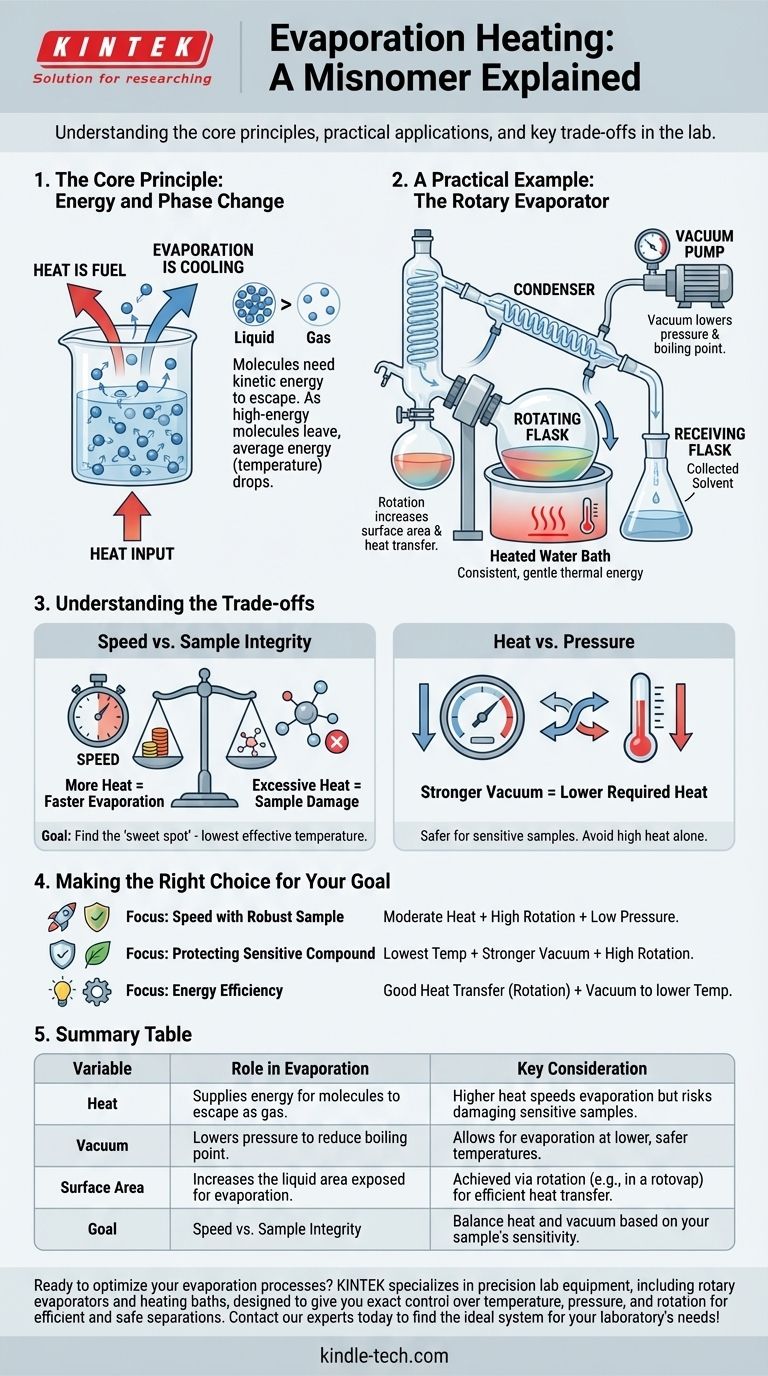
To be precise, the term "evaporation heating" is a misnomer that can cause confusion. Evaporation is fundamentally a cooling process. The term you've encountered likely refers to the practice of applying heat to a liquid to accelerate its evaporation, a common technique used in laboratory and industrial settings to separate substances.
The core principle is straightforward: evaporation requires energy. By "heating" a liquid, you are simply supplying the necessary thermal energy to speed up the natural process of its molecules escaping into a gaseous state.
