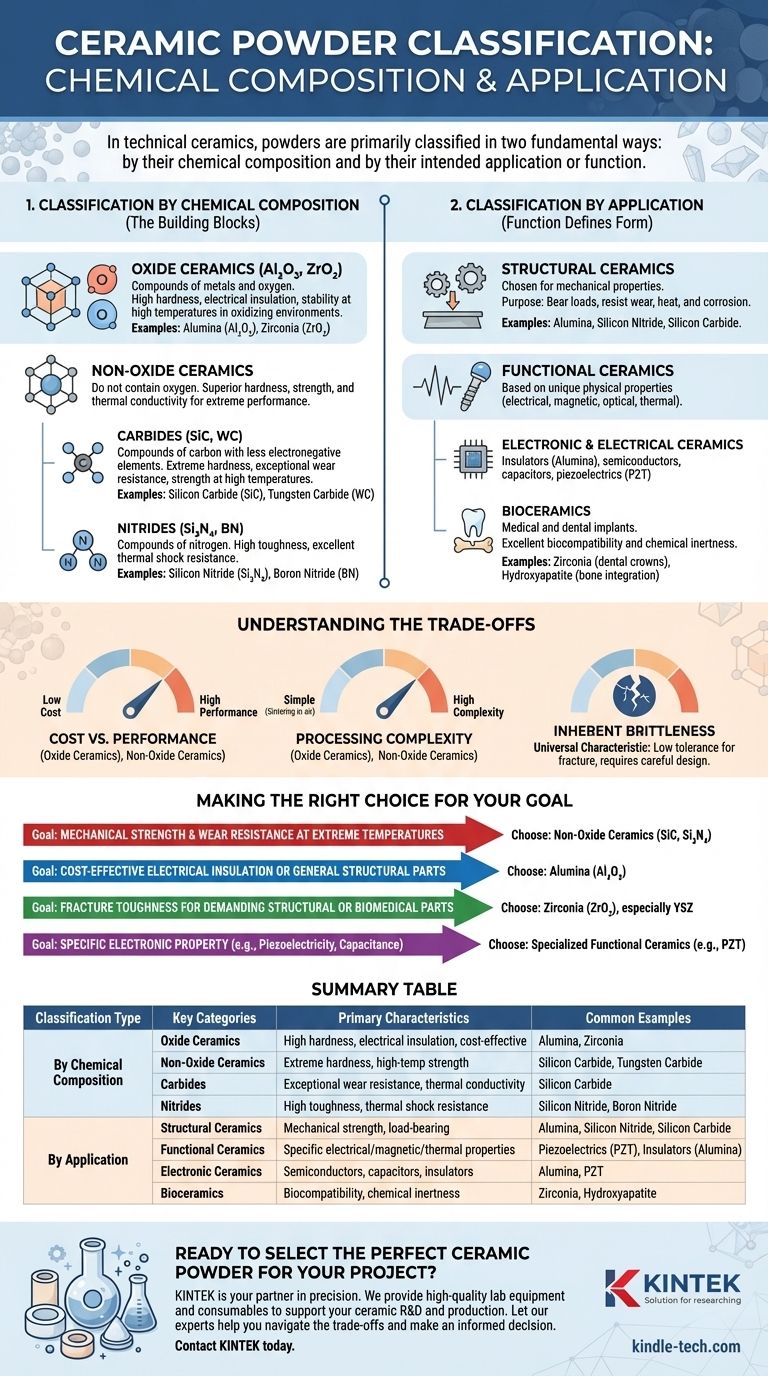
In technical ceramics, powders are primarily classified in two fundamental ways: by their chemical composition and by their intended application or function. Chemical composition—whether a material is an oxide, carbide, or nitride—dictates its intrinsic properties, while the application—whether it's for structural, electronic, or biomedical use—defines the performance requirements it must meet.
Understanding these classification systems is not merely an academic exercise. It is the foundational step in materials selection, as the category a powder belongs to directly predicts its processing behavior, cost, and the final performance characteristics of the manufactured component.

Classification by Chemical Composition: The Building Blocks
The most fundamental way to categorize a ceramic powder is by its chemical makeup. This classification provides the clearest insight into a material's inherent properties, such as its melting point, hardness, and chemical stability.
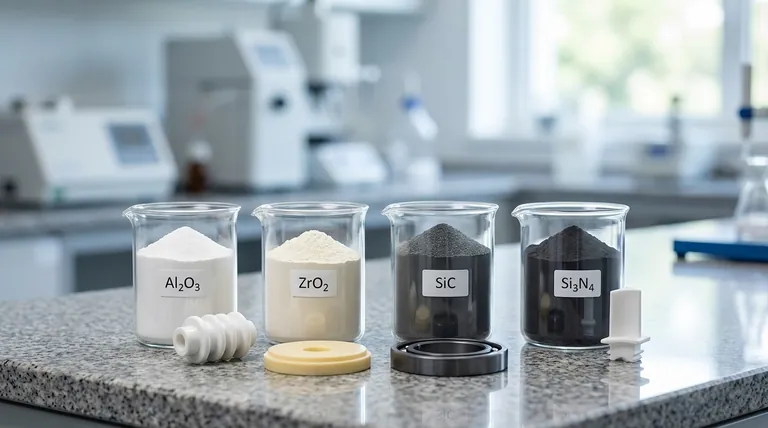
Oxide Ceramics (Al₂O₃, ZrO₂)
Oxide ceramics are compounds of metals and oxygen. They are the most widely used and cost-effective class of advanced ceramics.
