In short, thin-film interference is the principle behind anti-reflection coatings on your eyeglasses and camera lenses. This physical phenomenon is also responsible for the shimmering, iridescent colors you see on soap bubbles, oil slicks, and even in the manufacturing of advanced semiconductors and medical devices.
The core application of thin-film interference is not just creating color, but precisely controlling light. By engineering incredibly thin, transparent layers of material, we can dictate which wavelengths of light are reflected and which are transmitted, making it a foundational tool in modern optics and manufacturing.

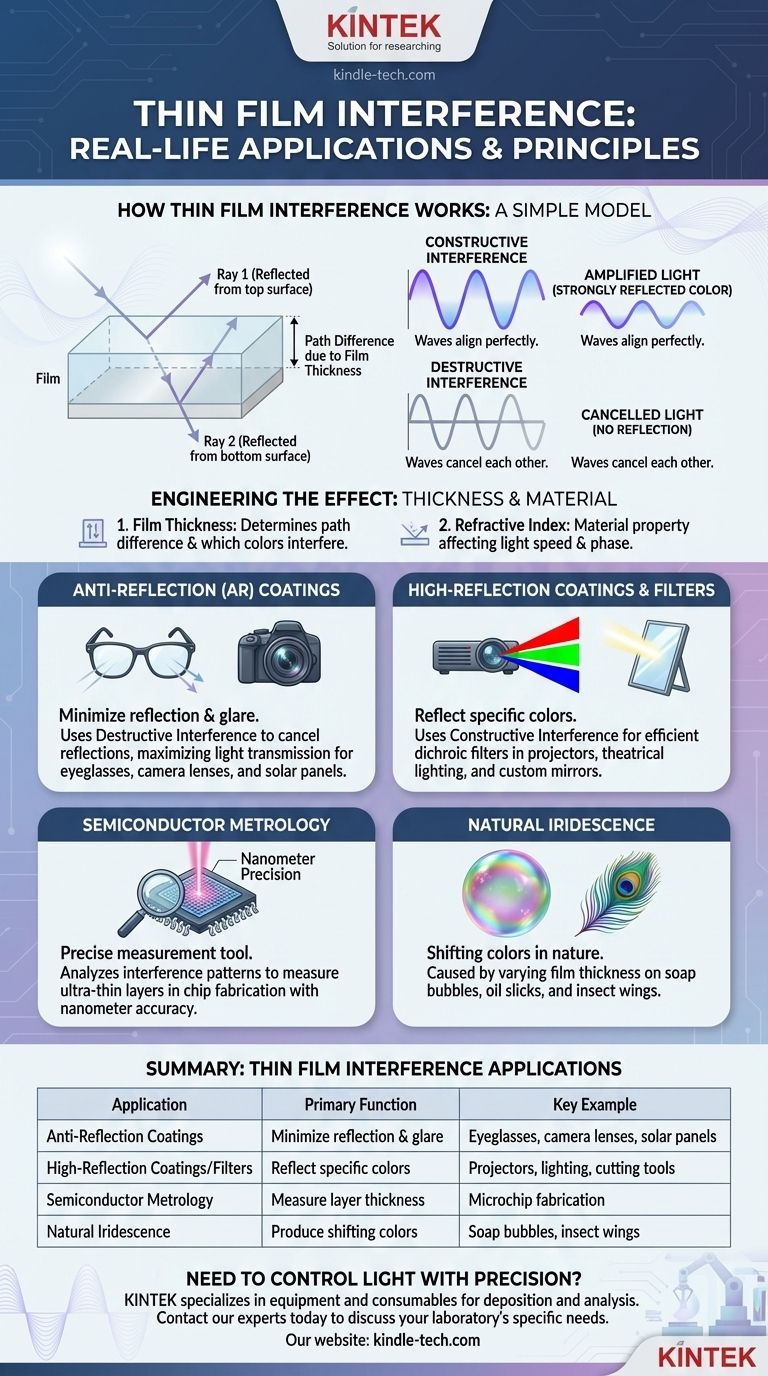
How Thin Film Interference Works: A Simple Model
To understand the applications, you first need a clear mental model of the principle itself. It all comes down to how light waves interact when they are reflected from two different surfaces.
The Two-Wave Interaction
Imagine light hitting a thin, transparent film, like an anti-reflection coating on a lens. Some of the light reflects off the top surface of the film. The rest of the light passes through the film and reflects off the bottom surface.
