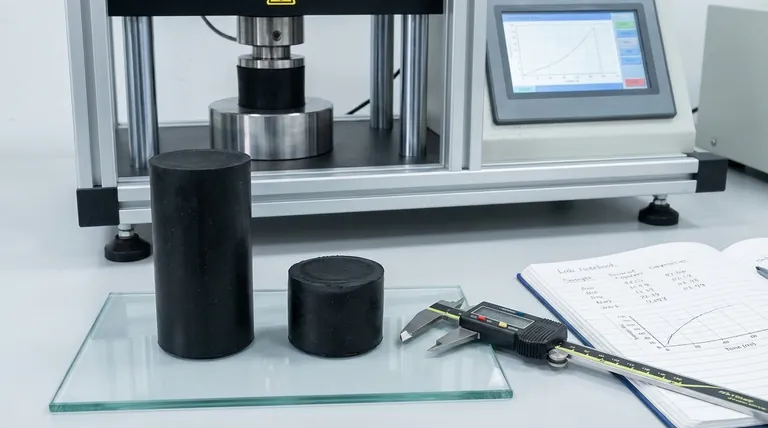
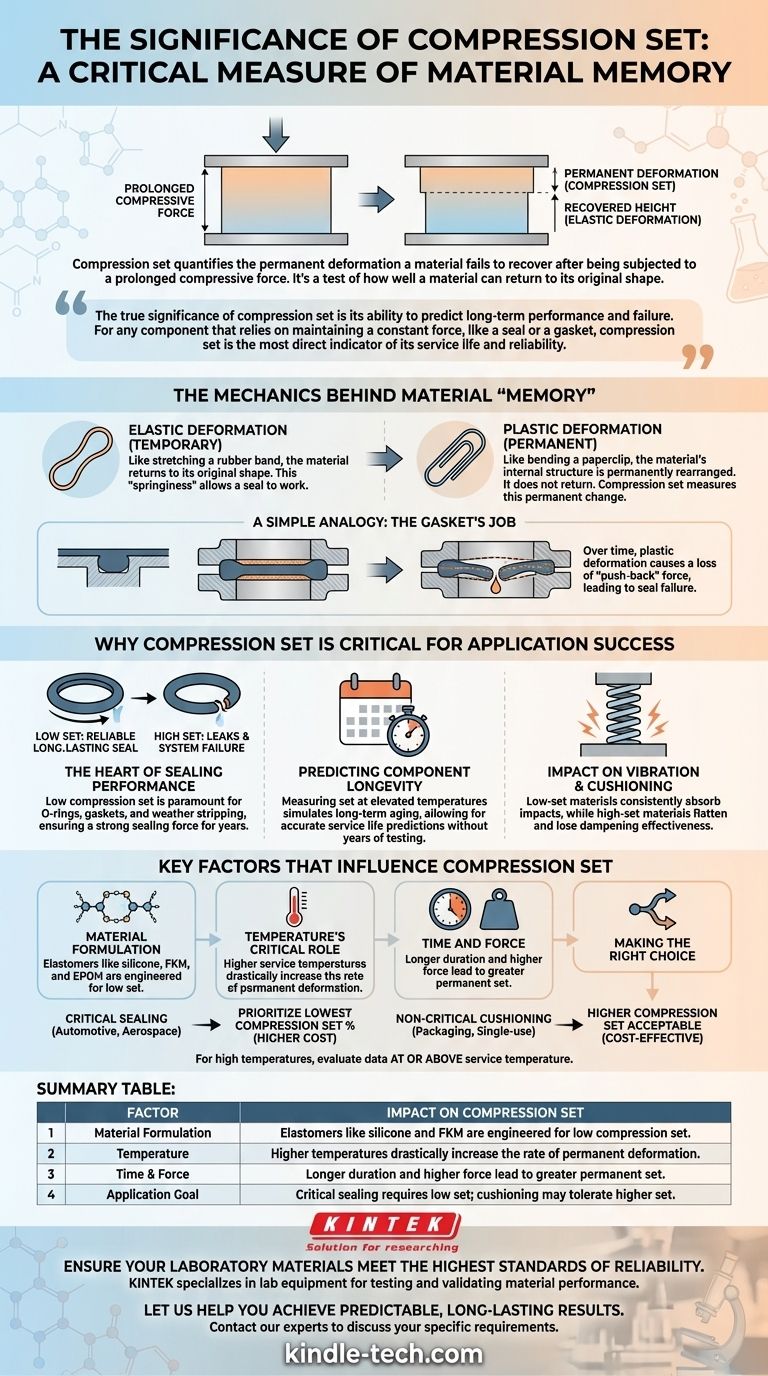
In material science, compression set is a critical measure of a material's memory. It quantifies the permanent deformation—the height a material fails to recover—after being subjected to a prolonged compressive force. In simple terms, it's a test of how well a material can return to its original shape after being squeezed for an extended period.
