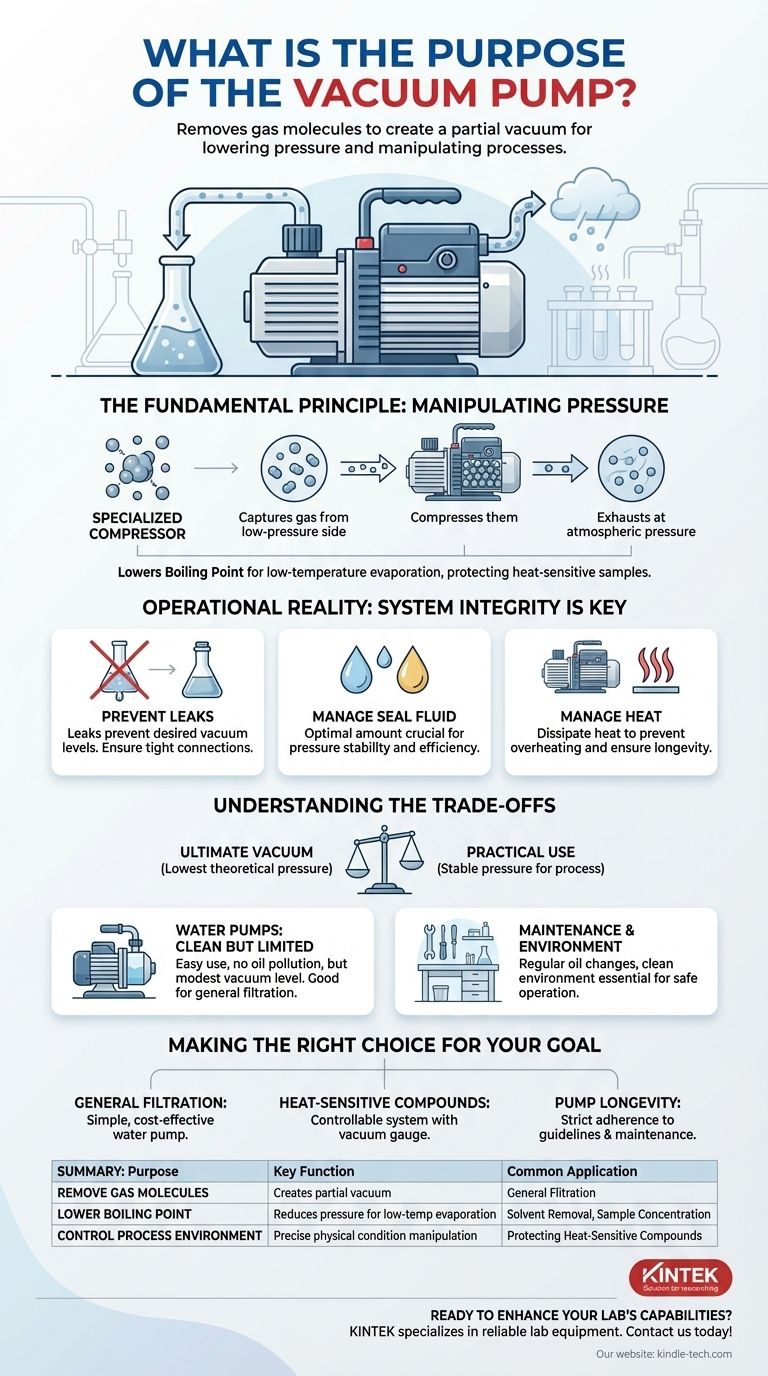
At its core, the purpose of a vacuum pump is to remove gas molecules from a sealed volume to create a partial vacuum, or a space with reduced pressure. In a laboratory or industrial context, this isn't about creating "emptiness" for its own sake, but about lowering the system pressure to manipulate physical processes, most commonly to reduce a liquid's boiling point.
A vacuum pump is a tool for controlling a system's environment. By reducing pressure, it enables processes like low-temperature evaporation that would otherwise be impossible or would damage the materials involved.

The Fundamental Principle: Manipulating Pressure
A common misconception is that vacuum pumps "suck" air out. It is more accurate to think of them as specialized compressors.
