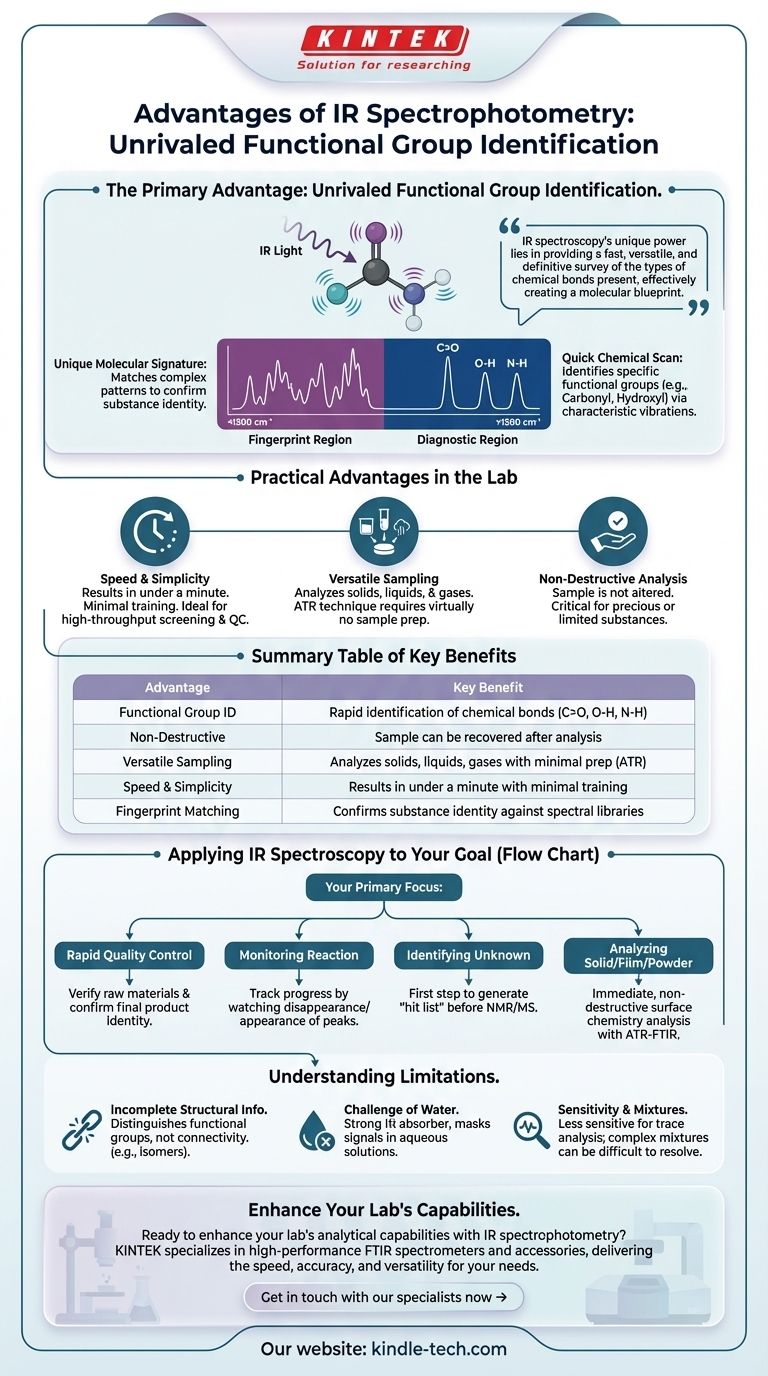
At its core, the primary advantage of Infrared (IR) spectrophotometry is its exceptional ability to rapidly and non-destructively identify the functional groups within a molecule. This technique provides a quick "chemical snapshot" of a sample by measuring how its molecular bonds vibrate when exposed to infrared light, making it a cornerstone of chemical analysis for both qualitative and quantitative purposes.
While other methods may determine a molecule's complete atomic connectivity or mass, IR spectroscopy's unique power lies in providing a fast, versatile, and definitive survey of the types of chemical bonds present in a sample, effectively creating a molecular blueprint.

The Primary Advantage: Unrivaled Functional Group Identification
IR spectroscopy is fundamentally a tool for "seeing" vibrations. Because different types of bonds (like C=O, O-H, or N-H) vibrate at characteristic frequencies, an IR spectrum acts as a direct report of a sample's chemical composition.
The Diagnostic Region: A Quick Chemical Scan
The region of the spectrum above ~1500 cm⁻¹ is known as the diagnostic region. Peaks here are often well-separated and correspond directly to specific functional groups.
An analyst can glance at this region and immediately confirm the presence or absence of key molecular building blocks, such as the strong, sharp peak of a carbonyl (C=O) group near 1700 cm⁻¹, or the broad, characteristic peak of an alcohol's hydroxyl (O-H) group above 3200 cm⁻¹.
