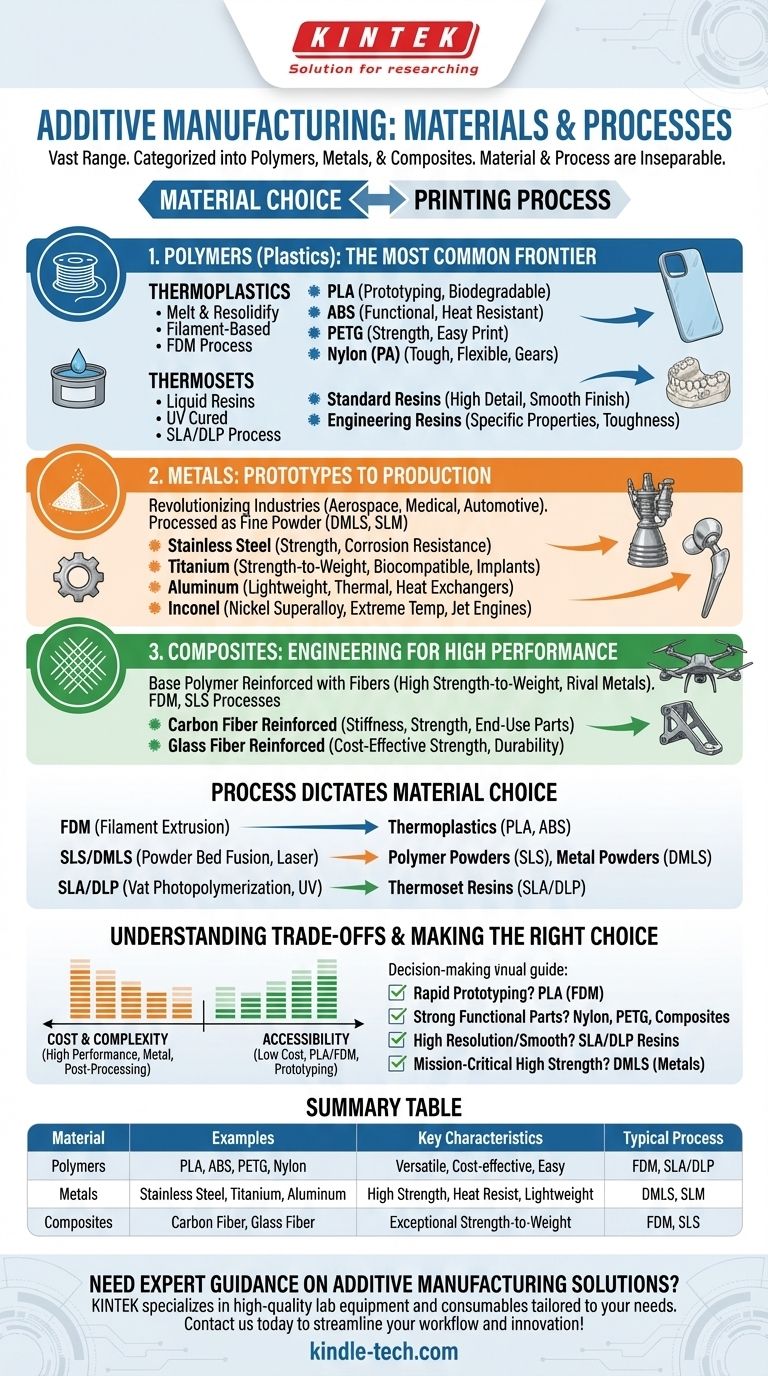
The short answer is that additive manufacturing works with a vast and rapidly expanding range of materials, primarily categorized into three groups: polymers (plastics), metals, and composites. While plastics are the most common, advancements now allow for printing everything from biocompatible titanium for medical implants to specialized ceramic components for high-temperature applications.
The most critical concept to understand is that the choice of material is inseparable from the choice of printing process. You don't just choose a material; you choose a material-and-process combination that delivers the specific properties your final part requires.

The Primary Material Categories in Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing materials are defined by their chemical composition and the form they take for printing, such as filament, liquid resin, or fine powder.
Polymers (Plastics): The Most Common Frontier
Polymers are by far the most widely used materials in 3D printing, valued for their versatility, low cost, and ease of use. They are broadly split into two types.
Thermoplastics are plastics that can be melted and solidified multiple times without degrading. This makes them ideal for filament-based printing. Common examples include:
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): Easy to print and biodegradable, making it perfect for rapid prototyping and non-functional models.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Stronger and more temperature-resistant than PLA, used for functional parts like phone cases and automotive trim.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): A good balance of strength, temperature resistance, and ease of printing. Often used for mechanical parts.
- Nylon (PA): Known for its exceptional toughness, flexibility, and durability, making it ideal for gears, living hinges, and other high-wear parts.
