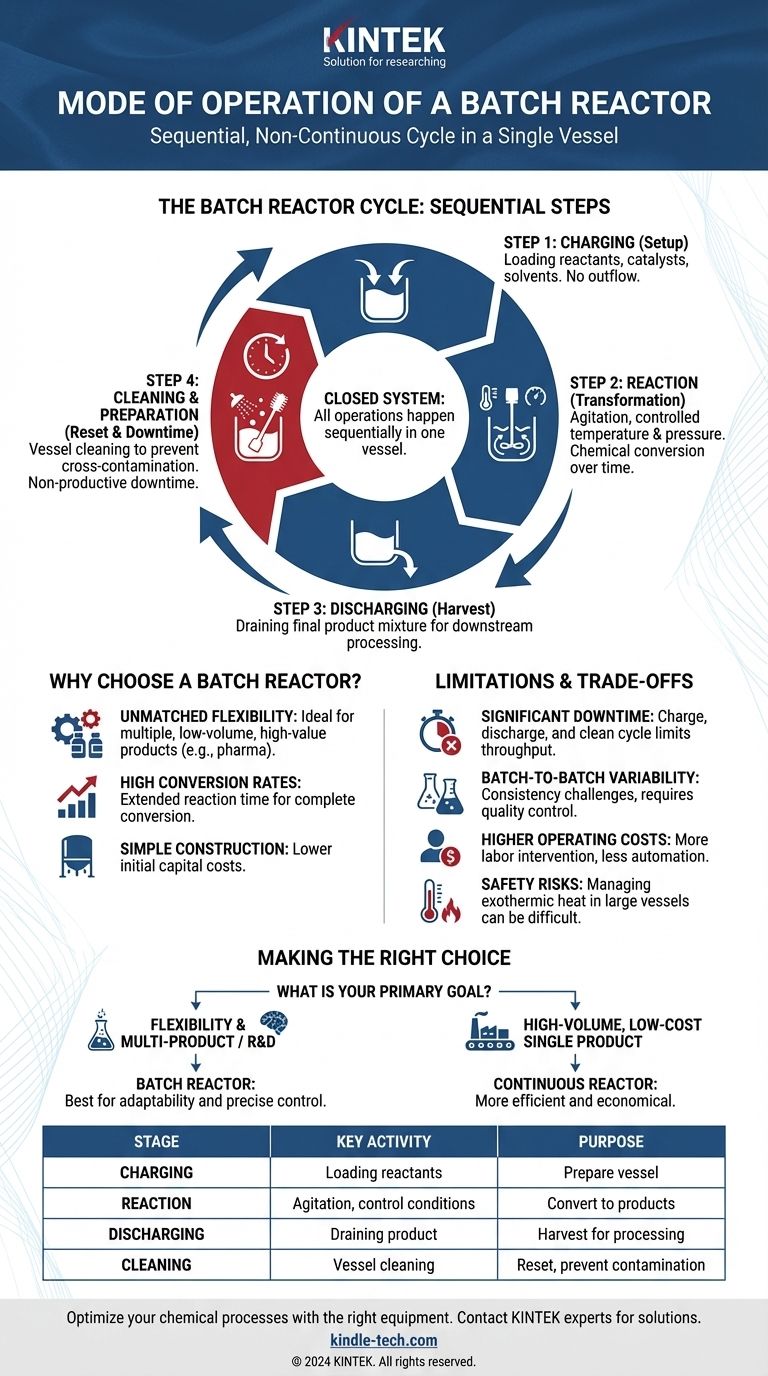
At its core, a batch reactor operates in a sequential, non-continuous cycle. Reactants are loaded into a vessel, the chemical reaction is allowed to proceed under controlled conditions for a set amount of time, and then the final product mixture is discharged. This entire process occurs in a single piece of equipment before the cycle begins again.
A batch reactor is a closed system where all operations—charging, reacting, and discharging—happen sequentially in the same vessel. Its defining characteristic is its operational flexibility, which comes at the cost of non-productive downtime between batches.

The Anatomy of a Batch Reactor Cycle
Understanding the mode of operation means understanding its distinct, sequential steps. Each step serves a specific purpose, and the time spent on non-reaction steps is a critical factor in the reactor's overall efficiency.
Step 1: Charging (The Setup)
The cycle begins by loading, or charging, the reactants into the reactor vessel. This may also include adding solvents, catalysts, or other necessary agents. During this phase, there is no outflow from the vessel.
