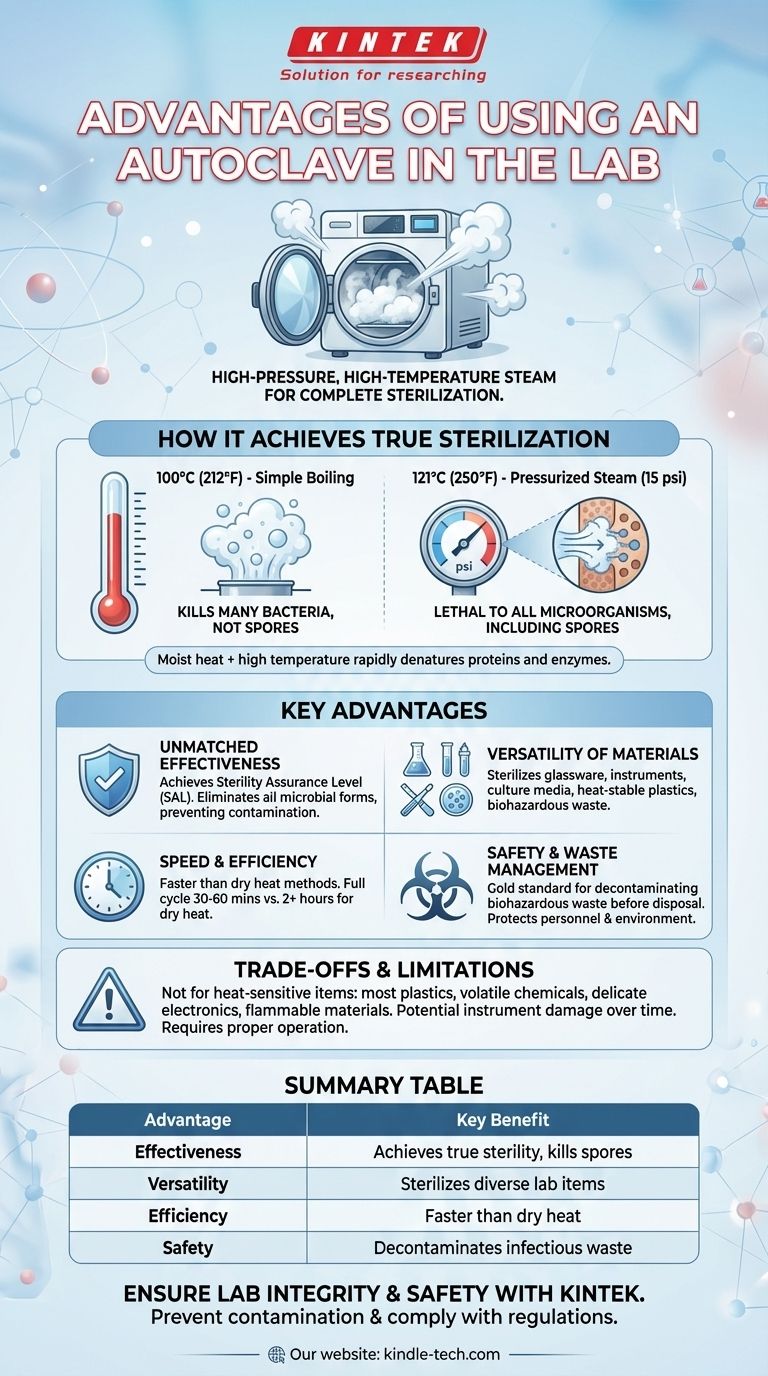
The primary advantage of an autoclave is its ability to achieve complete sterilization by using high-pressure, high-temperature steam. This method is exceptionally effective at killing all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and highly resistant bacterial spores, ensuring that lab equipment and media are truly sterile and free of contaminants.
An autoclave’s core value is not just heat, but the use of pressurized steam. This moist heat rapidly penetrates materials and denatures essential proteins and enzymes in microbes, providing a level of sterility that dry heat or chemical disinfectants often cannot match.
How an Autoclave Achieves True Sterilization
An autoclave operates on a principle that is far more effective than simple boiling. It is a sealed chamber that functions like a sophisticated pressure cooker for the laboratory.
Beyond Simple Boiling
At standard atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). While this temperature kills many active bacteria, it is insufficient to eliminate resilient endospores produced by certain bacterial species like Bacillus and Clostridium.
The Power of Pressurized Steam
By increasing the pressure inside the sealed chamber, an autoclave raises the boiling point of water. A typical cycle runs at 15 psi (pounds per square inch) above atmospheric pressure, which allows the steam to reach a temperature of 121°C (250°F).
