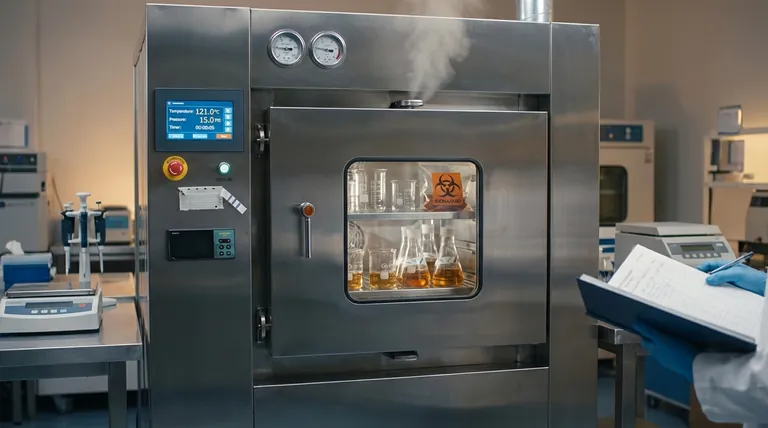
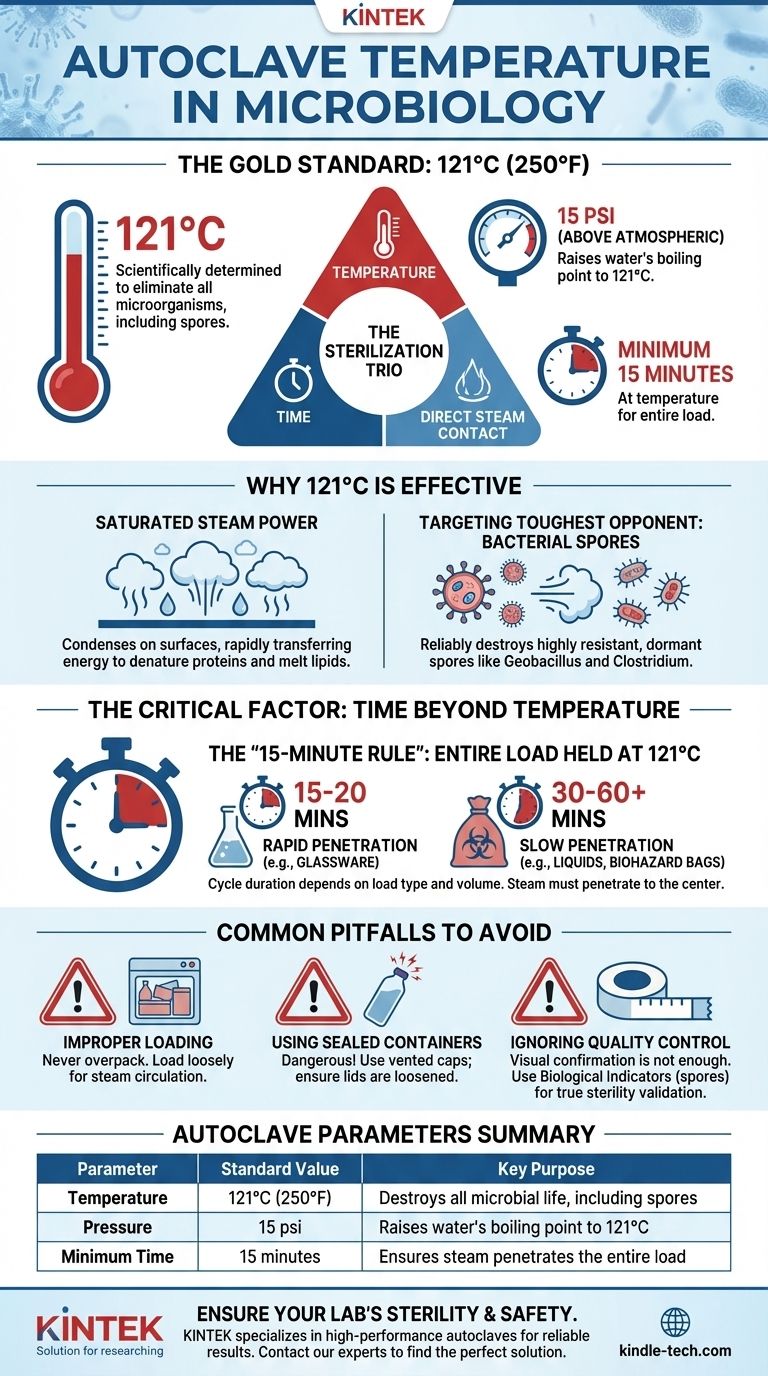
For most microbiology applications, the standard autoclave temperature is 121°C (250°F). This temperature is achieved and maintained by using saturated steam under a pressure of approximately 15 pounds per square inch (psi) above atmospheric pressure. The minimum exposure time at this temperature is typically 15 minutes.
