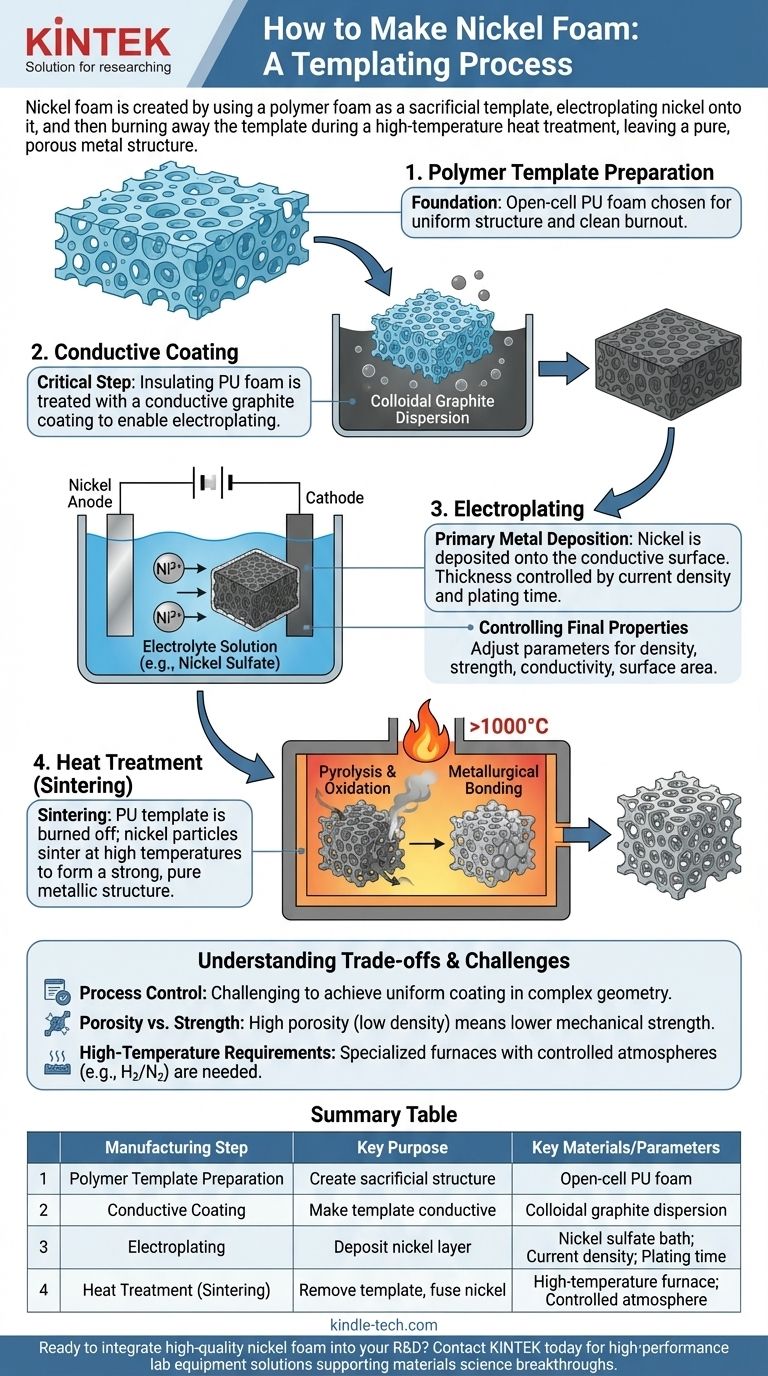
In essence, nickel foam is created by using a polymer foam as a sacrificial template. Nickel is electroplated onto this template, which is then burned away during a high-temperature heat treatment process, leaving behind a pure, porous metal structure that replicates the original foam's open-cell network.
The key to understanding nickel foam production is to see it not as simple coating, but as a templating process. You are building a metallic skeleton around a polymer mold and then removing that mold to create a self-supporting, open-cell metal.

The Core Principle: Replicating a Sacrificial Template
The entire manufacturing process is designed to create a metallic replica of a polymer's internal structure. The choice of materials and process steps are all in service of this goal.
The Foundation: The Polymer Foam
The process begins with a block of open-cell polyurethane (PU) foam. This material is chosen for its highly interconnected, uniform pore structure and its ability to be completely burned away at high temperatures without leaving significant residue.
The Critical Step: Making the Template Conductive
Polyurethane is an electrical insulator, but electroplating requires a conductive surface. Before any metal can be deposited, the foam must be treated to allow it to carry an electric current.