How a Vacuum Pump Works
A vacuum pump captures gas molecules from the low-pressure (vacuum) side and compresses them. This compressed gas is then exhausted into the outside environment at normal atmospheric pressure.
This process involves a high-pressure ratio, which is why many applications require multi-stage pumps to achieve a deeper vacuum level.
The Power of a Lower Boiling Point
The primary application in many lab settings is to facilitate evaporation at a lower temperature. The pressure above a liquid directly impacts the energy needed for its molecules to escape as a gas.
By reducing the pressure with a vacuum pump, you effectively lower the boiling point. This is critical for concentrating a solution or removing a solvent without using high temperatures that could degrade a heat-sensitive sample.
Operational Reality: System Integrity is Key
The pump is only one component of a vacuum system. Its performance is entirely dependent on the proper setup and maintenance of all connected parts.
Preventing Leaks
A vacuum pump cannot overcome a significant leak in the system. Ensuring all connections, seals, and glassware are properly fitted and leak-free is the first step to achieving and maintaining the desired vacuum level.
The Role of Seal Fluid
Many pumps use a fluid—either water or oil—to create the seal necessary for compression. The management of this fluid is critical.
For a water-circulating pump, using the optimal amount of seal water is essential. Too little water will cause the vacuum level to fluctuate, while too much wastes energy without improving performance.
Managing Heat
The work of compressing gas generates significant heat. Pumps are designed with cooling fins and fans to dissipate this heat into the ambient air.
Continuous operation or overloading a pump beyond its capacity can lead to overheating, which severely shortens its lifespan and can cause failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single vacuum pump is perfect for every task. Understanding their limitations is crucial for effective use and longevity.
Ultimate Vacuum vs. Practical Use
Every pump has a rated ultimate vacuum, which is the lowest pressure it can theoretically achieve. For a typical circulating water vacuum pump, this is around 2000-4000 Pa.
However, the goal is not always to achieve the deepest vacuum possible. The key is to use a vacuum meter to maintain the correct, stable pressure required for your specific process.
Water Pumps: Clean but Limited
Water vacuum pumps are praised for their ease of use, simple cleaning, and environmental friendliness, as they produce no oil-based air pollution.
Their main trade-off is a relatively modest vacuum level. They are excellent for general filtration and simple solvent evaporation but may be insufficient for processes requiring deeper vacuums.
Maintenance and Environment
To ensure a long life, a pump must be operated in a clean, dust-free environment and within its specified temperature range. Regular maintenance, such as oil changes (for oil-sealed pumps) and replacing worn parts, is not optional but essential for safe and efficient operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting and using a vacuum pump correctly depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is general filtration or robust solvent removal: A simple, low-maintenance water-circulating vacuum pump is often a cost-effective and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is protecting heat-sensitive compounds: You need a controllable system with a vacuum gauge to maintain a specific, stable pressure that lowers the boiling point just enough without damaging the sample.
- If your primary focus is pump longevity and reliability: Adhere strictly to the manufacturer's guidelines, avoid continuous overloading, and perform all recommended maintenance tasks promptly.
Understanding the vacuum pump transforms it from a simple device into a precise tool for controlling the physical environment of your work.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Key Function | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Remove Gas Molecules | Creates a partial vacuum by compressing and exhausting gas. | General Filtration |
| Lower Boiling Point | Reduces pressure to enable evaporation at lower temperatures. | Solvent Removal, Sample Concentration |
| Control Process Environment | Allows precise manipulation of physical conditions. | Protecting Heat-Sensitive Compounds |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with the right vacuum pump?
KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment, including vacuum pumps tailored for your specific processes like filtration and solvent evaporation. Our experts can help you select the ideal pump to protect your samples and improve efficiency.
Contact us today for a consultation and discover the KINTEK difference!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Variable Speed Peristaltic Pump
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is the primary use of a Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump? Expert Guide to Gas Evacuation and Rough Vacuum Ranges
- What are the common configurations and typical performance specifications of Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps? Expert Guide
- What are the limitations of rotary vane pumps? Understanding Oil Dependence and Gas Compatibility
- Why is a gas ballast valve necessary on a rotary vane vacuum pump? Protect Your Oil and Extend Pump Life
- What is a Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump? Efficiency and Performance for Laboratory Vacuum Systems



















