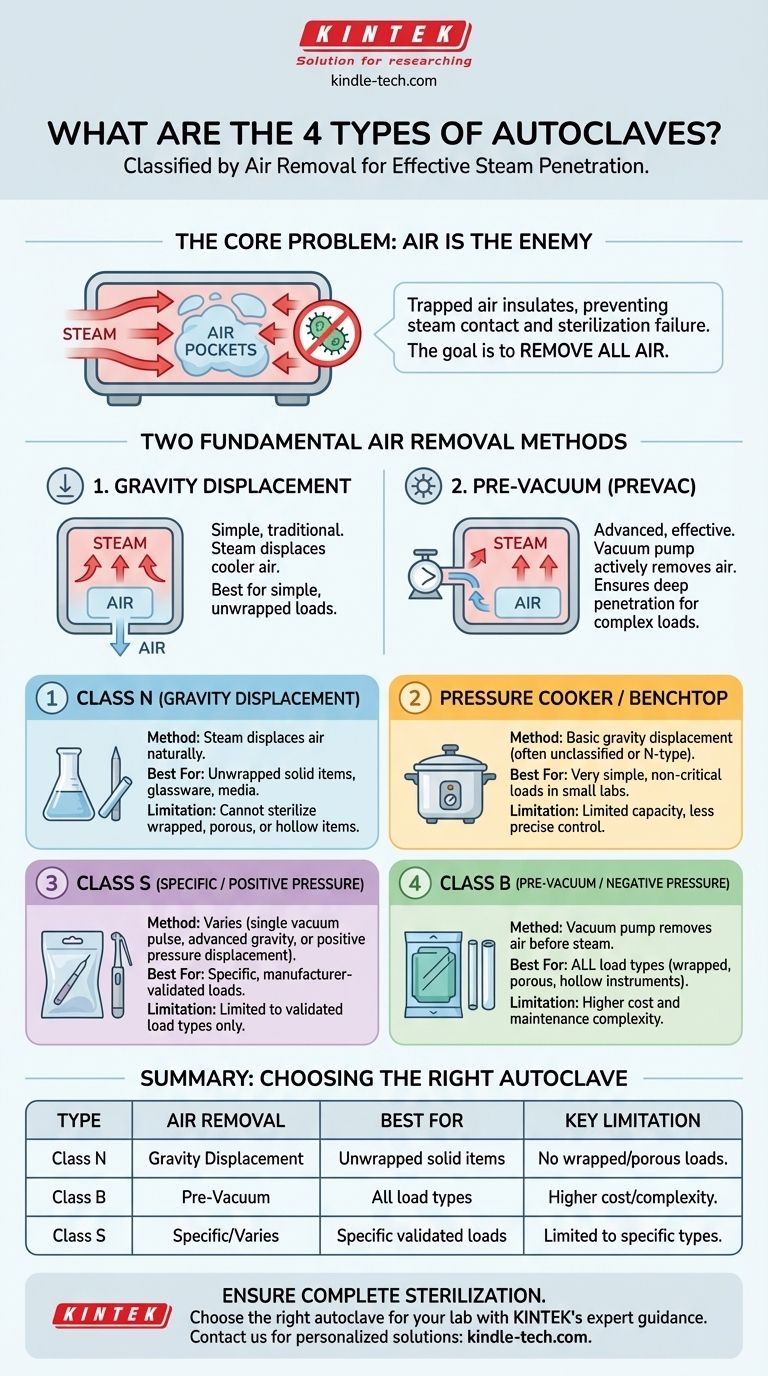
The four primary types of autoclaves are best understood by how they remove air to allow for steam penetration. The most common classifications are the Pressure Cooker/Laboratory Bench (Class N), Gravity Displacement, Positive Pressure Displacement (Class S), and Negative Pressure Displacement/Pre-vacuum (Class B). These types fundamentally differ in their efficiency and the complexity of the loads they can effectively sterilize.
While autoclaves can be categorized by size or function, the most critical distinction is the mechanism used to remove air from the chamber. The choice between a simple Gravity Displacement system and a more advanced Pre-vacuum system dictates what can be safely sterilized.
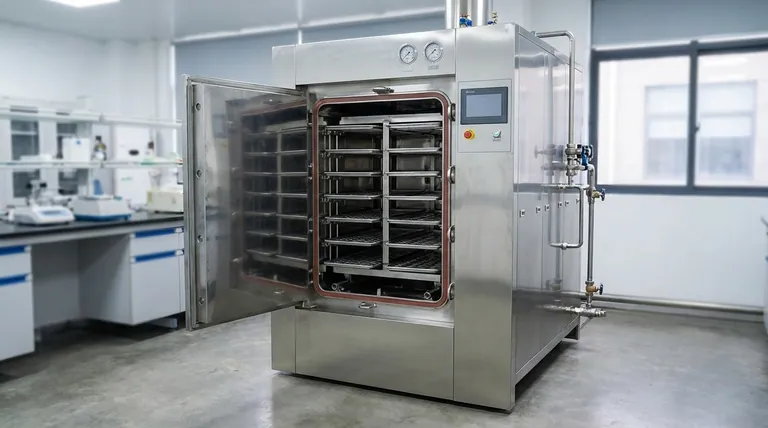

The Core Problem: Air is the Enemy of Sterilization
Before comparing types, it's crucial to understand the central challenge in steam sterilization. Pressurized steam is exceptionally effective at killing microorganisms, but only if it makes direct contact with every surface.
Why Trapped Air Prevents Sterilization
Air pockets trapped within a load (such as in porous fabrics, hollow instruments, or wrapped packs) act as an insulating barrier. This barrier prevents steam from reaching and heating the surfaces to the required temperature, leading to sterilization failure.
