Rotary Evaporator Components
Main Parts and Functions
The rotary evaporator is composed of several key components, each playing a crucial role in the evaporation process. These components include the rotary motor, evaporation tube, vacuum system, fluid heating pots, condensation tubes, condensation sample collection bottles, and mechanisms for raising and lowering the evaporation vial.
-
Rotary Motor: This motor drives the rotation of the evaporation tube, creating a centrifugal force that spreads the sample into a thin film. This film enhances the surface area for efficient evaporation.
-
Evaporation Tube: The evaporation tube holds the sample to be evaporated. Its rotation under vacuum conditions facilitates the even distribution of the sample, ensuring rapid and efficient evaporation.
-
Vacuum System: The vacuum system reduces the pressure within the evaporation chamber, lowering the boiling point of the solvent. This allows for faster evaporation at lower temperatures, preventing sample degradation.
-
Fluid Heating Pots: These pots provide the necessary heat to the evaporation tube. The controlled heating ensures uniform temperature distribution, promoting consistent evaporation rates.
-
Condensation Tubes: Condensation tubes cool the evaporated solvent vapors, causing them to condense back into liquid form. This process is crucial for solvent recovery and sample purification.
-
Condensation Sample Collection Bottles: These bottles collect the condensed solvent, allowing for easy recovery and reuse. Proper collection ensures no loss of valuable solvent.
-
Mechanisms for Raising and Lowering the Evaporation Vial: These mechanisms enable precise control over the position of the evaporation vial. Adjusting the height and angle optimizes the evaporation process, ensuring maximum efficiency.
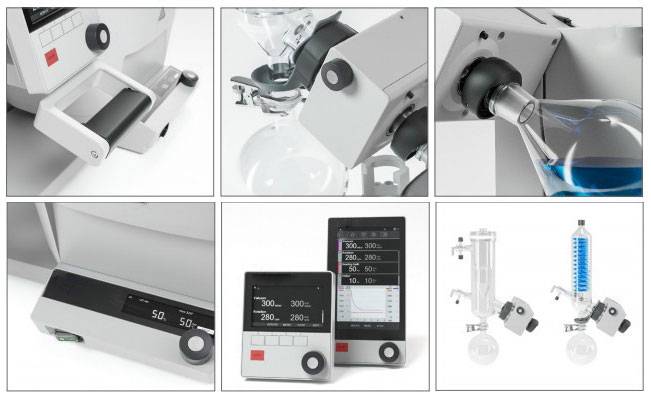

Each of these components works in harmony to achieve efficient solvent evaporation, concentration, and recovery, making the rotary evaporator an indispensable tool in various scientific and industrial applications.
Glass Assembly and Vacuum System
The vacuum system in a rotary evaporator can range from a basic water pump to more sophisticated vacuum pumps, each designed to create the necessary pressure differential for efficient evaporation. The choice of vacuum pump often depends on the specific distillation goals and the characteristics of the solvent being processed.
The glass assembly, which includes the evaporation and condensation components, can vary significantly in complexity. This variability is tailored to meet the unique requirements of different distillation processes. For instance, solvents with high boiling points may necessitate a more intricate glass assembly to ensure effective condensation and sample collection. Conversely, simpler setups may suffice for solvents with lower boiling points or when the distillation goals are less demanding.
In summary, the vacuum system and glass assembly are critical components that must be carefully selected and configured to optimize the performance of the rotary evaporator.
Applications and Advantages
Application Areas
Rotary evaporators play a pivotal role in various scientific and industrial processes, particularly in the pharmaceutical, chemical, and biological sectors. These devices are indispensable for evaporation, concentration, crystallization, drying, separation, and solvent recovery. Each of these processes is critical for refining raw materials and synthesizing complex compounds.
For instance, in the pharmaceutical industry, rotary evaporators are used to concentrate active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) from their initial solutions, ensuring purity and potency. In the chemical industry, these devices help in the separation of different chemical components, which is essential for the synthesis of new compounds. In the biological field, rotary evaporators are crucial for drying biological samples, such as proteins and nucleic acids, to preserve their integrity for further analysis.
Moreover, the solvent recovery feature of rotary evaporators is particularly beneficial in industries where solvents are expensive and environmentally hazardous. By efficiently recovering and reusing solvents, these devices not only reduce operational costs but also contribute to environmental sustainability.
In summary, the multifaceted applications of rotary evaporators across various industries underscore their significance in modern scientific and industrial operations.

Advantages and Disadvantages
The rotary evaporator offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice in various scientific and industrial applications. One of the key benefits is the formation of a large heat area due to the creation of a liquid film on the inner surface of the evaporation tube. This film significantly enhances the heat transfer efficiency, allowing for rapid evaporation of solvents. Additionally, the design effectively inhibits sample boiling, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the sample during the evaporation process.
However, the rotary evaporator is not without its drawbacks. A notable disadvantage is the potential for sample loss due to uncontrolled boiling. This issue can arise under certain conditions, particularly when the vacuum pressure is not adequately controlled. To mitigate this risk, operators can adjust the strength of the vacuum pump to maintain optimal pressure levels. Alternatively, the addition of anti-boiling particles can help stabilize the sample and prevent excessive boiling, thereby reducing the likelihood of sample loss.
Handling and Operation
Handling Precautions
When handling a rotary evaporator, it is crucial to follow specific guidelines to prevent damage and ensure the longevity of the equipment. The primary focus should be on the proper techniques for carrying, transporting, and moving the device.
Carrying the Rotary Evaporator
- Support Both Ends: Always support the rotary evaporator from both the top and the base when lifting. This prevents undue stress on any single part of the device.
- Use Appropriate Lifting Tools: If the equipment is heavy, use appropriate lifting tools such as a trolley or a dolly to avoid strain on the back and arms.
Transporting the Rotary Evaporator
- Secure the Equipment: Ensure that the rotary evaporator is securely fastened within its transport case to prevent any movement during transit.
- Avoid Sudden Movements: When transporting, avoid sudden stops or turns that could cause the equipment to shift or fall.
Moving the Rotary Evaporator
- Check for Obstacles: Before moving the rotary evaporator, ensure the path is clear of any obstacles that could cause a trip or fall.
- Maintain a Steady Pace: Move at a steady pace to avoid jerky motions that could dislodge or damage the equipment.
By adhering to these handling precautions, you can significantly reduce the risk of damage to your rotary evaporator, ensuring its continued efficient operation.

