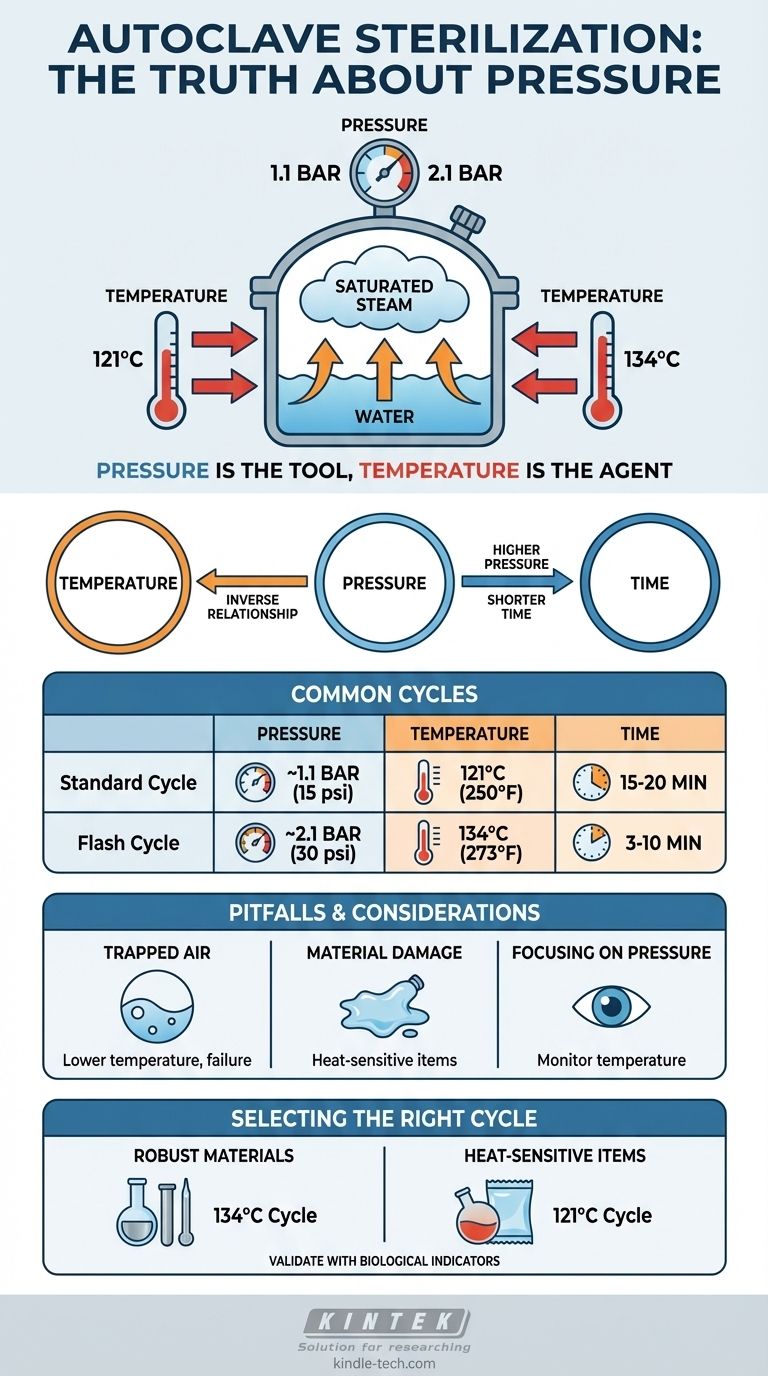
The standard pressure for autoclave sterilization typically ranges from approximately 1.1 bar (15 psi) to 2.1 bar (30 psi) above atmospheric pressure. However, focusing on pressure alone is misleading. This pressure is required to achieve the necessary sterilization temperatures of 121°C (250°F) and 134°C (273°F), respectively. The temperature and direct contact with saturated steam are the true agents of sterilization, not the pressure itself.
The crucial factor in autoclave sterilization isn't the pressure value, but the high-temperature saturated steam that the pressure creates. Pressure is simply the physical tool used to raise the boiling point of water, allowing steam to reach temperatures capable of destroying all microbial life.

Why Pressure is Essential for Sterilization
Overcoming the Limits of Boiling Water
At normal atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). While this temperature can kill many bacteria, it is not sufficient to reliably eliminate highly resistant bacterial spores.