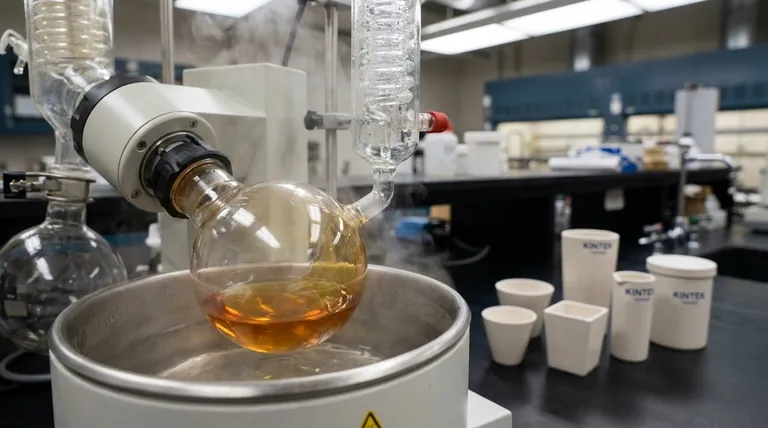

The Core Principle: Energy and Phase Change
Evaporation is Fundamentally Cooling
For a liquid molecule to escape and become a gas, it must have enough kinetic energy to break the bonds holding it to its neighbors.
When the highest-energy molecules escape, the average energy of the remaining molecules drops. Since temperature is a measure of average kinetic energy, the liquid's temperature decreases. This is why sweat cools your skin.
Heat is the Fuel for Evaporation
To make a liquid evaporate faster, you must continuously supply energy to it. This external heat increases the kinetic energy of the liquid's molecules, allowing more of them to reach the "escape velocity" needed to transition into a gas.
Without this added heat, the liquid would quickly cool down, and the rate of evaporation would plummet.
A Practical Example: The Rotary Evaporator
The most common context for this concept is in a laboratory device called a rotary evaporator ("rotovap"). Its goal is to gently remove a solvent from a sample.
The Role of the Heated Bath
A rotovap uses a heated water bath to provide consistent, gentle thermal energy to a rotating flask containing the solvent. This is the "heating" part of the process.
This controlled heating ensures a steady supply of energy to fuel the evaporation without causing sudden, violent boiling that could ruin the sample.
Why Rotation is Key
As noted, the rotation of the flask is critical. It spreads the liquid into a thin film on the inside wall of the flask.
This dramatically increases the surface area of the liquid, which vastly improves the rate of both heat transfer from the bath and solvent evaporation from the surface.
The Power of Vacuum
In addition to heat, these systems use a vacuum to lower the pressure inside the flask. Lowering the pressure reduces the liquid's boiling point.
This means the solvent can be evaporated at a much lower temperature than normal, which is essential for protecting heat-sensitive samples from damage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Speed vs. Sample Integrity
The primary trade-off is between the speed of evaporation and the safety of your sample. Applying more heat will make the solvent evaporate faster.
However, excessive heat can degrade or destroy a temperature-sensitive compound you are trying to isolate. The goal is to find the "sweet spot" of the lowest effective temperature.
Heat vs. Pressure
You can achieve the same rate of evaporation with different combinations of heat and pressure.
Using a stronger vacuum allows you to use less heat, which is always safer for the sample. Relying solely on high heat without reducing pressure is inefficient and risky.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To control evaporation effectively, you must balance heat, surface area, and pressure.
- If your primary focus is speed with a robust sample: You can use a combination of moderate heat, high rotation speed (for surface area), and low pressure (vacuum).
- If your primary focus is protecting a sensitive compound: Rely on the lowest possible temperature and compensate by using a stronger vacuum and high rotation speed.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Ensure good heat transfer through flask rotation and use a vacuum to lower the required temperature, as this prevents energy loss from overheating.
Ultimately, mastering evaporation is about precisely controlling the energy you supply to the system.
Summary Table:
| Variable | Role in Evaporation | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Heat | Supplies energy for molecules to escape as gas. | Higher heat speeds evaporation but risks damaging sensitive samples. |
| Vacuum | Lowers pressure to reduce boiling point. | Allows for evaporation at lower, safer temperatures. |
| Surface Area | Increases the liquid area exposed for evaporation. | Achieved via rotation (e.g., in a rotovap) for efficient heat transfer. |
| Goal | Speed vs. Sample Integrity: Balance heat and vacuum based on your sample's sensitivity. |
Ready to optimize your evaporation processes? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including rotary evaporators and heating baths, designed to give you exact control over temperature, pressure, and rotation for efficient and safe separations. Whether you're working with robust or highly sensitive compounds, our solutions help you achieve perfect results. Contact our experts today to find the ideal system for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- How long does it take for THC to evaporate? The Real Science Behind Potency Loss
- What temperature does evaporation occur? Unlock the Secrets to Controlling the Rate of Evaporation
- Do cannabinoids evaporate? How to Preserve Potency and Prevent Degradation
- What precautions should be taken in a chemistry lab? Master the RAMP Framework for Ultimate Safety
- What is deposition in environmental chemistry? Understanding How Air Pollution Harms Ecosystems



