Operating Procedures
To ensure a smooth and efficient evaporation process, follow these detailed steps:
-
Connecting the Evaporator:
- Begin by securely connecting the evaporation tube to the rotary motor. Ensure all fittings are tight to prevent any leakage during operation.
- Next, attach the vacuum system to the evaporation tube. This could be a simple water pump or a more complex vacuum pump, depending on your setup.
-
Filling the Heating Tank:
- Fill the heating tank with the appropriate solvent or heating medium. The level should be sufficient to cover the evaporation tube but not exceed the maximum fill line.
- Ensure the heating medium is compatible with the solvents being evaporated to prevent any chemical reactions or contamination.
-
Adjusting the Angle and Height:
- Position the evaporation tube at the correct angle to optimize solvent flow and evaporation efficiency. Typically, an angle between 15° and 30° is recommended.
- Adjust the height of the evaporation tube to ensure it is submerged in the heating medium without touching the bottom of the tank. This ensures even heating and prevents damage to the glassware.
-
Starting the Rotation and Heating:
- Turn on the rotary motor to start the rotation of the evaporation tube. The speed should be set according to the solvent's viscosity and the desired evaporation rate.
- Begin heating the tank gradually to avoid thermal shock. Monitor the temperature closely to ensure it does not exceed the solvent's boiling point.
-
Completing the Evaporation Process:
- As the solvent evaporates, it will pass through the condensation tubes and collect in the sample collection bottles. Monitor the process to ensure efficient condensation and collection.
- Once the evaporation is complete, turn off the heating and rotation. Carefully detach the vacuum system and allow the remaining solvent to cool before handling.
By following these steps, you can ensure a successful and safe evaporation process with your rotary evaporator.
Packing and Closing the Box
When it comes to packing the rotary evaporator for storage or transport, it is crucial to follow a meticulous process to ensure all components are securely in place and the box is properly closed. Here are the key steps to follow:
-
Component Check: Begin by verifying that all parts of the rotary evaporator are present. This includes the rotary motor, evaporation tube, vacuum system components, fluid heating pots, condensation tubes, and collection bottles. Ensure that any mechanical or motorized mechanisms for raising and lowering the evaporation vial are also accounted for.
-
Secure Placement: Carefully place each component in the designated compartments within the storage box. Use the original packing materials provided, such as foam inserts or dividers, to protect delicate glass assemblies and other sensitive parts. This helps in preventing any movement or damage during transit.
-
Box Closure: Once all parts are securely placed, close the box gently. Ensure that the lid aligns properly with the base and use the appropriate fastening methods, such as latches or straps, to secure the box. Double-check that all fasteners are properly tightened to prevent any accidental opening during handling.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your rotary evaporator is safely packed and ready for storage or transport, minimizing the risk of damage and ensuring all components remain intact.
Troubleshooting

Common Issues and Solutions
When operating a rotary evaporator, several common issues may arise, each requiring specific solutions to ensure smooth and effective operation. Here are some of the most frequent problems and their corresponding remedies:
Motor Not Rotating
- Possible Causes:
- Power supply issues.
- Motor malfunction.
- Faulty connection between the motor and control panel.
- Solutions:
- Check the power supply and ensure it is functioning correctly.
- Inspect the motor for any visible damage or wear.
- Verify the connections between the motor and control panel, ensuring they are secure and properly aligned.
Bath Not Heating
- Possible Causes:
- Heating element failure.
- Faulty temperature sensor.
- Insufficient power supply to the heating system.
- Solutions:
- Test the heating element to confirm it is working.
- Replace or recalibrate the temperature sensor if it is not functioning properly.
- Ensure the power supply to the heating system is adequate and stable.
Bath Pot Flush Temperature Detection
- Possible Causes:
- Clogged or dirty temperature sensor.
- Incorrect sensor placement.
- Sensor malfunction.
- Solutions:
- Clean the temperature sensor to remove any debris or buildup.
- Adjust the sensor's position to ensure it is correctly placed in the bath pot.
- Replace the sensor if it is not reading temperatures accurately.
Vacuum Pumping Not Working
- Possible Causes:
- Vacuum pump malfunction.
- Leak in the vacuum system.
- Incorrect settings on the vacuum pump.
- Solutions:
- Inspect the vacuum pump for any issues and repair or replace it if necessary.
- Check the entire vacuum system for leaks and seal any gaps.
- Review and adjust the vacuum pump settings to ensure they are optimal for the process.
By addressing these common issues with the appropriate solutions, users can maintain the efficiency and longevity of their rotary evaporators.
Related Products
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
Related Articles
- A Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Rotary Vacuum Evaporator for Solvent Removal
- Step-by-Step Guide to Operating a Short Path Distillation Apparatus
- Choosing the Right Rotary Vacuum Evaporator for Your Lab
- How to Choose Laboratory Vacuum Pumps for Maximum Efficiency and Cost Savings
- Exploring the Science Behind Rotary Evaporators: How They Work and Their Applications