The true significance of compression set is its ability to predict long-term performance and failure. For any component that relies on maintaining a constant force, like a seal or a gasket, compression set is the most direct indicator of its service life and reliability.

The Mechanics Behind Material "Memory"
To understand why compression set is so important, you must first understand how materials respond to force. The concept boils down to the difference between a temporary bounce-back and a permanent change.
Elastic vs. Plastic Deformation
When you apply a compressive force to a material, it deforms. This deformation can be one of two types.
Elastic deformation is temporary. Like stretching a rubber band, the material returns to its original shape once the force is removed. This "springiness" is what allows a seal to work.
Plastic deformation is permanent. Like bending a paperclip, the material's internal structure is permanently rearranged. It does not return to its original shape. Compression set is a direct measurement of this permanent, plastic deformation.
A Simple Analogy: The Gasket's Job
Imagine a gasket between two metal flanges. Its job is to fill the gap and exert a constant outward force—a "push-back"—to prevent leaks.
Initially, this force is strong. Over time, under the constant pressure and heat, the material begins to experience plastic deformation. It loses some of its ability to push back. This loss of force, caused by compression set, is what eventually leads to seal failure.
Why Compression Set is Critical for Application Success
In many applications, a component's physical shape is less important than the force it exerts. Compression set directly tells you how that force will degrade over time, making it a key predictor of success or failure.
The Heart of Sealing Performance
For any sealing application—o-rings, gaskets, or weather stripping—low compression set is paramount. A seal with low compression set will continue to exert a strong sealing force for years, ensuring a reliable, long-lasting connection.
Conversely, a material with high compression set will quickly "pack down" and lose its sealing force. This will inevitably lead to leaks, contamination, or system failure.
Predicting Component Longevity
By measuring compression set, especially at elevated temperatures, engineers can simulate the effects of long-term aging. This data allows for accurate predictions of a component's service life without waiting for years of real-world testing.
Impact on Vibration and Cushioning
This principle also applies to parts designed to absorb energy, such as vibration dampeners or cushioning pads. A material with low compression set will consistently absorb impacts and return to its ready state, while a high-set material will flatten and lose its dampening effectiveness.
Key Factors That Influence Compression Set
Compression set is not a single, fixed value. It is highly dependent on the material's formulation and the conditions it is exposed to.
Material Formulation
This is the most significant factor. Elastomers like silicone, fluorocarbon (FKM), and EPDM are engineered to have very low compression set, making them ideal for demanding sealing applications. The specific grade and cure system of the polymer also have a massive impact.
Temperature's Critical Role
Heat is an accelerant. Higher service temperatures drastically increase the rate of compression set. For this reason, it is crucial to evaluate compression set data at a temperature relevant to the application's operating environment, not just at room temperature.
Time and Force
The duration and magnitude of the compressive force also play a role. The longer a material is held in compression, and the more it is squeezed, the more permanent set it will develop.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating a material's compression set is about aligning its properties with the demands of your specific application. It ensures you are not over-engineering with a costly material or, more critically, under-engineering and designing for failure.
- If your primary focus is long-term, critical sealing (e.g., automotive gaskets, aerospace o-rings): Prioritize materials with the lowest possible compression set percentage, even at a higher cost.
- If your primary focus is non-critical cushioning or single-use applications (e.g., packaging foam): A material with a higher compression set is often perfectly acceptable and far more cost-effective.
- If your application involves high temperatures: You must evaluate compression set data specifically measured at or above your service temperature, as room-temperature values can be dangerously misleading.
Understanding a material's compression set is fundamental to moving from theoretical design to real-world reliability.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Compression Set |
|---|---|
| Material Formulation | Elastomers like silicone and FKM are engineered for low compression set. |
| Temperature | Higher temperatures drastically increase the rate of permanent deformation. |
| Time & Force | Longer duration and higher force lead to greater permanent set. |
| Application Goal | Critical sealing requires low set; cushioning may tolerate higher set. |
Ensure your laboratory materials meet the highest standards of reliability. Understanding compression set is critical for selecting the right elastomers and polymers for seals, gaskets, and dampeners. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables you need to test and validate material performance.
Let us help you achieve predictable, long-lasting results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your research and quality control processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Filter Testing Machine FPV for Dispersion Properties of Polymers and Pigments
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP for Small Workpiece Production 400Mpa
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the pyrolysis of natural rubber? A Sustainable Solution for Tire and Rubber Waste
- What fillers for rubber compounds? Choose the Right Filler for Performance vs. Cost
- What machine makes molding? Injection Molding Machines for Mass Production
- What are the different types of powder mixers? Choose the Right Mixer for Your Materials
- How many types of mixers are there? Find the Right Mixing Mechanism for Your Material
- What is the difference between monolayer and multilayer film? Choose the Right Packaging for Your Product
- What is the difference between single layer film and multi layer film? A Guide to Material Selection
- What is the screw extrusion process? A Guide to Continuous Plastic Profiling



















