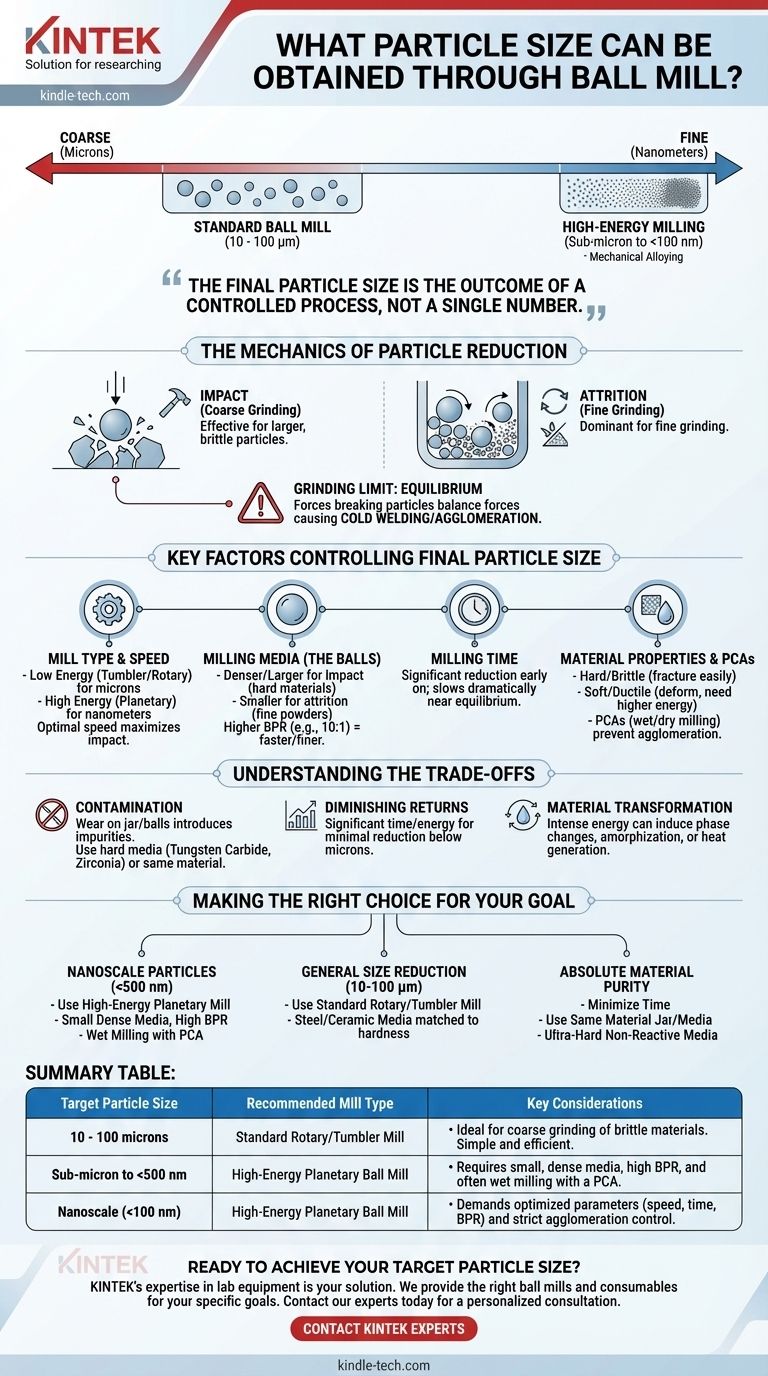
For a standard ball mill, you can typically achieve particle sizes in the range of 10 to 100 microns. However, by using a high-energy planetary ball mill and optimizing process parameters, it is possible to reduce materials down to the sub-micron level, often achieving particle sizes well below 100 nanometers through a process known as mechanical alloying or high-energy milling.
The final particle size from a ball mill is not a single number but the outcome of a controlled process. Your ability to reach the desired size—from coarse microns to fine nanometers—depends entirely on your understanding and manipulation of the key variables at play.

The Mechanics of Particle Reduction
To control the outcome, you must first understand the process. Ball milling reduces particle size through a combination of two primary physical mechanisms occurring inside the milling jar.
Impact and Attrition
Impact is the primary force for coarse grinding. It occurs when grinding balls are lifted by the rotation of the jar and fall onto the material, shattering it like a hammer. This is most effective for breaking down larger, brittle particles.
Attrition (or shear) is the dominant force for fine grinding. This happens as balls and particles are compressed and rub against each other and the jar wall, shearing and grinding the material into much smaller fragments.
Reaching a Grinding Limit
You cannot mill a material indefinitely to get infinitely smaller particles. Eventually, the process reaches a state of equilibrium. The forces that break particles apart are balanced by forces that cause them to fuse back together, a phenomenon known as cold welding or agglomeration.
