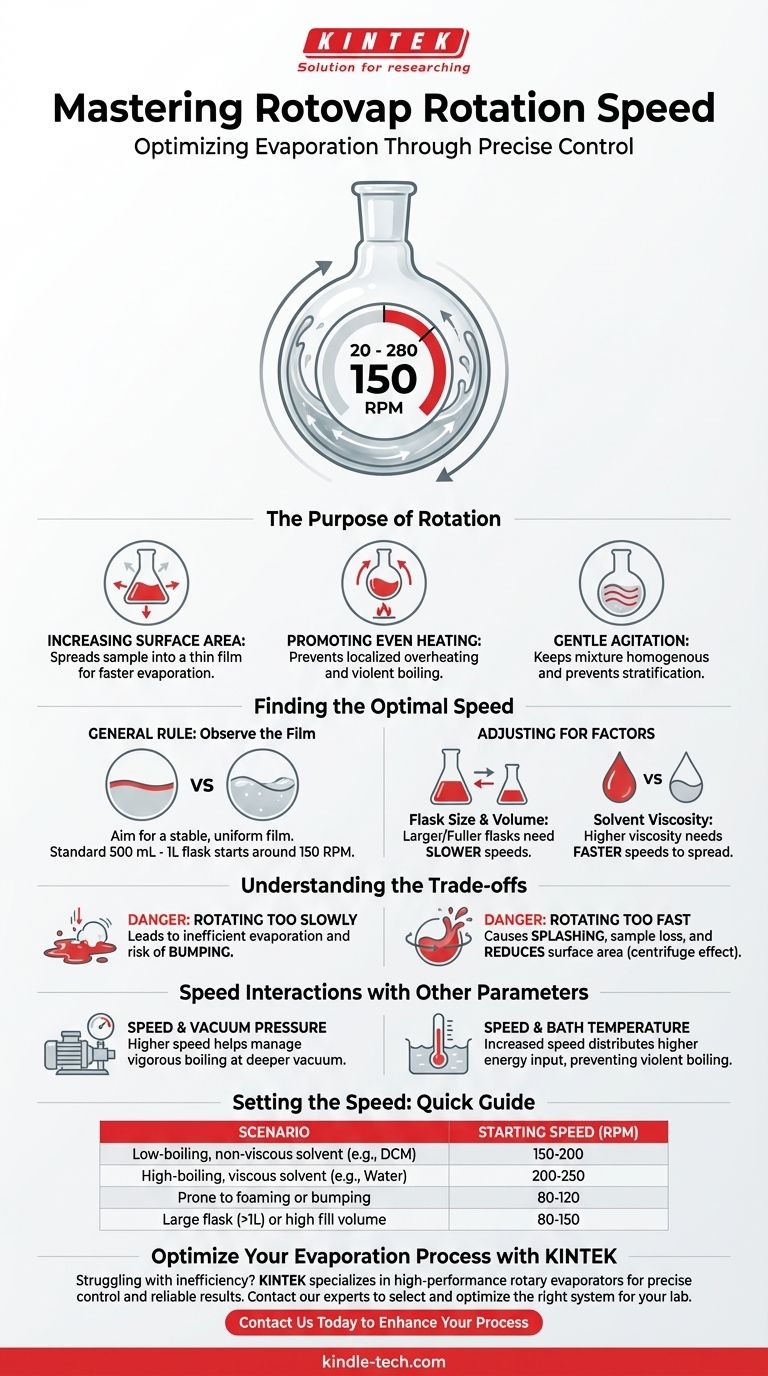
In short, a typical laboratory rotovap (rotary evaporator) operates at a rotation speed between 20 and 280 revolutions per minute (RPM). However, the correct speed is not a single number but a variable you must set to match your specific solvent, flask size, and fill volume for efficient and safe evaporation.
The goal of rotation is not speed itself, but the creation of a large, thin, and uniform film of solvent on the inner wall of the flask. This maximizes the surface area for evaporation while preventing the violent boiling known as "bumping."

The Purpose of Rotation in a Rotovap
Understanding why the flask spins is key to using a rotovap effectively. Rotation is not arbitrary; it serves three critical functions that work together to accelerate solvent removal.
Increasing Surface Area
The primary purpose of rotation is to continuously spread your liquid sample into a thin film across a large area of the flask's inner surface. A larger surface area dramatically increases the rate at which solvent molecules can escape into the vapor phase.
Promoting Even Heating
Rotation ensures that the entire sample is constantly passed through the heated water bath. This prevents localized overheating, which can degrade sensitive compounds or cause violent, uncontrolled boiling.
