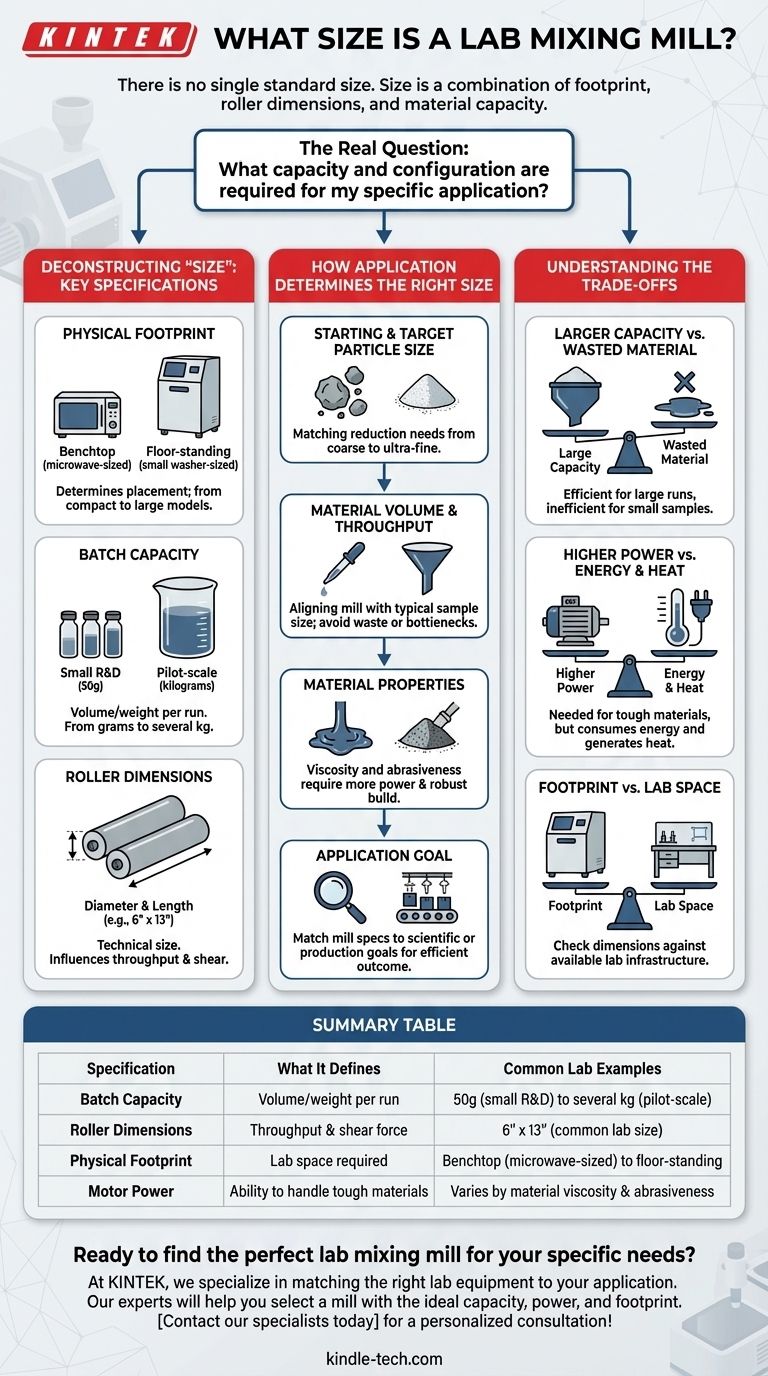
In practice, there is no single standard size for a lab mixing mill. The term "size" is not defined by a single dimension but by a combination of its physical footprint, the dimensions of its rollers, and its material processing capacity. These factors vary significantly based on the mill's intended application, from small benchtop units for R&D to larger pilot-scale models.
The most critical question isn't "what size is a lab mill," but rather, "what capacity and configuration are required for my specific application?" The right "size" is a function of your material volume, desired particle characteristics, and available lab space.

Deconstructing "Size": The Key Specifications
To properly evaluate a lab mixing mill, you must understand the different ways its size is specified. Each metric tells a different part of the story about the machine's capabilities and requirements.
Physical Footprint
A lab mill's external dimensions determine where it can be placed. Most are designed as benchtop units, roughly the size of a large microwave oven.
However, more powerful models intended for tougher materials or slightly larger batches can be floor-standing, approaching the size of a small washing machine and weighing several hundred pounds.
Batch Capacity
This is the most important functional "size." It defines the volume or weight of material the mill can process effectively in a single batch.
