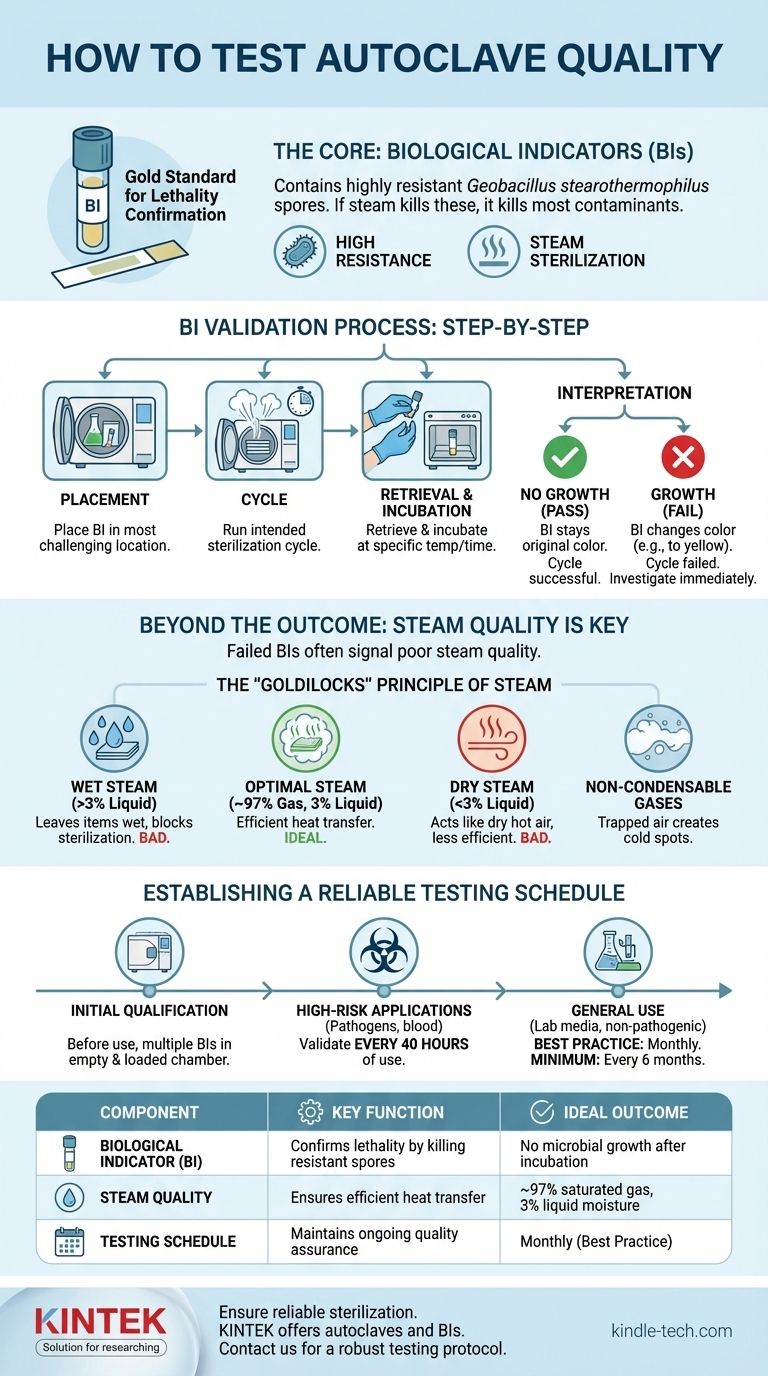
At its core, testing an autoclave's quality hinges on verifying its ability to kill highly resistant microorganisms. This is achieved using biological indicators (BIs), typically containing spores of Geobacillus stearothermophilus. These indicators are run through a sterilization cycle and then cultured; the absence of microbial growth confirms the autoclave is operating effectively and its steam is successfully sterilizing the load.
While biological indicators confirm a sterilization outcome, true quality assurance involves understanding the factors that produce that outcome—primarily steam quality and a consistent testing schedule. A successful test confirms a past cycle, but a comprehensive strategy ensures future reliability.

The Foundation of Autoclave Validation: Biological Indicators
The biological indicator is the gold standard for confirming lethality in a sterilization cycle. It provides direct evidence that the conditions necessary to kill highly resistant life were met.
What is a Biological Indicator?
A BI contains a known population of bacterial spores, most commonly Geobacillus stearothermophilus. These spores are chosen because they are significantly more resistant to steam sterilization than common pathogenic microorganisms.
If conditions are sufficient to kill these highly resistant spores, it provides a high degree of confidence that all other potential contaminants have also been destroyed.
The Validation Process Step-by-Step
- Placement: Place the BI vial or strip in the most challenging location within the autoclave load (e.g., inside a dense pack or a large flask).
