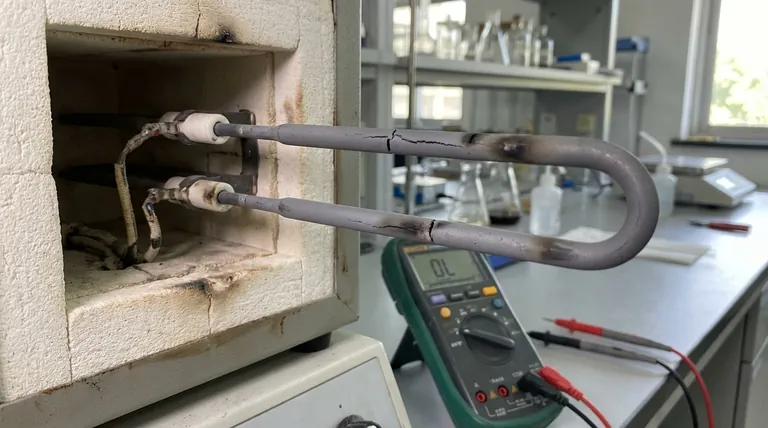
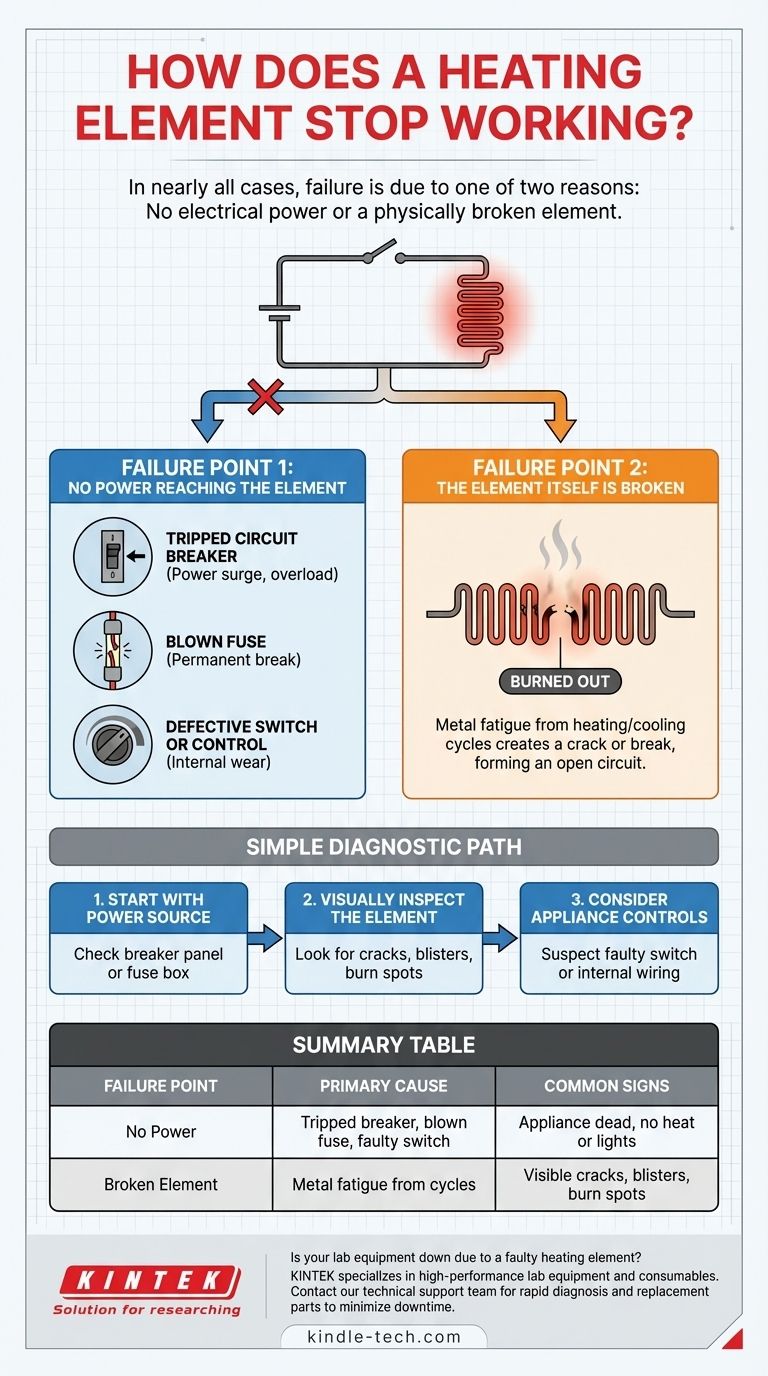
In nearly all cases, a heating element stops working for one of two reasons. It either isn't receiving electrical power, or the element itself has physically broken and can no longer complete the electrical circuit.
