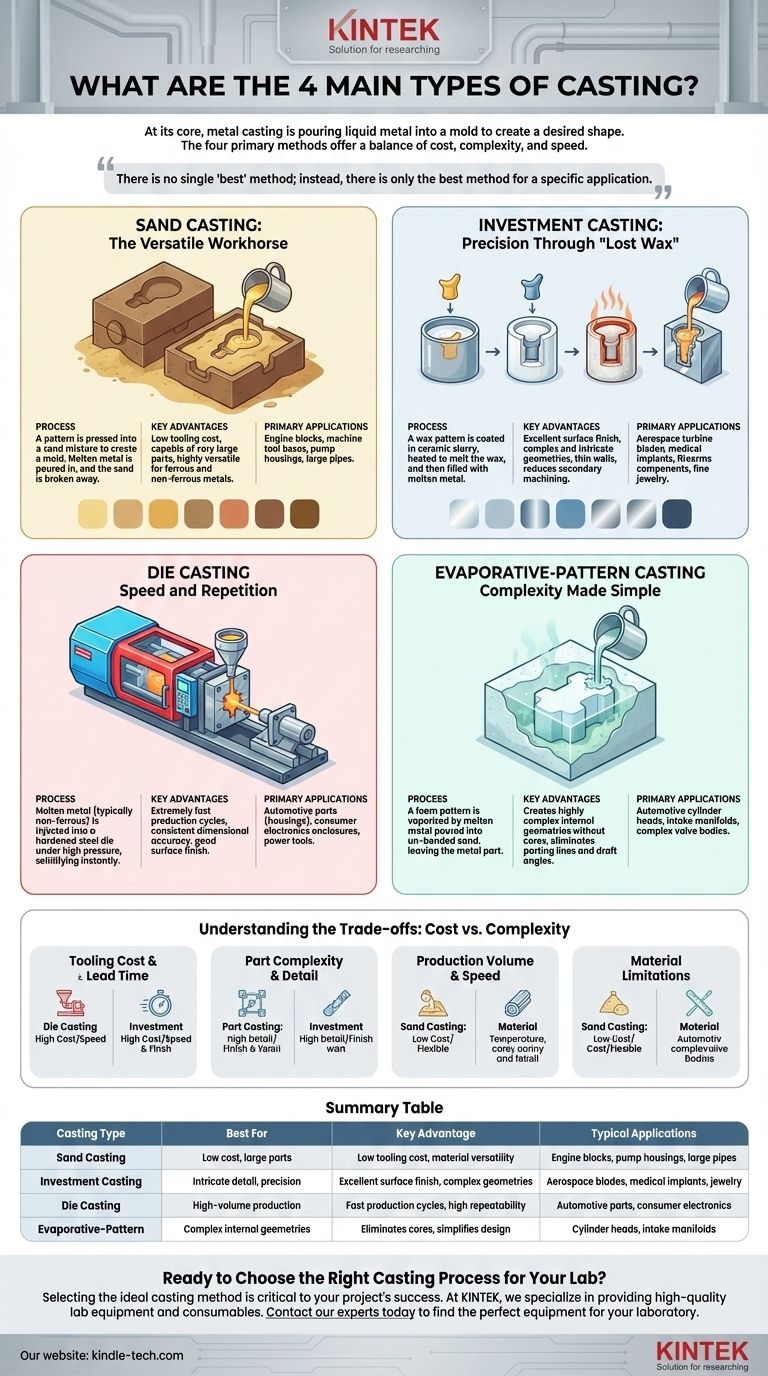
At its core, metal casting is a manufacturing process where liquid metal is poured into a mold to create a desired shape. The four primary methods to accomplish this are sand casting, investment casting, die casting, and evaporative-pattern casting. Each technique offers a unique balance of cost, complexity, and production speed, making the choice of method critical to a project's success.
The fundamental challenge in casting is selecting a process that balances tooling cost, production volume, and the final part's required precision. There is no single "best" method; instead, there is only the best method for a specific application.

Sand Casting: The Versatile Workhorse
Sand casting is one of the oldest and most widely used casting methods. Its adaptability and low cost make it a foundational process in heavy industry.
The Process
A pattern of the final part is pressed into a specialized sand mixture to create a two-part mold. Molten metal is poured into the cavity, and once it solidifies, the sand mold is broken away to reveal the finished part.
Key Advantages
The primary benefits of sand casting are its low tooling cost and its ability to produce very large parts. It is also highly versatile, capable of handling a wide range of ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
Primary Applications
This method is ideal for producing parts where surface finish is not the highest priority, such as engine blocks, machine tool bases, pump housings, and large pipes.
Investment Casting: Precision Through "Lost Wax"
Investment casting, also known as the "lost-wax" process, is renowned for its ability to produce parts with exceptional detail and accuracy.