- Cycle: Run the intended sterilization cycle as you normally would.
- Retrieval & Incubation: After the cycle, carefully retrieve the BI. It is then activated (if needed) and incubated at the appropriate temperature for a specified time. A non-processed control BI is incubated alongside it.
- Interpretation: The control BI should show growth. The test BI is then observed for any signs of growth, often indicated by a color change in the growth medium.
Interpreting the Results
The outcome is straightforward:
- No growth (Pass): The autoclave cycle was successful.
- Growth (Fail): The cycle failed to achieve sterilization. This requires immediate investigation into the autoclave's function, loading procedures, and cycle parameters.
Beyond the Outcome: Assessing Steam Quality
A failed BI test is often a symptom of a deeper problem. The single most important factor for effective autoclaving is the quality of the steam itself.
The "Goldilocks" Principle of Steam
Optimal steam for sterilization is not just hot vapor; it is a precise mixture. The ideal composition is approximately 97% saturated gas and 3% liquid moisture.
This mixture is critical because it efficiently transfers its immense thermal energy (latent heat of condensation) to the items being sterilized upon contact.
The Problem with "Wet" Steam
If the steam has too much moisture (>3% liquid), it can leave items wet after the cycle. This moisture can interfere with drying, damage sensitive equipment, and even insulate microorganisms, shielding them from the sterilizing heat.
The Danger of "Dry" or Superheated Steam
Conversely, if steam contains too little moisture, it begins to act like dry hot air. Dry air is a far less efficient sterilant than saturated steam, requiring much higher temperatures and longer exposure times to achieve the same level of killing.
The Role of Non-Condensable Gases
Gases like air that are trapped in the autoclave chamber are "non-condensable" at sterilization temperatures. These gases form insulating pockets that prevent steam from making direct contact with item surfaces, creating cold spots where microorganisms can survive.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Simply running a test is not enough. How you test and what you monitor are critical for meaningful results.
Over-reliance on a Single Test Point
Placing a single BI in an empty, easy-to-reach spot does not validate a real-world process. A test is only as good as its placement. It must be positioned in the part of your typical load that is hardest for steam to penetrate.
Ignoring Physical Monitors
Your autoclave's gauges for temperature, pressure, and time are your first line of defense. A BI test confirms a past result, but watching the physical monitors during every cycle can alert you to a problem—like a slow rise to temperature—in real time.
Improper Loading Procedures
The most common cause of sterilization failure is not a broken autoclave, but an improperly loaded one. Overpacking the chamber, using sealed containers, or stacking items in a way that blocks steam flow will guarantee cold spots and failed cycles.
Establishing a Reliable Testing Schedule
Your testing frequency should be dictated by the risk level of the materials you process.
Initial Qualification
Before any autoclave is put into service, it must be thoroughly tested to confirm it operates correctly. This often involves multiple BIs placed throughout an empty and a fully loaded chamber.
High-Risk Applications
For autoclaves inactivating human pathogens, blood, tissues, or clinical samples, testing is far more frequent. The standard requirement is to validate performance after every 40 hours of use.
General Use and Best Practices
For autoclaves sterilizing general laboratory media or non-pathogenic materials, testing every six months is a common minimum. However, a widely accepted best practice is to test at least once per month to ensure ongoing confidence in the sterilization process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your testing strategy should directly align with your operational needs and risk profile.
- If your primary focus is clinical or pathogenic waste: You must adhere to the stringent 40-hour testing schedule to ensure public and environmental safety.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing general lab media or equipment: A monthly biological indicator test is the recommended best practice for consistent quality assurance.
- If you are commissioning a new autoclave: Perform initial qualification with multiple biological indicators in various locations before it is ever placed into service.
Ultimately, a robust testing protocol transforms validation from a simple pass/fail check into a continuous process of quality assurance.
Summary Table:
| Test Component | Key Function | Ideal Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Biological Indicator (BI) | Confirms lethality by killing resistant spores | No microbial growth after incubation |
| Steam Quality | Ensures efficient heat transfer for sterilization | ~97% saturated gas, 3% liquid moisture |
| Testing Schedule | Maintains ongoing quality assurance | Monthly (best practice) to every 40 hours (high-risk) |
Ensure your lab's sterilization process is reliable and compliant. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including autoclaves and biological indicators. Our experts can help you establish a robust testing protocol to protect your research and ensure safety. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How does an autoclave sterilize instruments supplies and equipment? A Guide to High-Pressure Steam Sterilization
- How do you sterilize glassware by autoclave? Master the 3-Step Process for Reliable Sterility
- How much time is required for autoclave sterilization of instruments? Understand the Full Cycle for Safety
- What precautions should be taken when using an autoclave in the laboratory? A Guide to Safe Sterilization
- What are the settings for autoclave sterilization? Ensure Reliable Sterility with Proper Parameters











