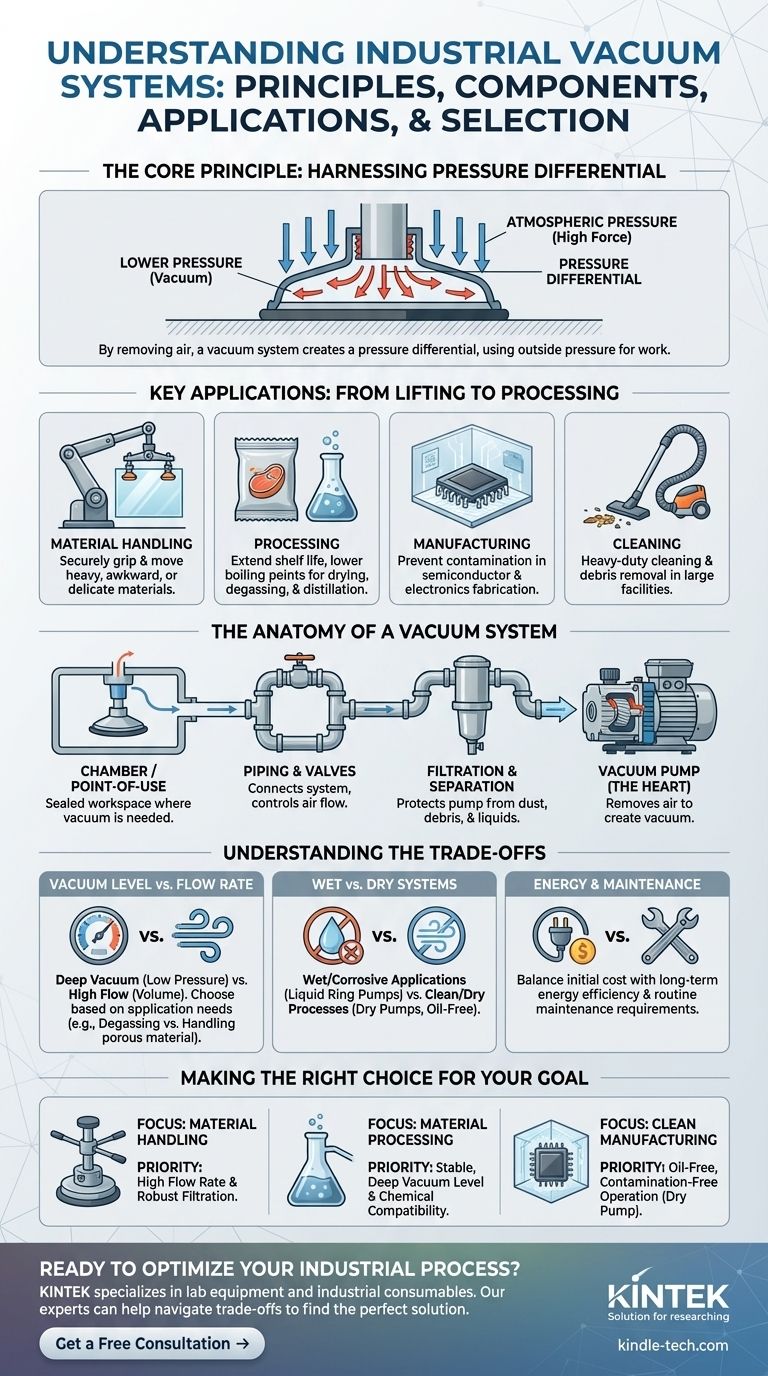
At its core, an industrial vacuum system is a coordinated set of components engineered to remove air and other gas molecules from a sealed space or process. This action creates a pressure lower than the surrounding atmosphere. This controlled, sub-atmospheric pressure is then harnessed to perform a specific task within an industrial setting.
An industrial vacuum system is not just a pump; it's a complete solution. Its true purpose is to leverage a pressure differential to lift materials, alter physical processes, or create ultra-clean environments that would otherwise be impossible.

Why Industries Rely on a Vacuum
An industrial vacuum is a powerful and versatile tool. Its utility comes from the fundamental principle that higher-pressure air will always try to rush into a lower-pressure area.
The Principle: Harnessing Pressure Differential
When a vacuum system removes air from a chamber or suction cup, it creates a pressure differential. The higher atmospheric pressure on the outside pushes against the object or material, creating a powerful force.
This force can be used for physical work, such as lifting heavy objects, or to influence chemical and physical processes, such as lowering the boiling point of a liquid.
Key Applications: From Lifting to Processing
The applications for industrial vacuums are incredibly diverse, spanning nearly every sector.
- Material Handling: Vacuum lifters use suction cups to securely grip and move heavy, awkward, or delicate materials like glass panes, metal sheets, and concrete slabs.
- Processing: In food production, vacuums remove oxygen to extend shelf life. In chemical plants, they are used for drying, distillation, and degassing liquids by lowering their boiling point.