The Goal of Every Autoclave
Therefore, the primary technical goal of any autoclave cycle is to first remove all air from the chamber and the load. The different "types" of autoclaves are simply different engineering solutions to this one fundamental problem.
The Two Fundamental Air Removal Methods
At a high level, all autoclaves fall into one of two categories based on how they solve the air removal problem.
Gravity Displacement
This is the simpler and more traditional method. As hot, pressurized steam fills the chamber, it displaces the cooler, denser air, which is forced out through a drain port at the bottom of the chamber.
This method is reliable for simple loads like media, glassware, and unwrapped solid instruments. However, it is less effective at removing air from complex shapes, wrapped items, or porous materials.
Pre-Vacuum (Prevac)
This is a more advanced and effective method. Before introducing steam, a vacuum pump actively removes air from the sterilization chamber and the load itself. This ensures there are no trapped air pockets.
By creating a vacuum, this method allows for instantaneous and deep steam penetration, even into dense or complex loads. This process is faster and provides a higher assurance of sterility for challenging items.
Understanding the Common Classifications (N, B, and S)
The European Standard EN 13060 provides a clear classification system based on the types of loads an autoclave can process. This system directly corresponds to the air removal method used.
Class N Autoclaves
Class N autoclaves are designed for sterilizing "Naked" or unwrapped, solid items, such as basic laboratory glassware or certain instruments.
They typically use the gravity displacement method for air removal. They are not suitable for sterilizing textiles, porous loads, hollow items, or any products in pouches, as the steam penetration cannot be guaranteed.
Class B Autoclaves
Class B autoclaves can sterilize any type of load, including porous, hollow, and wrapped instruments. The "B" stands for "Big," signifying their broad range of applications.
These are pre-vacuum autoclaves. They employ a vacuum pump to remove air before the sterilization phase, ensuring complete steam penetration for even the most complex loads. This makes them standard in dental, medical, and veterinary settings.
Class S Autoclaves
Class S autoclaves are an intermediate category for sterilizing "Specific" products, as specified by the manufacturer.
Their capabilities fall between Class N and Class B. A Class S autoclave may use a single pre-vacuum pulse or an advanced gravity displacement method. They are designed for loads that a Class N cannot handle but do not require the high-end pre-vacuum capabilities of a Class B.
Key Trade-offs to Consider
Choosing an autoclave involves balancing performance against cost and complexity.
Cycle Time and Throughput
Pre-vacuum (Class B) autoclaves are significantly faster. The active air removal and post-sterilization vacuum drying phases shorten the total cycle time, increasing throughput for busy environments.
Load Versatility
The primary limitation of gravity displacement (Class N) is its inability to reliably sterilize wrapped or porous loads. For medical or dental applications where instruments are packaged, a pre-vacuum (Class B) unit is essential.
Cost and Complexity
Gravity displacement systems are mechanically simpler, making them less expensive to purchase and maintain. Pre-vacuum autoclaves include a vacuum pump and more complex control systems, which increases their initial cost and potential maintenance needs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice should be dictated entirely by the type of load you need to sterilize.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing laboratory media, glassware, or unwrapped solid instruments: A simple and cost-effective Class N or gravity displacement autoclave is sufficient.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing wrapped medical/dental instruments, porous loads, or hollow items: A Class B pre-vacuum autoclave is the necessary choice to ensure reliable sterility and safety.
- If your primary focus is a specific, known load that a Class N cannot handle: A Class S autoclave may be a suitable and economical alternative, provided it is validated for that exact load type.
Ultimately, understanding how an autoclave removes air is the key to selecting the right tool for your specific sterilization needs.
Summary Table:
| Autoclave Type | Air Removal Method | Best For | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class N (Gravity Displacement) | Steam displaces air naturally | Unwrapped solid items, glassware, media | Cannot sterilize wrapped, porous, or hollow items |
| Class B (Pre-Vacuum) | Vacuum pump removes air before steam | All load types (wrapped, porous, hollow instruments) | Higher cost and maintenance complexity |
| Class S (Specific) | Varies (single vacuum pulse, advanced gravity) | Specific loads as per manufacturer specs | Limited to validated load types only |
Ensure Complete Sterilization for Your Laboratory Needs
Choosing the right autoclave is critical for maintaining sterility and safety in your lab. Whether you need a simple gravity displacement system for basic glassware or a high-performance pre-vacuum autoclave for complex medical instruments, KINTEK has the solution.
Why Choose KINTEK for Your Lab Equipment?
- Expert Guidance: Our specialists help you select the perfect autoclave for your specific applications
- Quality Assurance: All equipment meets strict sterilization standards and reliability requirements
- Comprehensive Support: From installation to maintenance, we ensure your lab operates efficiently
Contact KINTEL today to discuss your autoclave requirements and get a personalized solution for your laboratory sterilization challenges. Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How does an autoclave contribute to the reliability of results in biofilm formation experiments? Ensure Data Integrity
- What are the methods of validation of autoclave? Ensure Sterility with a 3-Pillar Approach
- Why do we autoclave at 121 degree Celsius? The Science Behind Sterilization
- Why is autoclaving so vital? The Definitive Guide to Steam Sterilization
- For what purpose are high-pressure autoclaves used in the synthesis of additives for composite polymer electrolytes?
- Why is autoclave temperature 121°C? The Science Behind Sterilization's Critical Point
- What are the key features and application of autoclave? Essential Sterilization for Medical, Lab, and Industrial Needs
- What to avoid when using an autoclave? Prevent Common and Dangerous Sterilization Errors



















