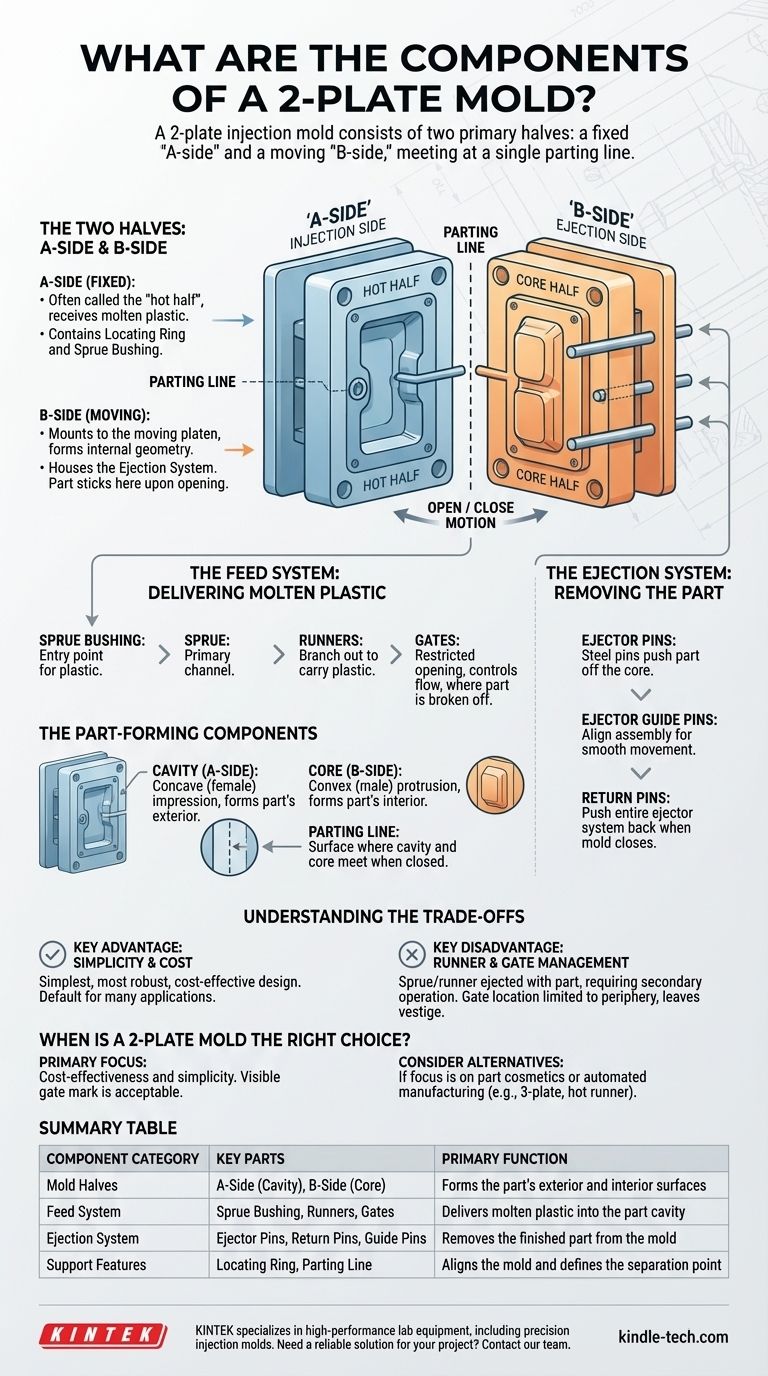
At its core, a 2-plate injection mold is comprised of two primary halves: a fixed "A-side" and a moving "B-side." These halves contain systems for delivering molten plastic, shaping the part, and ejecting the final product. Key components include the sprue bushing, runners, gates, the cavity and core, and the ejector system.
The fundamental design of a 2-plate mold splits its functions between two halves. The A-side delivers the plastic and forms the part's exterior, while the B-side forms the interior and contains the mechanism to push the finished part out.

The Two Halves: A-Side and B-Side
The most basic principle of a 2-plate mold is its division into two sections that meet at a single parting line.
The A-Side (Cavity or Fixed Half)
This half of the mold attaches to the stationary platen of the injection molding machine. It's often called the "hot half" or "injection side."
Its primary role is to receive molten plastic from the machine's nozzle. It contains the locating ring, which aligns the entire mold with the machine, and the sprue bushing.