Step 2: Reaction (The Transformation)
Once charged, the reaction is initiated. The contents are typically agitated with an impeller to ensure they are well-mixed, promoting uniform temperature and concentration throughout the vessel.
Crucially, conditions like temperature and pressure are carefully controlled using external heating/cooling jackets or internal coils. The reaction proceeds for a predetermined time, during which the chemical composition of the mixture changes continuously as reactants are converted into products.
Step 3: Discharging (The Harvest)
After the desired reaction time has elapsed and the target conversion is reached, the reaction is stopped. The entire resulting mixture, including products, by-products, and any unreacted starting materials, is then drained or discharged from the reactor for downstream processing like separation and purification.
Step 4: Cleaning & Preparation (The Reset)
This final step is often the most significant contributor to a batch reactor's inefficiency. The vessel must be cleaned and prepared for the next run to prevent cross-contamination. This downtime is non-productive time that limits the overall throughput of the facility.
Why Choose a Batch Reactor?
Despite the downtime, batch reactors are a cornerstone of the chemical industry for several key reasons.
Unmatched Flexibility
A single batch reactor can be used to produce many different products. This makes it ideal for manufacturing low-volume, high-value products like pharmaceuticals or specialty chemicals, or for facilities that need to switch production frequently.
High Conversion Rates
Because the reactants can be held in the reactor for an extended period, it is possible to achieve very high conversion rates. This is a significant advantage for reactions that proceed slowly or need to be driven to completion.
Simple Construction
Relative to continuous systems, the basic design of a batch reactor is mechanically simple. This generally translates to lower initial capital costs for the equipment itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Limitations of Batch Operation
The choice of a batch reactor comes with significant operational trade-offs that must be considered.
Significant Downtime
As mentioned, the charge, discharge, and clean cycle represents unproductive time. For high-volume commodity chemicals, this inefficiency makes batch processing economically unviable compared to continuous alternatives.
Batch-to-Batch Variability
Achieving perfect consistency between every batch can be a challenge. Minor variations in charging volumes, reaction time, or temperature profiles can lead to slight differences in product quality, which requires stringent quality control.
Higher Operating Costs per Unit
The stop-and-start nature of batch processing often requires more labor intervention per unit of product compared to a highly automated continuous plant. This can lead to higher overall operating costs, especially at scale.
Safety with Exothermic Reactions
Managing heat removal can be difficult in large batch reactors. For highly exothermic reactions, the risk of a thermal runaway—a dangerous, uncontrolled increase in temperature and pressure—is a serious safety consideration that can be more easily managed in continuous systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the decision to use a batch reactor is dictated by the specific goals of your chemical process.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and producing multiple products in one plant: The batch reactor is the ideal choice due to its adaptability.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost production of a single product: A continuous reactor, such as a Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor (CSTR) or a Plug Flow Reactor (PFR), will almost always be more efficient and economical.
- If your primary focus is process development or producing high-value, low-volume goods: The batch reactor's operational simplicity and precise control over reaction time make it superior for R&D and specialty chemical manufacturing.
Choosing the right reactor is about matching the operational mode to the economic and technical demands of your process.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Activity | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Charging | Loading reactants, catalysts, solvents | Prepare the vessel for the reaction. |
| Reaction | Agitation, temperature/pressure control | Convert reactants to products. |
| Discharging | Draining the final product mixture | Harvest the results for further processing. |
| Cleaning | Vessel cleaning and preparation | Reset the system for the next batch, preventing contamination. |
Optimize your chemical processes with the right equipment. Batch reactors are essential for flexible, high-conversion production of pharmaceuticals and specialty chemicals. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to meet your specific laboratory needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research and development or small-scale manufacturing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of high-pressure reactors in semiconductor catalyst preparation? Optimize Your Heterojunctions
- What is the role of a high-pressure reactor in h-BN magnetic nanocomposite synthesis? Master Precision Deposition
- Why is a High-temperature and High-pressure Autoclave necessary for zirconium alloy testing? Ensure Nuclear Safety.
- Which critical experimental conditions does a high-pressure autoclave provide? Optimize Mixed Sulfide Leaching
- What is the significance of the hydrothermal environment in HA preparation? Optimize Mesoporous Structure and Purity



















