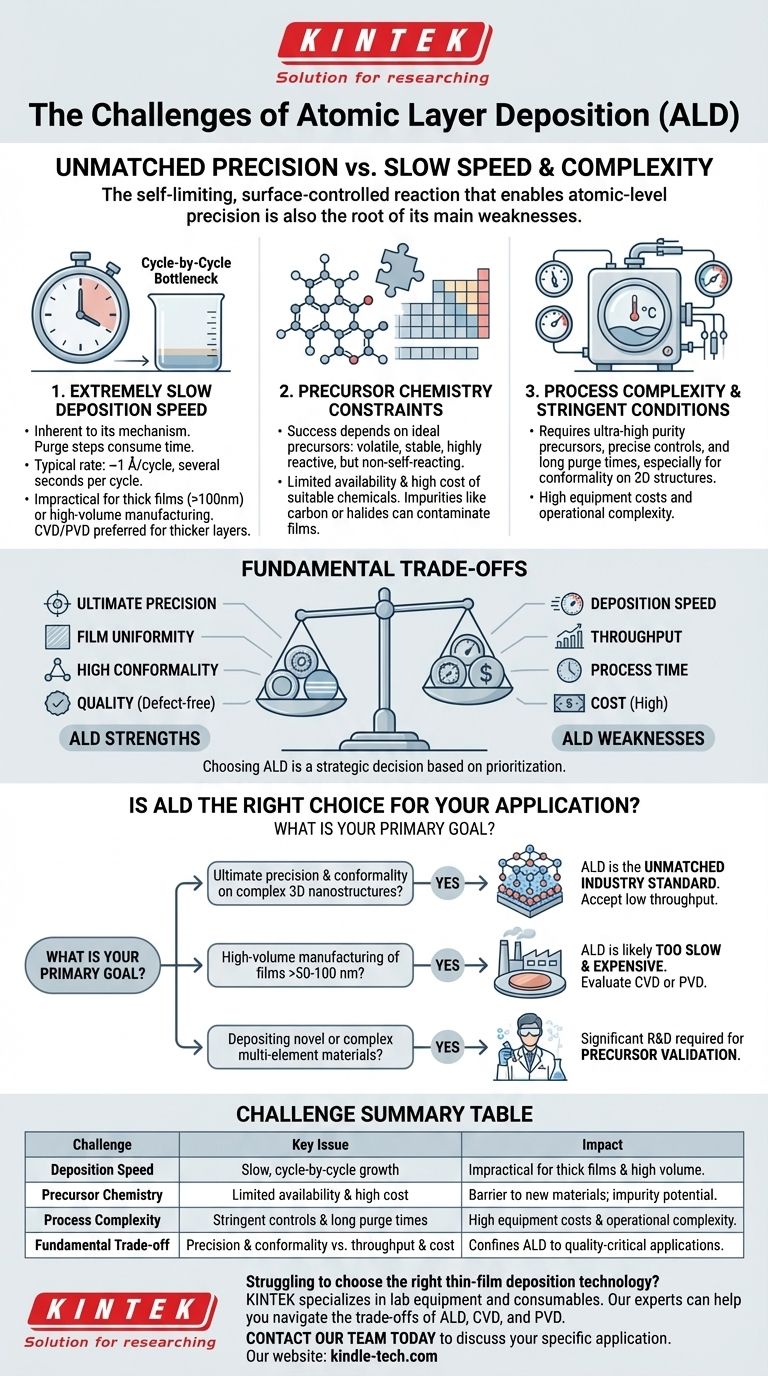
The primary challenges of Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) are its extremely slow deposition rate, the limited availability and high cost of suitable chemical precursors, and the stringent process conditions required to maintain its layer-by-layer growth mechanism. These factors often confine ALD to applications where ultimate precision and film quality are more critical than manufacturing throughput or cost.
The core challenge of ALD is that its greatest strength—the self-limiting, surface-controlled reaction that enables atomic-level precision—is also the direct cause of its main weaknesses: slow speed and high operational complexity.

The Core Challenge: Deposition Speed
The most frequently cited limitation of ALD is its inherently slow deposition rate. This is not an incidental flaw but a direct consequence of its fundamental mechanism.