Capacity is typically measured in liters or kilograms. A small R&D mill might handle as little as 50 grams, while a larger pilot-scale lab mill could process several kilograms at a time.
Roller Dimensions
The technical "size" of a two-roll mill is almost always described by the diameter and length of its rollers. This is a standard industry specification.
For example, a common lab mill size might be listed as 6" x 13", meaning it has rollers with a 6-inch diameter and a 13-inch working length. These dimensions directly influence the mill's throughput and the amount of shear it can apply.
How Application Determines the Right Size
Choosing the correct mill size is a process of matching the machine's specifications to your scientific or production goals. The wrong choice can lead to wasted material, inefficient processing, or an inability to achieve the desired outcome.
Starting and Target Particle Size
The primary function of many mills is particle size reduction. The energy and design required to break down large, coarse particles are different from what's needed for ultra-fine grinding.
You must select a mill capable of handling your starting particle size and efficiently achieving your target particle size without over-processing the material.
Material Volume and Throughput
Consider your typical sample volume. If you are working with very small quantities for initial formulation, a large mill is impractical and wasteful.
Conversely, if you need to produce kilogram-scale batches for pilot studies, a small R&D mill will be a significant bottleneck, requiring numerous runs to produce enough material.
Material Properties
The characteristics of your material, such as viscosity and abrasiveness, heavily influence the required power and build of the mill.
Mixing high-viscosity polymers requires a mill with a powerful motor and a robust frame, which generally leads to a larger and heavier machine, even if the batch capacity is relatively small.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a mill size involves balancing competing priorities. Being aware of these trade-offs is crucial for making an informed decision.
Larger Capacity vs. Wasted Material
A mill with a large batch capacity will have a high minimum fill level. Using it for a small sample is inefficient, leads to significant material loss on the rollers, and makes cleanup difficult.
Higher Power vs. Energy and Heat
More powerful motors, needed for tough materials, consume more energy. They also generate more frictional heat, which can be a critical issue if you are processing heat-sensitive compounds.
Footprint vs. Lab Space
The most straightforward trade-off is physical size versus available laboratory space. Always confirm the machine's dimensions and weight to ensure it fits on your bench or in its designated area and that your infrastructure can support it.
Selecting the Right Mill for Your Needs
To make the best choice, align the mill's specifications directly with the primary goal of your work.
- If your primary focus is early-stage R&D with small samples: Prioritize a compact, benchtop mill with the lowest possible minimum batch capacity to conserve valuable materials.
- If your primary focus is process development or pilot batches: Select a larger, more robust mill where batch capacity and throughput are the most important specifications.
- If your primary focus is working with high-viscosity or very tough materials: Focus on motor power (horsepower or kilowatts) and the strength of the frame, as these are more critical than capacity alone.
Ultimately, defining your application with precision is the first and most critical step to selecting a correctly sized lab mill.
Summary Table:
| Specification | What It Defines | Common Lab Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Batch Capacity | Volume/weight per run | 50g (small R&D) to several kg (pilot-scale) |
| Roller Dimensions | Throughput & shear force | 6" x 13" (common lab size) |
| Physical Footprint | Lab space required | Benchtop (microwave-sized) to floor-standing |
| Motor Power | Ability to handle tough materials | Varies by material viscosity and abrasiveness |
Ready to find the perfect lab mixing mill for your specific needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in matching the right lab equipment to your application. Whether you're in R&D working with small, precious samples or scaling up for pilot production, our experts will help you select a mill with the ideal capacity, power, and footprint.
We supply reliable lab mixing mills and consumables to ensure your processes are efficient and effective.
Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation and let us help you optimize your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Jar Mill with Agate Grinding Jar and Balls
People Also Ask
- What is the function of ultrasonic homogenizers in g-C3N4 preparation? Unlocking Maximum Catalytic Activity
- What is a ball mill used in pharmaceutical industry? Achieve Superior Particle Size Reduction for Drug Efficacy
- What is the primary role of grinding equipment in the pretreatment of copper concentrate for bioleaching?
- What is a particle pulverizer? A Guide to Controlled Size Reduction for Materials
- What are the different types of grinding balls? A Guide to Steel vs. Ceramic Media for Optimal Milling
- How is an agate mortar utilized during the final processing stages of solid electrolyte powders? Ensure High Purity.
- What is the function of a Wiley grinding mill in the processing of elephant grass? Optimize Your Chemical Analysis
- What are the advantages of an ultrasonic homogenizer for PHA recovery? Boost Efficiency in Biopolymer Research



