The key to effective sterilization is not just temperature, but the combination of temperature, time, and direct contact with pressurized steam. This trio is required to reliably destroy all forms of microbial life, including the most resilient bacterial spores.

Why 121°C is the Gold Standard
The selection of 121°C is not arbitrary. It is a scientifically determined benchmark designed to guarantee the complete elimination of microorganisms for applications like preparing culture media and decontaminating waste.
The Power of Saturated Steam
Dry heat is a poor conductor of thermal energy. Saturated steam, however, is exceptionally effective at transferring heat.
Under pressure, the steam condenses on cooler surfaces, rapidly transferring a large amount of energy that denatures essential proteins and melts lipids in microbial cells, causing them to die.
Targeting the Toughest Opponent: Bacterial Spores
The primary target for sterilization are bacterial endospores, such as those from the genera Geobacillus and Clostridium. These are dormant, highly resistant structures that can survive boiling and many chemical disinfectants.
A temperature of 121°C is proven to reliably destroy even the most heat-resistant spores within a practical timeframe, ensuring true sterility. If your process can kill these spores, it is considered effective against all other microbes.
The Critical Role of Pressure
In an open environment, water boils at 100°C (212°F), a temperature insufficient for killing bacterial spores quickly.
The pressure inside an autoclave (typically 15 psi) serves one primary purpose: to increase the boiling point of water to 121°C. The pressure itself has a minimal killing effect; it is the enabler of the high temperature.
The Factor Beyond Temperature: Time
Achieving 121°C is only half the battle. The duration of the cycle is equally critical and depends heavily on the items being sterilized.
The "15-Minute Rule" Explained
The standard 15-minute cycle refers to the time the entire load is held at 121°C. This does not include the time it takes for the autoclave to heat up or cool down.
This duration is generally sufficient for sterilizing hard, non-porous items like glassware or metal instruments that allow for rapid steam penetration.
Why Load Type Dictates Cycle Time
The most common point of failure in autoclaving is an insufficient cycle time for the specific load. Steam must penetrate to the very center of the load to be effective.
Large volumes of liquid, dense materials (like biohazard bags), or tightly wrapped surgical packs require significantly longer cycles. For example, a 2-liter flask of media may need 30 minutes or more at 121°C to ensure the liquid in the center reaches the target temperature.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Successful sterilization depends on proper technique. Avoiding these common mistakes is essential for ensuring safety and the integrity of your work.
Improper Loading
Never overpack an autoclave. Items should be loaded loosely to allow steam to circulate freely around and into every object. Leaving space between items is critical for effective sterilization.
Using Sealed Containers
Autoclaving a tightly sealed bottle or container is extremely dangerous and can cause an explosion. Always use vented caps or ensure lids are loosened to allow pressure to equalize. Glassware should be made of borosilicate glass (Pyrex or Kimax) that can withstand the temperature changes.
Ignoring Quality Control
Visual confirmation is not enough. Sterilization must be validated.
- Autoclave tape has stripes that change color when exposed to heat, but this only confirms the chamber reached temperature, not that the load is sterile.
- Biological indicators, containing heat-resistant spores like Geobacillus stearothermophilus, are the gold standard. If the spores are killed after the cycle, you have confirmed true sterilization.
How to Apply This to Your Project
The correct cycle parameters depend entirely on your objective. Use these guidelines as a starting point for developing your specific lab protocols.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing clean instruments or glassware: A standard 15-20 minute cycle at 121°C after proper loading is generally effective.
- If your primary focus is preparing liquid culture media: Increase the cycle time based on volume—a 1-liter flask may need 30 minutes, while a 4-liter flask could require an hour or more.
- If your primary focus is decontaminating biohazardous waste: Use longer cycles (45-60 minutes) and add a small amount of water to the autoclave bag to generate sufficient steam for penetrating dense materials.
Mastering these core principles of steam sterilization is fundamental to ensuring the safety of your laboratory and the validity of your experimental results.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Standard Value | Key Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 121°C (250°F) | Destroys all microbial life, including spores |
| Pressure | 15 psi (above atmospheric) | Raises water's boiling point to 121°C |
| Minimum Time | 15 minutes (at temperature) | Ensures steam penetrates the entire load |
Ensure your lab's sterility and safety with the right equipment.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance autoclaves and lab equipment designed to meet the rigorous demands of microbiology. Our solutions provide reliable temperature control and consistent results for sterilizing media, glassware, and biohazardous waste.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect autoclave for your laboratory's needs and achieve guaranteed sterilization.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How should solid materials in bags be prepared for decontamination? Master Steam Penetration for Safe Sterilization
- What role does an autoclave play in remediation experiments? Ensure Precision by Eliminating Biological Noise
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing
- What is the primary purpose of an autoclave in the preparation of media for the biological leaching of uranium?
- What is the necessity of using a steam autoclave for dental alloys? Ensure Pure Bacterial Adhesion Data



















