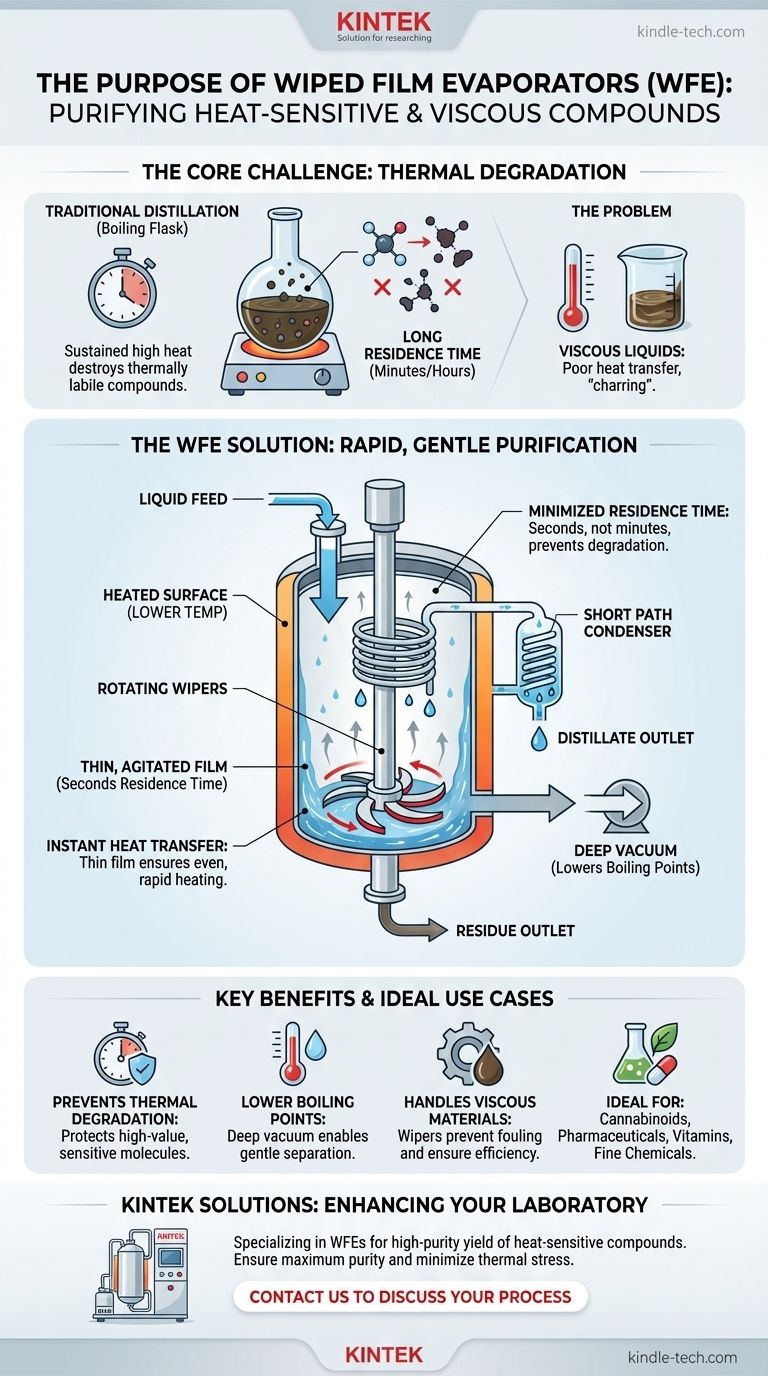
In essence, a wiped film evaporator is a specialized distillation tool designed to purify heat-sensitive, viscous, or high-boiling-point compounds. It operates under a deep vacuum and uses a system of rotating wipers to create an extremely thin film of liquid on a heated cylindrical surface. This design drastically reduces the time the material is exposed to high temperatures, enabling separation and purification that would be impossible with traditional methods.
Traditional distillation often fails because valuable compounds decompose or degrade when held at high temperatures for extended periods. A wiped film evaporator solves this fundamental problem by minimizing the "residence time" on the heated surface, enabling the purification of thermally sensitive materials that would otherwise be destroyed.

The Core Problem: Thermal Degradation
To understand the purpose of a wiped film evaporator, you must first understand the limitations of conventional distillation.
The Failure of Traditional Boilers
In a standard distillation setup, a batch of liquid is heated in a boiling flask for an extended period. While simple and effective for robust compounds like ethanol, this sustained heat exposure can be destructive.