The core principle to understand is that a heating element is part of a simple circuit. Failure occurs when that circuit is interrupted, either because the power supply is cut off upstream or because the element—the final component in the path—has burned out.

The Two Core Reasons for Failure
To diagnose a non-functioning heating element, you must first determine which part of its electrical circuit has failed. The problem is almost always located in the power delivery system or within the element itself.
Failure Point 1: No Power Reaching the Element
A perfectly good heating element cannot function without electricity. An interruption in the power supply is a common and often easily fixable cause of failure.
This interruption can happen at several points:
- Tripped Circuit Breaker: The most frequent cause. A power surge or overloaded circuit will cause a breaker in your home's electrical panel to trip as a safety measure.
- Blown Fuse: In older homes or certain appliances, a fuse may blow to protect the circuit, permanently breaking the connection until it's replaced.
- Defective Switch or Control: The knob or button you use to turn on the heat can wear out internally, preventing it from sending the signal for power to flow.
Failure Point 2: The Element Itself Is Broken
Heating elements work by resisting the flow of electricity, which generates intense heat. This process inevitably causes wear and tear on the element's material.
Over hundreds of cycles of heating up and cooling down, the metal coil becomes brittle. Eventually, a crack or break forms, creating a gap that electricity cannot cross. This is often referred to as "burning out," and at this point, the element has created an open circuit and must be replaced.
A Simple Diagnostic Path
Before assuming the worst, you can perform a logical, step-by-step diagnosis to isolate the problem.
Start with the Power Source
Always check the easiest things first. Go to your home's main electrical panel and look for a tripped circuit breaker or a blown fuse associated with the appliance. This resolves the issue in a significant number of cases.
Visually Inspect the Element
If the power supply is confirmed to be on, turn your attention to the element itself. A failed element often provides clear visual cues.
Look for obvious signs of damage, such as blisters on the surface, visible cracks or breaks in the coil, or distinct burn spots. If you see any of these, the element has failed and is the source of the problem.
Consider the Appliance Controls
If the breaker is on and the element looks physically intact, the issue may lie with the appliance's internal controls. A faulty switch or a loose internal wire can prevent power from ever reaching the element, even when everything else appears to be working correctly.
How to Make the Right Diagnosis
Your goal is to determine if the problem is external (power supply) or internal (the component). Following a logical path saves time and prevents unnecessary replacements.
- If you suspect a power issue: Always start by checking your home's circuit breaker or fuse box, as this is the simplest and most common fix.
- If the power is on but the element is cold: Carefully and safely inspect the heating coil for any visible cracks, blisters, or signs of burnout.
- If the element appears fine but still doesn't work: The fault likely lies with a control switch or internal wiring, which is a more complex issue to diagnose.
Understanding whether the problem lies with the power supply or the component itself is the key to a fast and effective repair.
Summary Table:
| Failure Point | Primary Cause | Common Signs |
|---|---|---|
| No Power | Tripped circuit breaker, blown fuse, faulty switch | Appliance is completely dead, no heat or lights |
| Broken Element | Metal fatigue from heating/cooling cycles | Visible cracks, blisters, or burn spots on the coil |
Is your lab equipment down due to a faulty heating element? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, ensuring your laboratory operates with precision and reliability. Our experts can help you diagnose issues and provide the right replacement parts to minimize downtime. Contact our technical support team today to get your equipment back online quickly!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- Infrared Heating Quantitative Flat Plate Press Mold
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance
- What function do molybdenum disilicide heating elements perform? Precision Heat for Pulverized Coal Research
- What are the heating elements for high temperature furnaces? Select the Right Element for Your Atmosphere
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design

