These two reflected light waves then travel back in the same direction and combine. The outcome of this combination depends on their alignment, or "phase."
Constructive vs. Destructive Interference
If the peaks and troughs of the two reflected light waves align perfectly, they amplify each other. This is constructive interference, which results in a strongly reflected color.
If the peaks of one wave align with the troughs of the other, they cancel each other out. This is destructive interference, which results in little to no reflection.
The Role of Thickness and Material
Engineers have two primary levers to control this effect:
- Film Thickness: The thickness of the film determines the path difference between the two reflected waves. Changing the thickness changes which colors (wavelengths) will interfere constructively or destructively.
- Refractive Index: The material used for the film (its refractive index) affects how much the light wave "slows down" inside the film, which also influences the final phase relationship.
Key Applications in Technology and Nature
By precisely controlling thickness and material, we can engineer specific outcomes for a wide range of technologies.
Anti-Reflection (AR) Coatings
This is the most common commercial application. For eyeglasses, camera lenses, and solar panels, the goal is to maximize light transmission, not reflection.
A coating is designed with a specific thickness so that reflected light waves undergo destructive interference. This cancellation prevents reflections and glare, allowing more light to pass through to your eye or the device's sensor.
High-Reflection Coatings and Filters
The opposite effect is also useful. By designing a film to cause constructive interference for specific colors, we can create highly efficient, custom mirrors.
These "dichroic filters" are used in projectors and theatrical lighting to split white light into pure colors by reflecting one color while transmitting others. Similar principles are used to create durable, reflective coatings on cutting tools and other components.
Semiconductor Manufacturing
In the world of microelectronics, thin-film interference is not part of the final product's function but is a critical measurement tool (metrology).
During chip fabrication, extremely thin layers of materials like silicon, nitrides, and dielectrics are deposited. Manufacturers shine light on the wafer and analyze the interference pattern to measure the thickness of these layers with nanometer precision, ensuring the chip functions correctly.
Natural Iridescence
Nature has been using thin-film interference for millions of years. The shifting rainbow of colors on a soap bubble or an oil slick is caused by the film's varying thickness, which reflects different colors at different points. The vibrant, metallic colors on some insects and bird feathers are also produced by intricate, layered nanostructures that function as thin films.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, this principle is not without its engineering challenges and inherent constraints.
Angle Dependency
The colors and effects produced by thin-film interference are often dependent on your viewing angle. You can see this clearly as the colors on a soap bubble shift when you move your head. For high-performance optics, engineers must design multi-layer coatings to minimize this angular shift.
Material Constraints
The choice of material is critical. It must have the right refractive index to produce the desired effect, but it also needs to be durable, stable, and adhere properly to the underlying surface. Materials like titanium nitride (TiN) or diamond-like carbon (DLC) are chosen for their optical properties and their toughness.
Manufacturing Precision
Achieving a uniform film thickness of a few hundred nanometers across a large surface is a significant technical challenge. This process requires sophisticated vacuum deposition equipment and is a major reason why high-quality optical coatings are expensive.
Applying This Knowledge
Understanding thin-film interference moves it from an abstract concept to a visible, tangible part of the world around you.
- If your primary focus is consumer technology: Recognize that the clarity of your glasses, phone screen, and camera photos is a direct result of engineered destructive interference in AR coatings.
- If your primary focus is engineering or manufacturing: View interference not just as an optical effect, but as an essential metrology technique for controlling processes at the nanometer scale.
- If your primary focus is observing the natural world: See the shimmering colors on a puddle or an insect's wing as a beautiful, real-world demonstration of the wave nature of light.
Ultimately, thin-film interference allows us to turn a fundamental property of light into a precise tool for shaping our technological world.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Function | Key Example |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-Reflection Coatings | Minimize reflection & glare | Eyeglasses, camera lenses, solar panels |
| High-Reflection Coatings/Filters | Reflect specific colors | Projectors, theatrical lighting, cutting tools |
| Semiconductor Metrology | Measure layer thickness with nanometer precision | Microchip fabrication |
| Natural Iridescence | Produce shifting colors | Soap bubbles, oil slicks, insect wings |
Need to control light with precision? The principles of thin-film interference are at the heart of advanced optical coatings and precise manufacturing metrology. At KINTEK, we specialize in the equipment and consumables needed for deposition and analysis in these fields. Whether you are developing next-generation optics or require nanometer-level thickness control in your lab, our expertise can help you achieve superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the components of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition Systems
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What are the uses of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition


















