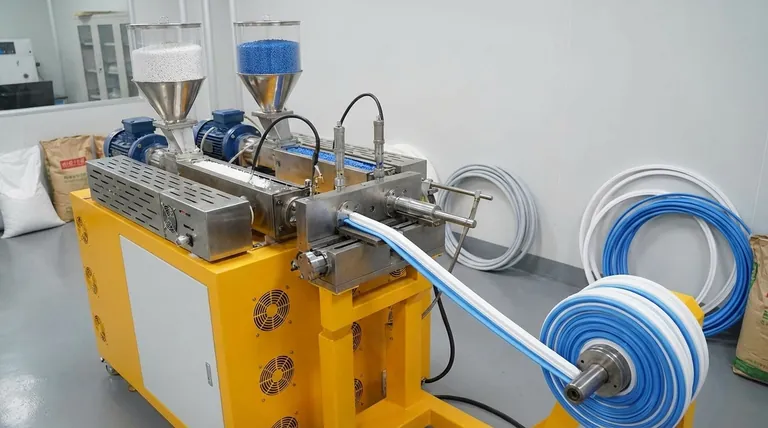
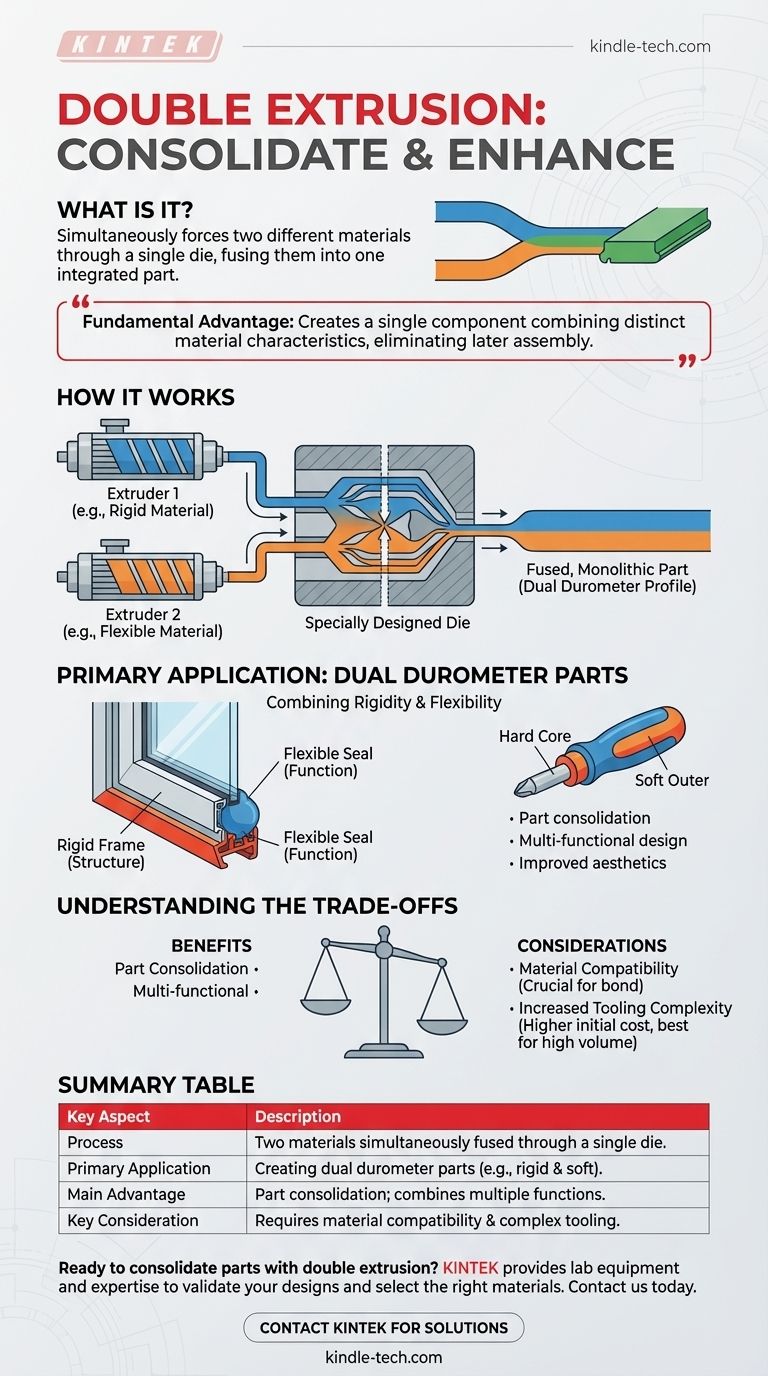
In essence, double extrusion is a manufacturing process that simultaneously forces two different materials through a single die. This co-extrusion technique fuses the materials together as they are formed, creating a single, integrated part with dual properties.