The B-Side (Core or Moving Half)
This half mounts to the moving platen of the machine. It contains the "core," which forms the internal geometry of the plastic part.
Crucially, the B-side also houses the entire ejection system. The finished part is designed to stick to the B-side when the mold opens, allowing this system to push it out.
The Feed System: Delivering Molten Plastic
This network of channels guides the hot plastic from the machine's nozzle into the part cavity.
Sprue Bushing and Sprue
The sprue bushing is the hardened steel entry point that makes contact with the machine nozzle. The channel running through it is the sprue, which is the primary path for the plastic entering the mold.
Runners and Gates
From the base of the sprue, channels called runners branch out to carry plastic toward the part.
The gate is the small, restricted opening where the runner meets the part cavity. It controls the flow of plastic and is where the part is later broken off from the runner system.
The Part-Forming Components
These are the machined surfaces that directly shape the final plastic part.
Cavity
The cavity is the concave (female) impression, typically in the A-side, that forms the exterior, cosmetic surface of the part.
Core
The core is the convex (male) protrusion, typically in the B-side, that forms the interior shape and features of the part.
Parting Line
The parting line is the surface where the faces of the cavity and core plates meet when the mold is closed.
The Ejection System: Removing the Part
Once the part has cooled, the mold opens and this system activates to remove it from the B-side.
Ejector Pins
These are steel pins that push directly against the finished part to force it off the core. Their placement is critical to avoid warping or damaging the part during ejection.
Ejector Guide Pins
These larger pins align the ejector plate assembly, ensuring the ejector pins move forward and backward smoothly and accurately without binding.
Return Pins
As the mold closes, return pins make contact with the A-side's surface, pushing the entire ejector system back to its starting position. This is a safety feature that ensures the ejector pins are clear before the next injection cycle begins.
Understanding the Trade-offs of a 2-Plate Design
While extremely common, the 2-plate design has inherent benefits and limitations.
Key Advantage: Simplicity and Cost
The 2-plate mold is the simplest, most robust, and most cost-effective type of injection mold to design and build. It is the default choice for a vast majority of applications.
Key Disadvantage: Runner and Gate Management
In a 2-plate mold, the sprue and runner system are ejected along with the part. This requires a secondary operation (manual or automated) to separate the runner from the part.
Furthermore, the gate must be located on the part's periphery at the parting line. This limits design options and always leaves a visible mark, or "vestige," where it was removed.
When is a 2-Plate Mold the Right Choice?
Use this framework to determine if this design meets your project's needs.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and simplicity: A 2-plate mold is almost always the best choice, especially if a visible gate mark is acceptable.
- If your primary focus is part cosmetics or automated manufacturing: Consider a 3-plate or hot runner mold, which can automatically separate the runner and offer more flexible gating locations away from the parting line.
Understanding these fundamental components is the first step toward designing effective parts and communicating clearly with manufacturing partners.
Summary Table:
| Component Category | Key Parts | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Mold Halves | A-Side (Cavity), B-Side (Core) | Forms the part's exterior and interior surfaces |
| Feed System | Sprue Bushing, Runners, Gates | Delivers molten plastic into the part cavity |
| Ejection System | Ejector Pins, Return Pins, Guide Pins | Removes the finished part from the mold |
| Support Features | Locating Ring, Parting Line | Aligns the mold and defines the separation point |
Need a reliable 2-plate mold for your next project? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including precision injection molds tailored for laboratory applications. Our expertise ensures durable, cost-effective molds that deliver consistent part quality for your research or production needs. Contact our team today to discuss your specific requirements and get a customized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Cylindrical Press Mold for Lab Applications
- Round Bidirectional Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- How do high-precision molds contribute to Li6PS5Cl electrolyte membrane formation? Achieve Perfect Density and Thickness
- Why is a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) Required for NaSICON? Achieve Maximum Green Density and Ionic Conductivity
- What is a pressing die? The Precision Tool for Shaping Powder into Solid Pellets
- How does a Hot Isostatic Press (HIP) improve W-Cu densification? Achieve Near-Theoretical Density with High Pressure
- How does a Hot Isostatic Press (HIP) machine improve AlFeTiCrZnCu alloys? Achieving 10 GPa Hardness and Maximum Density



