The Fingerprint Region: A Unique Molecular Signature
The more complex region below ~1500 cm⁻¹ is the fingerprint region. The absorptions here are caused by the intricate bending and stretching vibrations of the entire molecule.
While difficult to interpret peak by peak, this pattern is uniquely characteristic of a specific compound. By matching a sample's fingerprint region to a spectral library, one can confirm the identity of a substance with a high degree of confidence.
Practical Advantages in the Lab
Beyond its core analytical strength, modern IR spectroscopy, particularly Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR), offers significant practical benefits that make it a laboratory workhorse.
Speed and Simplicity
A high-quality FTIR spectrum can be acquired in under a minute with minimal user training. This speed makes it invaluable for high-throughput screening, quality control checks, and real-time reaction monitoring.
Versatility in Sample Handling
IR can analyze solids, liquids, and gases. Modern sampling techniques, especially Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR), have revolutionized its use. With ATR, a solid powder or liquid can be analyzed by simply placing it on a crystal, requiring virtually no sample preparation.
Non-Destructive Analysis
In most configurations, especially with ATR, the sample is not altered or destroyed during the analysis. This is critical when working with precious, rare, or limited quantities of a substance, as it can be fully recovered for use in other tests.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When Not to Use IR
To use a tool effectively, you must understand its limitations. IR is powerful, but it is not a universal solution.
Limitation 1: Incomplete Structural Information
IR excels at telling you what functional groups are present, but not necessarily how they are connected. It can easily distinguish a ketone from an alcohol, but it cannot, on its own, differentiate between structural isomers like 2-pentanone and 3-pentanone. For complete structure elucidation, you must use it in conjunction with techniques like NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry.
Limitation 2: The Challenge of Water
Water is a very strong IR absorber and its broad, intense peaks can overwhelm the spectrum, masking the signals from the solute. This makes analyzing samples in aqueous solutions difficult without specialized equipment or sample preparation steps.
Limitation 3: Sensitivity and Mixtures
Compared to methods like UV-Vis or fluorescence spectroscopy, IR is generally less sensitive. It is best suited for analyzing major components and is not ideal for trace analysis in the parts-per-billion range. Analyzing complex mixtures can also be challenging, as the many overlapping peaks can be difficult to resolve.
Applying IR Spectroscopy to Your Goal
Your choice of analytical technique depends entirely on the question you need to answer. IR spectrophotometry is the right choice in several common scenarios.
- If your primary focus is rapid quality control: Use IR to quickly verify the identity of a raw material or confirm that a final product has not been contaminated by matching its fingerprint region to a known standard.
- If your primary focus is monitoring a chemical reaction: Use IR to track the progress by watching for the disappearance of a reactant's characteristic peak or the appearance of a product's peak over time.
- If your primary focus is identifying an unknown compound: Use IR as the first analytical step to generate a "hit list" of possible functional groups, which dramatically narrows the search before moving to more complex structural analysis with NMR or mass spectrometry.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a solid, film, or powder: Use an ATR-FTIR setup for an immediate, non-destructive analysis of the material's surface chemistry with zero sample preparation.
Ultimately, IR spectrophotometry serves as an indispensable tool for understanding the chemical makeup of a substance at the fundamental level of its bonds.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Functional Group ID | Rapid identification of chemical bonds (C=O, O-H, N-H) |
| Non-Destructive | Sample can be recovered after analysis |
| Versatile Sampling | Analyzes solids, liquids, gases with minimal prep (ATR) |
| Speed & Simplicity | Results in under a minute with minimal training |
| Fingerprint Matching | Confirms substance identity against spectral libraries |
Ready to enhance your lab's analytical capabilities with IR spectrophotometry?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including FTIR spectrometers and accessories, to meet your specific laboratory needs. Our solutions deliver the speed, accuracy, and versatility highlighted in this article, empowering your team to perform rapid quality control, reaction monitoring, and compound identification efficiently.
Contact us today to discuss how our IR spectroscopy equipment can bring these advantages to your workflow. Let our experts help you select the perfect instrument to achieve superior chemical analysis results.
Get in touch with our specialists now →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Infrared High Resistance Single Crystal Silicon Lens
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Lab Electrochemical Workstation Potentiostat for Laboratory Use
- Infrared Thermal Imaging Temperature Measurement Double-Sided Coated Germanium Ge Lens
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What are the safety issues with nanomaterials? Navigating the Unique Risks of Nanoscale Materials
- What does a layered film mean? Unpacking the Depths of Cinematic Storytelling
- What is diamond identification? The Ultimate Guide to Verifying Natural vs. Lab-Grown Diamonds
- What affects melting point chemistry? A Guide to Molecular Forces and Lattice Energy
- What are pure silicon sputtering targets? Precision Source for High-Performance Thin Films

