Thermosets are liquid resins that become irreversibly solid when cured by UV light. They are used in processes that deliver extremely high detail and smooth surface finishes.
- Standard Resins: Excellent for creating detailed visual models and prototypes with a smooth, injection-molded-like finish.
- Engineering Resins: Formulated to have specific properties like high toughness, flexibility, or temperature resistance, mimicking engineering-grade plastics.
Metals: From Prototypes to Production Parts
Metal additive manufacturing has revolutionized industries like aerospace, medicine, and automotive by enabling the creation of complex, lightweight, and high-strength parts that are impossible to produce with traditional methods.
These materials are typically processed in a fine powder form. Key examples include:
- Stainless Steel: Valued for its strength, corrosion resistance, and ductility.
- Titanium: Offers an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and is highly biocompatible, making it a top choice for medical implants and aerospace components.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and possessing good thermal properties, used for heat exchangers and automotive parts.
- Inconel (Nickel superalloy): Retains its strength at extreme temperatures, making it critical for jet engine and rocket components.
Composites: Engineering for High Performance
Composites involve a base polymer (like Nylon) reinforced with chopped or continuous fibers to dramatically enhance its mechanical properties.
The primary benefit is achieving a high strength-to-weight ratio, often rivaling that of metals but at a fraction of the weight.
- Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers: The most common composite, offering exceptional stiffness and strength for jigs, fixtures, and end-use functional parts.
- Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers: A more cost-effective option than carbon fiber, providing significant strength and durability improvements over standard plastics.
How Printing Process Dictates Material Choice
The technology of the 3D printer determines which type and form of material it can process. This link is fundamental to understanding your options.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
This common desktop technology works by extruding a melted filament of thermoplastic (like PLA or ABS) layer by layer. It is cost-effective and versatile but offers lower resolution.
Powder Bed Fusion (SLS and DMLS)
These processes use a high-powered laser to fuse or melt particles of a fine powder.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is used for polymer powders, primarily Nylon.
- Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) is used for metal powders like titanium and aluminum.
Vat Photopolymerization (SLA and DLP)
These technologies use a UV light source to selectively cure a liquid thermoset resin in a vat, producing parts with exceptional detail and surface finish.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material is always a balance of cost, performance, and process complexity. There is no single "best" material.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between material performance and cost. A spool of standard PLA filament might cost $25, while a similar amount of a high-performance carbon-fiber composite can be five times that. Metal powders are an order of magnitude more expensive still.
Process Complexity and Post-Processing
Printing with basic thermoplastics on an FDM printer is relatively straightforward. In contrast, metal printing requires a highly controlled environment, extensive support structures, and significant post-processing steps like heat treatment and machining to achieve the final desired properties.
Design Limitations
The material and process combination imposes design constraints. For example, the need for support structures in FDM printing can impact surface finish, while the thermal stresses in metal printing must be accounted for in the design phase to prevent part failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application should always drive your material selection. Consider what the part needs to do before deciding what it should be made of.
- If your primary focus is rapid, low-cost prototyping: PLA used with FDM technology is the most accessible and cost-effective path for validating form and fit.
- If your primary focus is strong, functional plastic parts: Materials like Nylon, PETG, or carbon-fiber composites provide superior mechanical properties for end-use applications.
- If your primary focus is high-resolution detail and smooth surfaces: Vat photopolymerization (SLA/DLP) with thermoset resins is the ideal choice for visual models or mold patterns.
- If your primary focus is mission-critical, high-strength applications: Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) with materials like Titanium or Stainless Steel is required, despite the higher cost.
Ultimately, selecting a material is the strategic decision that defines the capability, cost, and purpose of your 3D printed part.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Examples | Key Characteristics | Typical Printing Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polymers (Plastics) | PLA, ABS, PETG, Nylon | Versatile, cost-effective, easy to use | FDM, SLA/DLP (Resins) |
| Metals | Stainless Steel, Titanium, Aluminum | High strength, heat resistance, lightweight | DMLS, SLM (Powder Bed Fusion) |
| Composites | Carbon Fiber, Glass Fiber Reinforced | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | FDM, SLS |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right materials and equipment for your additive manufacturing projects? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your laboratory's unique needs. Whether you're prototyping with polymers or producing end-use metal parts, our solutions ensure precision, reliability, and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your innovation and streamline your workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- Nickel Aluminum Tabs for Soft Pack Lithium Batteries
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic coating? A Guide to Sacrificial vs. Barrier Protection
- What are two disadvantages of metal? Understanding Corrosion and Weight Limitations
- Why is platinum unreactive? The Atomic Secrets Behind Its Remarkable Stability
- What is titanium disadvantages and advantages? Weighing Performance vs. Cost for Your Project
- What products are manufactured with titanium? The Ultimate Guide to High-Performance Materials