The fundamental advantage of double extrusion is its ability to create a single component that combines distinct material characteristics, such as a rigid frame with a flexible seal, eliminating the need for later assembly.

How Double Extrusion Works
Double extrusion, often called dual durometer extrusion, is a sophisticated method for creating composite profiles in one continuous operation. The magic happens within the tooling where the two material streams meet.
The Core Concept: Co-Extrusion
The process uses two separate extruders, each feeding a different raw material, typically in pellet form. These materials are heated and plasticized within their respective extruder barrels.
Both molten material streams are then channeled into a single, specially designed extrusion die.
The Role of the Die
The die is the heart of the process. It has intricate internal channels that guide the two molten materials to a precise point of convergence just before they exit the die opening.
As the materials are forced through the final die profile, they are shaped and fused together under immense pressure and heat, forming a molecular or mechanical bond.
The Result: A Fused, Monolithic Part
The final product emerges from the die as a single, continuous profile. It is not two separate parts glued or fastened together; it is one component with two seamlessly integrated materials.
The Primary Application: Dual Durometer Parts
The most common reason to employ this process is to create parts with varying hardness, or "durometer," to serve different functions.
Combining Rigidity and Flexibility
Manufacturers frequently use double extrusion to combine a rigid, structural material with a soft, pliable one.
This allows a single part to have a strong backbone for mounting or stability, while also incorporating a soft edge for sealing, cushioning, or providing a non-slip grip.
Common Real-World Examples
You can see this technology in everyday products. Common examples include window and door seals, where a rigid base clips into a frame while a soft bulb compresses to block air and water.
Other examples include wire insulation with a protective outer layer and tool grips that have a hard core with a soft, ergonomic outer surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, double extrusion is not a universal solution. It requires careful planning and has specific limitations that must be considered during the design phase.
Material Compatibility is Crucial
The two materials must be chemically compatible to ensure a strong, permanent bond. Not all plastics or rubbers can be successfully fused together.
Engineers must select materials that have similar melt temperatures and will adhere to one another upon cooling.
Increased Tooling Complexity
The die required for double extrusion is significantly more complex and expensive to design and manufacture than a standard single-material die.
This higher initial investment means the process is best suited for high-volume production runs where the cost can be amortized over many parts.
Is Double Extrusion Right for Your Project?
Making the right choice depends entirely on your product's functional requirements and production scale.
- If your primary focus is part consolidation: This process is an excellent choice for reducing assembly steps, labor costs, and potential points of failure.
- If your primary focus is multi-functional design: Double extrusion enables you to create elegant, integrated components that serve multiple purposes, such as providing both structure and sealing.
- If your primary focus is low-volume production: The high initial tooling cost may make other methods, like overmolding or mechanical assembly, more economically viable.
By engineering multiple properties into a single component, double extrusion offers a powerful way to create more efficient and effective products.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Two materials are simultaneously forced through a single die and fused together. |
| Primary Application | Creating dual durometer parts (e.g., a rigid frame with a soft seal). |
| Main Advantage | Part consolidation; combines multiple functions into one component. |
| Key Consideration | Requires material compatibility and involves complex, costly tooling. |
Ready to consolidate parts and enhance functionality with double extrusion?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables necessary for developing and testing advanced manufacturing processes like double extrusion. Our expertise can help you select the right materials and validate your designs for creating high-performance, multi-material components.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can streamline your R&D and production workflow. Let's engineer a more efficient product together!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Lab Blown Film Extrusion Three Layer Co-Extrusion Film Blowing Machine
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
People Also Ask
- What is the cost of blown film extrusion? From $20K to High-End Systems
- What is the blown film extrusion technique? Mastering Biaxial Orientation for Superior Film Strength
- What is the meaning of blowing film? A Guide to Biaxial Orientation and Stronger Plastic Films
- What products are blown film extrusion? From Grocery Bags to Industrial Sheeting
- What is the process of calendering? A Guide to High-Volume Plastic Film Production



