This combination of moist heat and high temperature is exceptionally lethal to all microorganisms. The moisture facilitates the rapid transfer of heat energy, which coagulates and denatures essential proteins and enzymes, leading to cell death.
Penetration and Uniformity
Pressurized steam can effectively penetrate porous materials, such as surgical gowns and media-filled flasks, and reach all surfaces of complex instruments. This ensures a uniform sterilization process that is difficult to achieve with methods like UV light (which only sterilizes surfaces) or dry heat (which has poor penetration).
Key Advantages in a Laboratory Setting
The scientific principles behind autoclaving translate into several practical and critical benefits for daily lab operations.
Unmatched Effectiveness
The primary advantage is its proven ability to achieve a Sterility Assurance Level (SAL) required for critical applications like microbiology, cell culture, and medical procedures. It reliably inactivates all forms of microbial life, preventing costly and dangerous contamination.
Versatility of Materials
Autoclaves are workhorses capable of sterilizing a wide variety of laboratory items, including:
- Glassware (flasks, beakers, test tubes)
- Surgical instruments and metal tools
- Culture media and other aqueous solutions
- Pipette tips and certain heat-stable plastics (like polypropylene)
- Biohazardous waste
Speed and Efficiency
While a full cycle can take 30 to 60 minutes, it is a highly efficient method for achieving complete sterility compared to alternatives. For example, dry heat sterilization requires much higher temperatures (e.g., 170°C) and significantly longer exposure times (2 hours or more) to achieve a similar effect.
Safety and Waste Management
Autoclaving is the gold standard for decontaminating biohazardous waste before disposal. It neutralizes potentially infectious materials, such as used petri dishes and contaminated cultures, protecting laboratory personnel, waste handlers, and the environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, an autoclave is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly and safely.
Not for Heat-Sensitive Materials
The combination of high heat, steam, and pressure will destroy or damage heat-labile (heat-sensitive) items. You should never autoclave:
- Most plastics (e.g., polyethylene, polystyrene)
- Volatile or corrosive chemicals (e.g., bleach, solvents, acids)
- Delicate electronic or optical equipment
- Flammable materials
Potential for Instrument Damage
While effective for metal instruments, repeated autoclaving can eventually dull sharp edges on items like scalpels or scissors. The moisture can also contribute to corrosion on lower-grade stainless steel over time.
Requires Proper Operation
Sterilization is only effective if the autoclave is used correctly. Common errors include overloading the chamber, packing items too tightly (preventing steam penetration), or selecting the wrong cycle time for the load. Failed sterilization runs can compromise entire experiments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct sterilization method depends entirely on the material you are working with and your experimental objective.
- If your primary focus is preparing sterile media or reusable labware for microbiology and cell culture: The autoclave is the indispensable gold standard for preventing contamination.
- If your primary focus is decontaminating biological waste before disposal: Autoclaving is the safest and most widely accepted method for regulatory compliance and personnel safety.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive solutions or plastics: You must use alternatives such as sterile filtration for liquids or chemical sterilization (e.g., ethylene oxide gas) for plastics and devices.
Ultimately, mastering the use of the autoclave is fundamental to ensuring the safety, reproducibility, and integrity of work conducted in nearly any life sciences laboratory.

Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Effectiveness | Achieves true sterility by killing all microbes, including spores. |
| Versatility | Sterilizes glassware, instruments, media, and biohazardous waste. |
| Efficiency | Faster and more effective than dry heat methods. |
| Safety | Safely decontaminates infectious waste before disposal. |
Ensure the integrity and safety of your lab work with a reliable autoclave from KINTEK.
As specialists in laboratory equipment, KINTEK provides autoclaves designed to meet the rigorous demands of microbiology, cell culture, and medical research. Our solutions help you prevent contamination, comply with safety regulations, and protect your personnel.
Ready to enhance your lab's sterilization protocol? Contact our experts today to find the perfect autoclave for your specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the specifications for sterilization? Achieve Your Required Sterility Assurance Level (SAL)
- What conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for reactor simulation? Expert Material Testing Solutions
- How do you autoclave lab equipment? A Step-by-Step Guide to Sterile Results
- What is the most effective method for sterilization of laboratory materials? Choose the Right Method for Your Lab
- Why is a PTFE-lined hydrothermal autoclave required for the preparation of Pt/Nb-TiO2 electrocatalysts?
- Can autoclave sterilize liquid? Master Safe and Effective Liquid Sterilization
- Does autoclave kill 100% of bacteria? Achieve Sterility Assurance with High-Temperature Steam
- What is the benefit of autoclave? Achieve Rapid, Reliable Sterilization for Your Lab



