Gentle Agitation
The spinning motion provides gentle agitation, which prevents thermal stratification and keeps the mixture homogenous. This ensures a smooth, steady rate of evaporation from the entire solution.
Finding the Optimal Rotation Speed
There is no single "best" speed. The optimal setting is the one that creates a stable, uniform film of liquid covering the maximum possible surface area inside the flask.
The General Rule: Observe the Film
For a standard 500 mL to 1 L flask, a starting speed of around 150 RPM is a good rule of thumb. The most important thing is to watch the solvent. You are looking for a smooth, even film, not a wave of liquid sloshing around.
Adjusting for Flask Size and Volume
Larger flasks require slower speeds to achieve the same film-spreading effect. A 2L flask might only need 100 RPM, while a 5L flask might need 60-80 RPM. Similarly, a nearly full flask should be spun slower to prevent splashing.
Adjusting for Solvent Viscosity
High-viscosity solvents, like water or dimethylformamide (DMF), require a slightly faster rotation to overcome their surface tension and spread out into a thin film. Low-viscosity solvents like dichloromethane (DCM) or ether spread easily at moderate speeds.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Setting the speed too high or too low can undermine the entire process, leading to inefficiency or sample loss.
Dangers of Rotating Too Slowly
If the speed is too low, the solvent will pool at the bottom of the flask. This leads to a small surface area, inefficient evaporation, and a high risk of bumping (sudden, violent boiling) as the liquid superheats.
Dangers of Rotating Too Fast
Excessive speed can cause the sample to splash up into the condenser, leading to a loss of your valuable compound. It can also create a "centrifuge effect," where the liquid forms a tight band around the equator of theflask, which actually reduces the effective surface area for evaporation. Finally, very high speeds place unnecessary mechanical stress on the glass joints.
How Speed Interacts with Other Parameters
Rotation speed does not work in a vacuum. It must be balanced with the other two key parameters of rotary evaporation: temperature and vacuum pressure.
Speed and Vacuum Pressure
A deeper vacuum lowers the solvent's boiling point. As the solvent begins to boil more vigorously, a slightly faster rotation can help manage the bubbling and maintain the thin film, preventing bumping.
Speed and Bath Temperature
A higher bath temperature increases the energy input and the rate of boiling. Just as with vacuum, increasing the rotation speed can help distribute this energy and maintain a smooth evaporation process without violent boiling.
Setting the Speed for Your Application
Use these guidelines as a starting point, but always let the behavior of the solvent be your ultimate guide.
- If your primary focus is removing a low-boiling, non-viscous solvent (like DCM or ether): Start around 150-200 RPM to manage the rapid boiling and create a large, stable surface film.
- If your primary focus is removing a high-boiling, viscous solvent (like water or DMF): You may need a slightly higher speed (e.g., 200-250 RPM) to effectively spread the liquid into a thin film.
- If your sample is prone to foaming or bumping: Begin with a slower, gentler speed (e.g., 80-120 RPM) and only increase it if necessary as the solvent volume decreases.
- If you are using a large flask (>1L) or a high fill volume: Reduce your speed (e.g., 80-150 RPM) to prevent splashing and reduce mechanical stress on the equipment.
Mastering rotation speed is about observing the solvent film, not just setting a number.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Effect on Rotation Speed |
|---|---|
| Flask Size | Larger flasks require slower speeds. |
| Solvent Viscosity | High-viscosity solvents need faster speeds. |
| Fill Volume | Higher volumes require slower speeds to prevent splashing. |
| Goal | Create a thin, uniform film for maximum surface area. |
Struggling with inefficient evaporation or sample loss? The correct rotovap speed is crucial for your lab's productivity and sample integrity. KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory equipment, including rotary evaporators designed for precise control and reliable results. Our experts can help you select the right system and optimize its settings for your specific solvents and applications. Contact us today to enhance your evaporation process and achieve superior results. Reach out to our lab equipment specialists now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a water circulating vacuum pump suitable for handling flammable or explosive gases? Inherent Safety Through Isothermal Compression
- What is the purpose of the compression chamber in a vacuum pump? The Heart of Vacuum Generation
- How does the impeller rotation affect the gas flow in a water circulating vacuum pump? A Guide to the Liquid Ring Principle
- How does a water circulating vacuum pump operate? Discover the Efficient Liquid Piston Principle
- What are the advantages of a water circulating vacuum pump? Superior Durability for Demanding Lab Environments



