Many valuable organic molecules are thermally labile, meaning they change or decompose when exposed to heat over time. This leads to a loss of potency, altered flavor profiles, or complete destruction of the target product.
The "Residence Time" Factor
Residence time is the amount of time a molecule spends in a given part of a system—in this case, on the hot surface of the evaporator.
In a boiling flask, residence time can be minutes or even hours. In a wiped film evaporator, it is often a matter of seconds. This dramatic reduction is the single most important advantage of the technology.
The Challenge of Viscous Liquids
High-viscosity (thick) liquids present another major challenge. They do not mix well, transfer heat poorly, and can "char" or "coke" onto hot surfaces, leading to inefficient evaporation and product degradation.
How a Wiped Film Evaporator Solves This
A wiped film evaporator (WFE), also known as a thin film evaporator, systematically overcomes these challenges through its unique mechanical design.
Creating the Agitated Thin Film
Liquid feed is introduced at the top of a heated, vertical cylinder. A central rotating assembly with blades or rollers—the wipers—makes contact with the inner surface.
These wipers continuously spread the feed liquid into a paper-thin, turbulent film across the entire heated wall. This prevents localized "hot spots" and ensures even, instantaneous heating.
Rapid, Efficient Heat Transfer
Because the film is so thin (often less than a millimeter), heat transfers from the jacketed wall into the liquid almost instantly. The target molecules do not have to wait for heat to slowly penetrate a large volume of liquid.
This efficiency means the wall temperature can often be set lower than in a traditional boiler while still achieving effective evaporation.
Short Path to Condensation
Once a molecule vaporizes from the film, it must be condensed back into a liquid to be collected. In a "short path" configuration of a WFE, the condenser is placed directly in the center of the evaporator, just centimeters away from the heated wall.
This short travel distance allows the system to operate under a very deep vacuum. A high vacuum lowers the boiling point of the liquid, further reducing the temperature required for separation and minimizing thermal stress on the molecules.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a wiped film evaporator is a specialized instrument with specific limitations.
Mechanical Complexity and Cost
Unlike a simple glass boiling flask, a WFE is a complex mechanical system with a motor, rotating shaft, precision wipers, and vacuum-tight seals. This results in significantly higher capital costs, maintenance requirements, and operational complexity.
Sensitivity to Solids
WFEs are designed for liquids. While some can handle small percentages of soft solids, they are not suitable for processing materials with significant amounts of hard or abrasive particulate matter, which can damage the wipers and the heated surface.
Not a Universal Solution
For simple, thermally stable mixtures (like separating salt from water or purifying basic solvents), a WFE is overkill. Simpler, more cost-effective evaporation methods are a better choice in those scenarios.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Choosing the right distillation technology depends entirely on the properties of your material and your purification goal.
- If your primary focus is purifying thermally sensitive, high-value compounds (like cannabinoids, vitamins, or pharmaceutical intermediates): A wiped film system is often the necessary and superior choice to prevent product loss and achieve high purity.
- If your primary focus is separating simple, stable mixtures with low viscosity: Traditional batch or fractional distillation is likely more cost-effective and operationally straightforward.
- If your primary focus is removing a small amount of volatile solvent from a viscous, heat-sensitive product: A wiped film evaporator is an ideal tool for this "finishing" step.
Ultimately, the wiped film evaporator is an enabling technology, unlocking the ability to purify complex, high-value molecules that could not survive conventional distillation.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Thin, agitated film | Reduces residence time to seconds, preventing thermal degradation |
| High vacuum operation | Lowers boiling points, enabling gentle separation |
| Continuous processing | Ideal for viscous or heat-sensitive materials like cannabinoids or pharmaceuticals |
| Short path to condenser | Maximizes efficiency for high-value compound purification |
Need to purify heat-sensitive or viscous materials without degradation? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including wiped film evaporators designed to handle high-value compounds like pharmaceuticals, cannabinoids, and vitamins. Our solutions ensure maximum purity and yield by minimizing thermal stress. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- 30T 40T Split Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a water circulating vacuum pump suitable for handling flammable or explosive gases? Inherent Safety Through Isothermal Compression
- What is the importance of a vacuum pump for Schottky hybrid interfaces? Achieve Atomic-Level Purity and Bonding
- How does the impeller rotation affect the gas flow in a water circulating vacuum pump? A Guide to the Liquid Ring Principle
- What is the purpose of the compression chamber in a vacuum pump? The Heart of Vacuum Generation
- What are the advantages of a water circulating vacuum pump? Superior Durability for Demanding Lab Environments



