They are valued for their high hardness, excellent electrical insulation properties, and good stability at high temperatures in oxidizing environments. Common examples include Alumina (Al₂O₃) and Zirconia (ZrO₂).
Non-Oxide Ceramics
This broad category includes materials that do not contain oxygen as a principal component. They are generally developed for extreme performance applications where oxides fall short.
Non-oxides often offer superior hardness, strength, and thermal conductivity but are typically more expensive and difficult to process.
Carbides (SiC, WC)
Carbide ceramics are compounds of carbon with less electronegative elements, like silicon or tungsten.
They are known for their extreme hardness, exceptional wear resistance, and strength at very high temperatures. Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Tungsten Carbide (WC) are prominent examples used in cutting tools and armor.
Nitrides (Si₃N₄, BN)
Nitride ceramics are compounds of nitrogen, valued for their high toughness and excellent thermal shock resistance.
Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) is a prime example, known for its unique combination of high strength and fracture toughness, making it suitable for bearings and automotive engine parts. Boron Nitride (BN) is notable for its high thermal conductivity and low dielectric constant.
Classification by Application: Function Defines Form
While chemical composition tells us what a material is, classifying by application tells us what it does. This approach is more practical for engineers and designers focusing on a specific end-use.
Structural Ceramics
These materials are chosen for their mechanical properties. Their primary purpose is to bear loads and resist wear, heat, and corrosion.
This category includes many high-performance oxides, carbides, and nitrides. Applications range from industrial bearings and cutting tools to turbine components and heat shields.
Functional Ceramics
The primary role of functional ceramics is based on their unique physical properties, not just their mechanical strength.
This diverse group is defined by specific electrical, magnetic, optical, or thermal behaviors.
Electronic and Electrical Ceramics
This sub-category of functional ceramics is vast. It includes materials used as insulators (like Alumina), semiconductors, capacitors, and piezoelectrics (like Lead Zirconate Titanate, or PZT), which convert mechanical pressure into electrical signals.
Bioceramics
Bioceramics are used for medical and dental implants due to their excellent biocompatibility and chemical inertness within the human body.
Key materials include Zirconia for its strength and fracture resistance in dental crowns and Hydroxyapatite for its ability to integrate with bone.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a ceramic powder involves navigating a series of critical trade-offs. No single material is ideal for every situation.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between performance and cost. Common oxide ceramics like Alumina are relatively inexpensive and easy to source.
In contrast, high-performance non-oxide ceramics like Silicon Nitride offer superior properties but come with significantly higher material and processing costs.
Processing Complexity
Oxide ceramics can typically be sintered (densified at high temperatures) in air. This simplifies the manufacturing process considerably.
Most non-oxide ceramics will oxidize at high temperatures and must be processed in controlled, inert atmospheres (like argon or nitrogen), which adds significant complexity and expense to manufacturing.
Inherent Brittleness
While some ceramics are tougher than others, brittleness remains a universal characteristic. This low tolerance for fracture must always be a central consideration in the design of any ceramic component, regardless of its classification.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final selection depends entirely on your primary objective. By aligning the material's classification with your application's demands, you can make a more informed decision.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and wear resistance at extreme temperatures: Non-oxide ceramics like Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) are the leading candidates.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective electrical insulation or general-purpose structural parts: Alumina (Al₂O₃) is the industry standard and an excellent starting point.
- If your primary focus is fracture toughness for demanding structural or biomedical parts: Zirconia (ZrO₂), particularly Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia (YSZ), is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is a specific electronic property like piezoelectricity or capacitance: You must investigate specialized functional ceramics designed for that exact purpose.
Mastering these classifications transforms ceramic powder from a simple commodity into a predictable and powerful engineering tool.
Summary Table:
| Classification Type | Key Categories | Primary Characteristics | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| By Chemical Composition | Oxide Ceramics | High hardness, electrical insulation, cost-effective | Alumina (Al₂O₃), Zirconia (ZrO₂) |
| Non-Oxide Ceramics | Extreme hardness, high-temperature strength | Silicon Carbide (SiC), Tungsten Carbide (WC) | |
| Carbides | Exceptional wear resistance, thermal conductivity | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | |
| Nitrides | High toughness, thermal shock resistance | Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄), Boron Nitride (BN) | |
| By Application | Structural Ceramics | Mechanical strength, load-bearing, wear resistance | Alumina, Silicon Nitride, Silicon Carbide |
| Functional Ceramics | Specific electrical, magnetic, or thermal properties | Piezoelectrics (PZT), Insulators (Alumina) | |
| Electronic Ceramics | Semiconductors, capacitors, insulators | Alumina, PZT | |
| Bioceramics | Biocompatibility, chemical inertness | Zirconia, Hydroxyapatite |
Ready to Select the Perfect Ceramic Powder for Your Project?
Choosing the right ceramic powder is critical to the performance and cost-effectiveness of your final component. Whether you need the high-temperature strength of Silicon Carbide, the cost-effective insulation of Alumina, or the biocompatibility of Zirconia, KINTEK is your partner in precision.
We provide high-quality lab equipment and consumables to support your ceramic R&D and production, ensuring you have the right materials for success.
Let our experts help you navigate the trade-offs and make an informed decision. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Alumina Granulated Powder for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the examples of ceramic powder? A Guide to Oxide and Non-Oxide Materials
- What are the high temperature properties of alumina? Discover Its Stability, Strength, and Limits
- What are the process advantages of selecting an alumina plate for CuO nanofilm synthesis? Achieve Superior Purity
- What is the maximum operating temperature of alumina? The Critical Role of Purity and Form
- What measures should be taken to prevent cross-contamination when using different sizes of alumina powder?



