- Manufacturing: The semiconductor and electronics industries rely on high-vacuum environments to prevent contamination during the fabrication of microchips and circuit boards.
- Cleaning: Centralized vacuum systems are used in large facilities for heavy-duty cleaning and removal of dust or debris.
The Anatomy of a Vacuum System
A complete system is more than just its pump. Each component plays a critical role in achieving and maintaining the desired vacuum level safely and efficiently.
The Vacuum Pump (The Heart)
This is the component that does the work of removing air. There are many types, such as rotary vane, liquid ring, and dry screw pumps, each suited for different vacuum levels and conditions. For deeper vacuums, multiple pumps are often used in series, as noted in the reference, where one pump "backs" another to achieve lower pressures.
The Chamber or Point-of-Use (The Workspace)
This is the sealed space where the vacuum is needed. It could be a large processing tank, a small suction cup on a robotic arm, or the nozzle of a cleaning hose.
Piping and Valves (The Arteries)
A network of pipes or hoses connects the pump to the point-of-use. Valves are installed within this network to control the flow of air, isolate parts of the system, and allow for a controlled return to atmospheric pressure.
Filtration and Separation (The Lungs)
Protecting the vacuum pump is paramount. Filters and separators are installed to remove any dust, debris, or liquids from the airstream before they can enter and damage the pump. This is especially critical in dirty or wet applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting or designing a vacuum system involves balancing competing priorities. Making the wrong choice can lead to poor performance, high energy bills, and frequent downtime.
Vacuum Level vs. Flow Rate
Vacuum level (measured in units like mbar or inHg) refers to how low the pressure is. Flow rate (measured in CFM or m³/h) refers to how much air the pump can move.
A system designed for a very deep vacuum (low pressure) may not have a high flow rate, and vice versa. Lifting a porous cardboard box requires high flow to overcome leaks, while a degassing process requires a deep, stable vacuum level.
Wet vs. Dry Systems
Handling moisture is a major consideration. Some processes, like food marination, inherently involve liquids. Using a "dry" pump not designed for moisture will lead to its rapid failure. Liquid ring vacuum pumps are specifically designed to handle wet and corrosive gas streams.
Energy Consumption and Maintenance
Industrial vacuum pumps can be significant energy consumers. Modern, efficient pump designs can offer a lower total cost of ownership, even if their initial price is higher. Furthermore, all systems require routine maintenance, such as oil changes and filter replacements, which must be factored into operating costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal system is always defined by the job it needs to do. By understanding the core components and their interplay, you can select a system optimized for your specific industrial challenge.
- If your primary focus is material handling or lifting: Prioritize a system with a high flow rate and robust filtration to handle potential air leaks and debris.
- If your primary focus is material processing (drying, degassing): Prioritize achieving and holding a specific, stable vacuum level, and ensure the pump materials are compatible with any chemicals involved.
- If your primary focus is clean manufacturing or laboratory work: Prioritize an oil-free "dry" pump to prevent any contamination of the process environment.
Understanding these fundamental principles empowers you to move beyond a simple pump and architect a complete vacuum system that serves as a reliable and effective industrial tool.
Summary Table:
| System Component | Key Function | Common Types |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Pump | Removes air/gas to create a pressure differential | Rotary Vane, Liquid Ring, Dry Screw |
| Chamber/Point-of-Use | The sealed workspace where the vacuum is applied | Processing Tank, Suction Cup, Nozzle |
| Filtration | Protects the pump from dust, debris, and liquids | Filters, Separators |
| Key Application | Primary System Focus | Critical Selection Factor |
| Material Handling | High Flow Rate & Robust Filtration | Ability to handle leaks and debris |
| Material Processing | Stable, Deep Vacuum Level | Chemical compatibility and pressure stability |
| Clean Manufacturing | Oil-Free, Contamination-Free Operation | Use of 'dry' pump technology |
Ready to Optimize Your Industrial Process with the Right Vacuum System?
Whether your goal is efficient material handling, precise processing, or maintaining a contaminant-free environment, selecting the right vacuum system is critical to your success and bottom line.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and industrial consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories and production facilities. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between vacuum level, flow rate, and system durability to find the perfect solution for your unique challenge.
Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how our expertise can enhance your operational efficiency and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is an oil-free diaphragm vacuum pump? The Ultimate Guide to Clean, Low-Maintenance Vacuum
- What are the advantages of using oil-free diaphragm vacuum pumps? Achieve Clean, Low-Maintenance Vacuum
- What are some typical applications for oil-free diaphragm vacuum pumps? Ensure Process Purity in Your Lab
- How should an oil-free diaphragm vacuum pump be maintained? A Proactive Guide to Maximize Pump Lifespan
- How does the working of oil-free diaphragm vacuum pumps differ from conventional pumps? A Guide to Clean vs. Deep Vacuum



