The Process
A wax pattern of the part is created and then repeatedly dipped into a ceramic slurry to form a hard shell. The shell is heated, melting the wax out (hence "lost wax"), leaving a precise cavity. Molten metal is poured in, and the ceramic shell is broken off after cooling.
Key Advantages
Investment casting delivers an excellent surface finish and can create highly complex and intricate geometries with thin walls. This often reduces the need for secondary machining.
Primary Applications
It is the preferred method for high-performance components like aerospace turbine blades, medical implants, firearms components, and fine jewelry.
Die Casting: Speed and Repetition
Die casting is a high-speed process that excels at producing large quantities of parts with high precision and repeatability.
The Process
This method involves injecting molten metal, typically a non-ferrous alloy like aluminum or zinc, into a hardened steel mold—called a die—under high pressure. The metal solidifies almost instantly, and the part is ejected.
Key Advantages
The main advantages are extremely fast production cycles and consistent, repeatable dimensional accuracy. It produces a good surface finish and can create complex shapes.
Primary Applications
Die casting is fundamental to mass production industries, used for automotive parts (transmission housings, engine components), consumer electronics enclosures, and power tools.
Evaporative-Pattern Casting: Complexity Made Simple
Often called "lost-foam" casting, this technique uses a pattern made of a material like polystyrene foam that is not removed from the mold.
The Process
A foam pattern of the part is placed in a flask and surrounded by un-bonded sand, which is compacted. When molten metal is poured in, it instantly vaporizes the foam pattern, perfectly replicating its shape.
Key Advantages
This process allows for the creation of highly complex internal geometries without the need for cores. It eliminates parting lines and draft angles, simplifying the design and reducing secondary processing.
Primary Applications
It is well-suited for parts that would otherwise require significant assembly or machining, such as automotive cylinder heads, intake manifolds, and complex valve bodies.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Complexity
Choosing the right casting method requires a clear understanding of the fundamental trade-offs between cost, speed, and precision.
Tooling Cost and Lead Time
Die casting has the highest initial tooling cost due to the hardened steel dies, making it suitable only for high-volume production. Sand casting has the lowest tooling cost, making it ideal for prototypes and small production runs. Investment and evaporative casting fall in between.
Part Complexity and Detail
Investment casting offers the highest level of detail and the best surface finish, making it perfect for intricate parts. Sand casting provides the least detail and a rougher surface.
Production Volume and Speed
Die casting is the undisputed leader for speed and high-volume runs, with cycle times measured in seconds. The other methods are significantly slower, making them better suited for lower-volume production.
Material Limitations
Sand casting is the most flexible, handling almost any metal alloy. Die casting is typically limited to non-ferrous metals with lower melting points, such as aluminum, zinc, and magnesium.
Selecting the Right Process for Your Goal
Your final decision must align with the primary objective of your project.
- If your primary focus is low cost and large parts: Sand casting is the default choice for its inexpensive tooling and material versatility.
- If your primary focus is intricate detail and a superb surface finish: Investment casting is the superior method for producing near-net-shape parts.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable production: Die casting offers unmatched speed and cost-effectiveness at scale.
- If your primary focus is complex internal geometry without assembly: Evaporative-pattern casting provides a unique solution for consolidating parts.
Choosing the correct casting process is a strategic decision that directly impacts your project's cost, quality, and timeline.
Summary Table:
| Casting Type | Best For | Key Advantage | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sand Casting | Low cost, large parts | Low tooling cost, material versatility | Engine blocks, pump housings, large pipes |
| Investment Casting | Intricate detail, precision | Excellent surface finish, complex geometries | Aerospace blades, medical implants, jewelry |
| Die Casting | High-volume production | Fast production cycles, high repeatability | Automotive parts, consumer electronics |
| Evaporative-Pattern | Complex internal geometries | Eliminates cores, simplifies design | Cylinder heads, intake manifolds |
Ready to Choose the Right Casting Process for Your Lab?
Selecting the ideal casting method is critical to your project's success, impacting cost, quality, and timeline. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need to support your foundry and materials research.
Whether you're developing new alloys, testing material properties, or ensuring quality control, our solutions help you achieve precise and reliable results.
Let's discuss your specific application needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
People Also Ask
- What are the specific functions of graphite molds in the vacuum hot-press sintering process? Expert Insights for Ceramics
- Why is precise temperature and pressure control necessary for combustible cartridge cases? Ensure Structural Integrity
- What role do high-temperature pressure molds play in SiCp/Al fabrication? Enhancing Densification and Thermal Uniformity
- What technical requirements must specialized pressure-bearing molds meet? Optimize Sulfide Electrolyte Densification
- What role do high-strength graphite molds play during vacuum hot pressing? Enhance Precision in CuAlMn Composites