This is typically achieved by immersing the foam in a colloidal graphite dispersion. As the dispersion dries, it leaves a thin, uniform coating of conductive graphite particles over the entire surface area of the foam's intricate internal struts.
Building the Metal Structure: Electroplating
Once the foam template is conductive, it becomes the cathode in an electroplating bath. This is the primary metal deposition stage.
The Electroplating Process
The conductive foam is submerged in an electrolyte solution rich in nickel ions (like a nickel sulfate bath). An electric current is passed through the bath, causing the nickel ions to deposit as solid metal onto the graphite-coated surfaces of the foam.
Controlling Final Properties
The thickness of the deposited nickel layer is a critical control parameter. By adjusting the current density and plating time, manufacturers can precisely control the final foam's density, mechanical strength, electrical conductivity, and specific surface area. A longer plating time results in thicker struts and a denser, stronger foam.
Finalizing the Foam: Heat Treatment (Sintering)
The plated foam is not yet the final product. It is a composite of polyurethane, graphite, and nickel. The final step is a carefully controlled heat treatment in a furnace, known as sintering.
The Dual Role of Sintering
This heating process accomplishes two essential tasks simultaneously:
- Pyrolysis: The original polyurethane foam template is burned away, leaving voids where the polymer once was. The graphite coating is also oxidized and removed.
- Metallurgical Bonding: At high temperatures, the deposited nickel particles fuse together, or sinter, forming strong metallic bonds. This transforms the fragile nickel coating into a robust, self-supporting metal structure.
The Result: A Pure Metal Foam
The object that emerges from the furnace is pure nickel foam. It is lightweight, highly porous, and retains the exact open-cell structure of the original polyurethane template.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While effective, this process involves complexities and inherent trade-offs that are critical to understand.
Process Control is Demanding
Achieving a completely uniform nickel coating throughout the foam's complex internal geometry is challenging. Any non-uniformity in the initial conductive coating or variations in the electric field within the plating bath can lead to inconsistencies in the final product's density and strength.
Porosity vs. Strength
There is a direct and unavoidable trade-off between the foam's porosity (and thus its low density and high surface area) and its mechanical strength. A foam with very high porosity will have thin struts and be mechanically weaker than a denser foam with thicker struts.
High-Temperature Requirements
The sintering stage requires specialized high-temperature furnaces with precise atmosphere control (e.g., a reducing atmosphere like hydrogen/nitrogen) to prevent unwanted oxidation of the nickel and ensure proper metallurgical bonding.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this manufacturing process allows you to specify or design a foam that is optimized for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is high surface area (for batteries, catalysts, or supercapacitors): Prioritize a template with small pores and control the electroplating to create a thin, uniform nickel layer that maximizes the surface-to-volume ratio.
- If your primary focus is filtration or fluid flow: The selection of the initial polyurethane foam's pore size and structure (pores per inch) is the most critical decision, as it directly defines the final foam's permeability.
- If your primary focus is lightweight structural support or energy absorption: Focus on creating thicker nickel struts through longer plating times and optimize the sintering process to maximize the strength of the metallic bonds.
By understanding this templating method, you can effectively tailor the properties of nickel foam to meet the specific demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Manufacturing Step | Key Purpose | Key Materials/Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Polymer Template Preparation | Create a porous, sacrificial structure. | Open-cell polyurethane (PU) foam. |
| Conductive Coating | Make the insulating template suitable for electroplating. | Colloidal graphite dispersion. |
| Electroplating | Deposit a metallic nickel layer onto the template. | Nickel sulfate bath; current density; plating time. |
| Heat Treatment (Sintering) | Remove the template and fuse the nickel into a strong, porous structure. | High-temperature furnace; controlled atmosphere. |
Ready to integrate high-quality nickel foam into your R&D or production line? The precise manufacturing process detailed above is key to achieving the perfect balance of porosity, strength, and surface area for your application—whether it's for advanced battery electrodes, efficient catalysts, or specialized filtration.
At KINTEK, we specialize in supplying the high-performance lab equipment and consumables necessary for materials science breakthroughs. Our expertise can support your work with nickel foam and other advanced materials.
Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Copper Foam
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
- Anion Exchange Membrane for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the characteristics of copper foam? Unlock High-Performance Thermal and Electrical Solutions
- What are the common applications of copper foam? A Guide to Its High-Performance Uses
- What are the proper storage conditions for nickel and copper foam? A Guide to Preserving Performance
- What are the available sizes and thicknesses for copper foam? Optimize Your Thermal and Filtration Performance
- What role does convection play in heat transfer? Understanding Heat Movement in Fluids