The Cycle-by-Cycle Bottleneck
ALD builds films one atomic layer at a time through a sequence of steps: precursor pulse, purge, reactant pulse, and another purge. The two purge steps, which are essential to prevent unwanted gas-phase reactions (CVD), often consume the majority of the cycle time.
This means that even a fast ALD process might only deposit about one angstrom (0.1 nanometers) per cycle, with each cycle taking several seconds.
Impact on High-Volume Manufacturing
This slow growth rate makes ALD impractical for applications requiring thick films (generally, anything more than ~100 nanometers). The time required would be commercially prohibitive.
For this reason, techniques like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) or Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) are preferred for depositing thicker layers where atomic-level control is less critical.
Precursor Chemistry and Material Constraints
The success of any ALD process is entirely dependent on the quality and properties of the chemical precursors used. Finding the right molecules is a significant scientific and engineering challenge.
The Ideal vs. The Real
Ideal ALD precursors must be volatile enough to be transported as a gas but stable enough not to decompose at the process temperature. Crucially, they must react aggressively with the surface but not with themselves.
Finding chemicals that meet all these criteria for a specific element is often difficult and can be the primary barrier to developing a new ALD process.
Limited Material Palette
While ALD can be used for a wide range of materials in a lab setting, the number of robust, commercially viable processes is much smaller. This is directly tied to the lack of suitable, high-purity precursors for many elements on the periodic table.
The Problem of Impurities
Imperfect reactions can lead to the incorporation of contaminants into the film. For instance, metal-organic precursors can leave behind carbon impurities, while metal halides can leave chlorine or fluorine.
Minimizing these impurities requires careful process optimization and sometimes necessitates very high temperatures, which can damage sensitive substrates.
Understanding the Fundamental Trade-offs
Choosing ALD involves a clear set of trade-offs. Understanding these is key to determining if it is the right technology for your goal.
Precision vs. Speed
This is the central dilemma of ALD. You gain unparalleled control over film thickness and uniformity at the direct expense of deposition speed. No other technique offers this level of control, but it always comes at the cost of time.
Conformality vs. Process Time
ALD's ability to coat complex, high-aspect-ratio 3D structures is one of its most powerful features. However, achieving this requires ensuring the precursor molecules can reach every surface and that purge gases can remove all excess.
This often necessitates extending the pulse and purge times significantly, further slowing down an already slow process.
Quality vs. Cost
Achieving high-purity, defect-free films requires investment in ultra-high purity precursors, sophisticated vacuum reactors, and precise temperature and pressure controls. This makes ALD a high-cost deposition method compared to alternatives like sputtering or evaporation.
Is ALD the Right Choice for Your Application?
Evaluating these challenges in the context of your specific goal is the most critical step.
- If your primary focus is ultimate precision and conformality on complex 3D nanostructures: ALD is the unmatched industry standard, and you must accept the trade-off of low throughput.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing of films thicker than 50-100 nm: ALD is likely too slow and expensive; you should evaluate faster methods like CVD or PVD.
- If your primary focus is depositing novel or complex multi-element materials: Your main challenge will be the significant research and development required to find and validate suitable chemical precursors.
By understanding these inherent challenges, you can strategically leverage ALD's unique capabilities for applications where they provide a decisive advantage.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Key Issue | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Deposition Speed | Slow, cycle-by-cycle growth | Impractical for thick films (>100nm) & high-volume manufacturing |
| Precursor Chemistry | Limited availability & high cost of ideal precursors | Barrier to new material development; potential for film impurities |
| Process Complexity | Stringent temperature/pressure controls & long purge times | High equipment costs and operational complexity |
| Fundamental Trade-off | Unmatched precision & conformality vs. throughput & cost | Confines ALD to applications where ultimate quality is critical |
Struggling to choose the right thin-film deposition technology for your project? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs of ALD, CVD, and PVD to find the optimal solution for your precision, throughput, and budget requirements. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and discover how our solutions can enhance your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and sputter? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition



