Key Factors Controlling Final Particle Size
Achieving your target particle size requires a systematic approach. The most critical variables you can control are the milling media, the mill's operational settings, and the properties of the material itself.
Mill Type and Speed
The energy of the system is paramount. A low-energy tumbler or rotary mill is suitable for micron-scale grinding. A high-energy planetary ball mill, which uses centrifugal forces to generate much higher impact energies, is necessary for reaching the nanometer scale. Mill speed is also critical; there is an optimal speed that maximizes the impact energy of the falling balls.
Milling Media (The Balls)
The choice of grinding media is crucial. Denser and larger balls produce higher impact forces, ideal for breaking down large, hard materials. Smaller balls increase the frequency of collisions and favor attrition, which is essential for producing very fine powders. The ball-to-powder weight ratio (BPR) also dictates efficiency; a higher BPR (e.g., 10:1 or 20:1) generally leads to faster and finer grinding.
Milling Time
Longer milling times will progressively reduce particle size. However, this effect is not linear. The most significant reduction occurs early in the process. As particles become smaller, the rate of reduction slows dramatically until it reaches the equilibrium point.
Material Properties
The starting material's characteristics define how it responds to milling. Hard, brittle materials (like ceramics or minerals) fracture easily and are ideal for ball milling. Soft, ductile materials (like certain metals) tend to deform and flatten rather than break, requiring higher energy and longer times to achieve size reduction.
Process Control Agents (PCAs)
For very fine or nanoscale grinding, agglomeration is a major obstacle. Using a Process Control Agent (PCA) can prevent this. In "wet milling," a liquid like ethanol or water is added to dissipate heat and create a slurry that keeps particles separated. In "dry milling," a small amount of a solid or liquid surfactant can be used to coat the particles and prevent them from welding together.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, ball milling is not without its limitations. An objective assessment requires acknowledging the potential downsides.
The Problem of Contamination
The constant impact and attrition will inevitably cause wear on the grinding jar and balls. This wear introduces material from the media into your sample as a contaminant. For high-purity applications, this is a critical concern, often requiring the use of extremely hard media (like tungsten carbide or zirconia) or media made of the same material as the sample.
The Law of Diminishing Returns
Achieving extremely fine particle sizes is energy- and time-intensive. Reducing a powder from 1 millimeter to 10 microns may be relatively quick. However, reducing that same powder from 10 microns to 1 micron could take significantly longer, and going from 1 micron to 100 nanometers longer still, all for a diminishingly small change.
Material Transformation
The intense energy input during high-energy milling can do more than just reduce size. It can induce phase transformations, change a material's crystalline structure into an amorphous one, or generate significant heat that might degrade sensitive organic or biological samples.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your milling strategy should be dictated by your end goal. There is no single "best" setup; there is only the best setup for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is nanoscale particles (<500 nm): You must use a high-energy planetary mill, small and dense grinding media (like zirconia), a high ball-to-powder ratio, and likely a wet milling process with a PCA to prevent agglomeration.
- If your primary focus is general size reduction (10-100 microns): A standard rotary mill with steel or ceramic media matched to the material's hardness will be efficient and effective.
- If your primary focus is maintaining absolute material purity: Minimize milling time, use a jar and media made of the same material as your powder if possible, or select an extremely hard, non-reactive media and account for minor contamination.
Ultimately, a ball mill is a powerful tool whose precision depends on your command of its core principles.
Summary Table:
| Target Particle Size | Recommended Mill Type | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 10 - 100 microns | Standard Rotary/Tumbler Mill | Ideal for coarse grinding of brittle materials. Simple and efficient. |
| Sub-micron to <500 nm | High-Energy Planetary Ball Mill | Requires small, dense media, high BPR, and often wet milling with a PCA. |
| Nanoscale (<100 nm) | High-Energy Planetary Ball Mill | Demands optimized parameters (speed, time, BPR) and strict agglomeration control. |
Ready to Achieve Your Target Particle Size?
Whether your laboratory needs involve coarse grinding or precise nanomaterial synthesis, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment is your solution. We specialize in providing the right ball mills and consumables—from durable milling jars to high-density grinding media—tailored to your specific material and particle size goals.
Let us help you optimize your milling process for maximum efficiency and purity. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover the KINTEK difference in laboratory performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the ball mill based on the principle of? Impact and Attrition for Efficient Grinding
- How do stainless steel grinding jars and balls contribute to mechanical alloying? Optimize HEA Powder Synthesis
- Why are excellent sealing and corrosion resistance required for WC-10Co ball milling? Ensure High-Purity Mixing Results
- Why is a ball mill jar lined with Y-ZrO2 required for Na3PS4 synthesis? Ensuring Purity in Sulfide Electrolytes
- What is the benefit of using tungsten carbide (WC) milling jars and balls? Achieve High-Energy Milling Efficiency



