The Role of a Pressurized Environment
An autoclave is a sealed pressure vessel. By increasing the pressure inside, it raises the boiling point of water far beyond 100°C.
This environment allows for the creation of saturated steam, which is steam that holds the maximum possible amount of water vapor at a given temperature and pressure.
Saturated Steam: The True Sterilizing Agent
This high-temperature, moisture-laden steam is the key to sterilization. When it comes into contact with cooler items, the steam condenses, rapidly transferring a large amount of thermal energy.
This intense heat effectively and irreversibly denatures the essential proteins and enzymes within microorganisms, leading to their death.
The Critical Relationship: Temperature, Pressure, and Time
The three core variables in autoclaving—temperature, pressure, and time—are intrinsically linked. Understanding their relationship is fundamental to achieving effective sterilization.
A Balancing Act
There is an inverse relationship between temperature and the required exposure time. Higher temperatures can sterilize more quickly.
For example, achieving a higher temperature requires a higher pressure setting, but this significantly reduces the necessary cycle time.
Common Sterilization Cycles
While specific cycles vary by the load and machine, two standards are nearly universal:
- 121°C Cycle: Achieved at approximately 1.1 bar (108 kPa or 15 psi). This cycle typically requires an exposure time of 15 to 20 minutes.
- 134°C Cycle: Achieved at approximately 2.1 bar (206 kPa or 30 psi). This cycle is much faster, often requiring only 3 to 10 minutes of exposure.
Direct Contact is Non-Negotiable
For any cycle to succeed, the steam must make direct contact with every surface of the items being sterilized. Improper loading that creates air pockets is a primary cause of sterilization failure.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Trade-offs
Simply setting the correct pressure does not guarantee success. Several factors can compromise the process.
The Danger of Trapped Air
If air is not properly removed from the chamber, the autoclave's gauge may show the target pressure, but the temperature will be lower than expected. This is because the total pressure is a mix of steam and air, and air is a poor conductor of heat, leading to sterilization failure.
Damage to Sensitive Materials
The high-temperature, high-pressure environment is harsh. A faster 134°C cycle can damage or melt certain plastics, degrade liquid media, or harm delicate instruments. The chosen cycle must be compatible with the materials being sterilized.
Focusing on Pressure Instead of Temperature
A common mistake is to focus only on the pressure reading. The goal is to maintain a specific temperature for a specific duration. Pressure is the means to that end, but temperature is the critical variable that must be monitored.
Selecting the Correct Cycle for Your Application
Use the goal of your sterilization process to determine the right parameters.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing robust materials (glassware, waste, surgical steel): The higher temperature/pressure cycle (134°C at ~2.1 bar) is often preferred for its speed and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive items (certain plastics, media, complex instruments): The lower temperature/pressure cycle (121°C at ~1.1 bar) is the safer standard to prevent damage, despite its longer duration.
- If your primary focus is ensuring absolute sterility: Always validate your process with biological indicators, such as those containing Bacillus stearothermophilus spores, which provide proof that the cycle was lethal to the most resistant organisms.
Ultimately, mastering the interplay between pressure, temperature, and time is what empowers you to achieve safe and reliable sterilization.
Summary Table:
| Sterilization Cycle | Typical Pressure (Gauge) | Temperature | Typical Exposure Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Cycle | ~1.1 bar (15 psi) | 121°C (250°F) | 15-20 minutes |
| Flash Cycle | ~2.1 bar (30 psi) | 134°C (273°F) | 3-10 minutes |
Achieve Uncompromising Sterilization with KINTEK
Ensure your laboratory's safety and compliance with autoclaves that deliver precise temperature and pressure control. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including autoclaves designed for reliable, effective sterilization of instruments, glassware, and media.
Let us help you select the right autoclave for your specific needs. Our experts will guide you to a solution that ensures sterility while protecting your sensitive materials.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and elevate your lab's sterilization protocols!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How does an autoclave ensure the reliability of experimental results? Achieving a Sterile Baseline for Lab Research
- Why is a 24-hour hydrothermal treatment in an autoclave necessary for BMO nanosheets? Unlock Superior Photocatalysis
- What role does an autoclave play in remediation experiments? Ensure Precision by Eliminating Biological Noise
- Why is the prevention of air entrapment critical for the autoclave sterilization process? Ensure 100% Sterility Today
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization



















