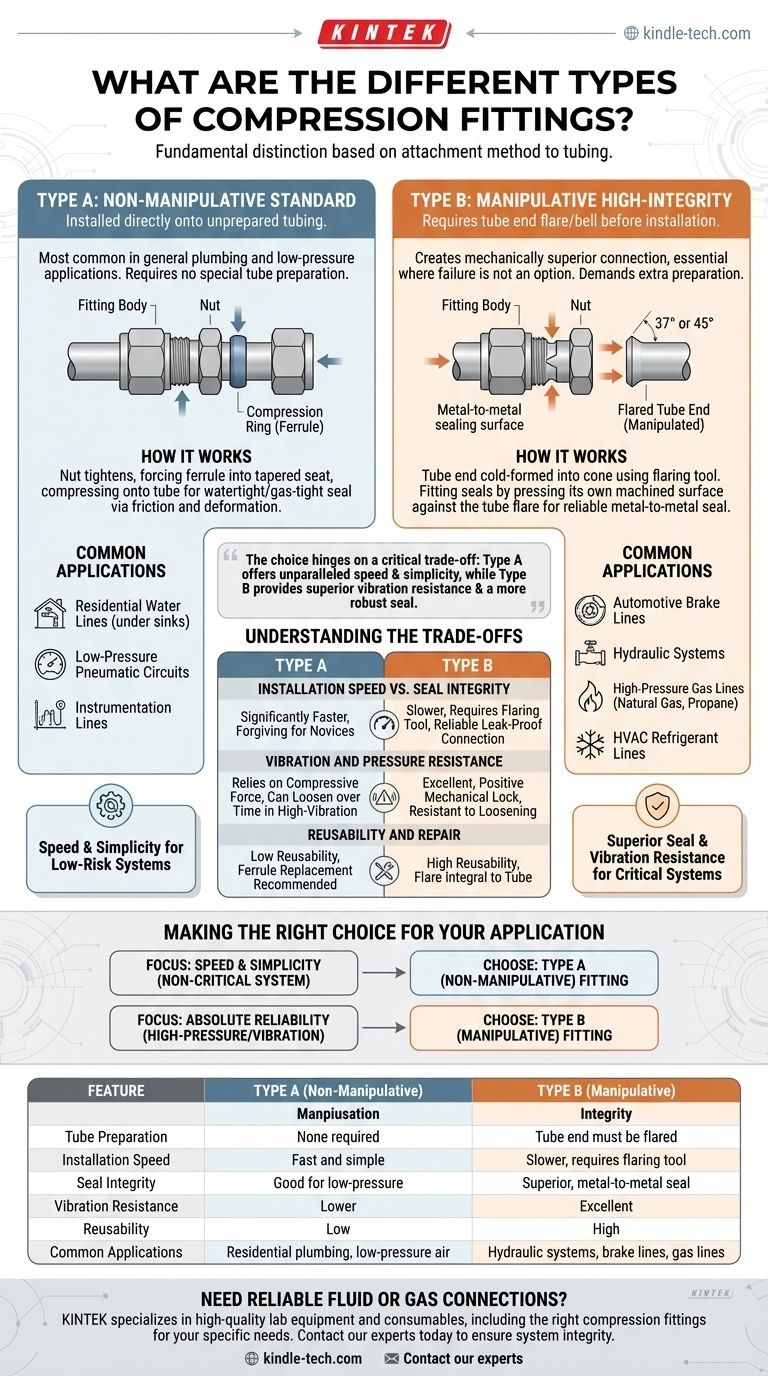
At a fundamental level, compression fittings are divided into two primary categories based on how they attach to the tubing. These are Type A (non-manipulative) fittings, which are installed directly onto an unprepared tube, and Type B (manipulative) fittings, which require the end of the tube to be flared or belled before installation.
The choice between compression fitting types hinges on a critical trade-off: Type A offers unparalleled speed and simplicity, while Type B provides superior vibration resistance and a more robust seal, making it the standard for demanding applications.

Type A: The "Non-Manipulative" Standard
Type A fittings are the most common type found in general plumbing and low-pressure applications due to their ease of use. They require no special preparation of the tube itself.
How It Works
This design uses three core components: the fitting body, a nut, and a compression ring (often called a ferrule or "olive").
As the nut is tightened, it forces the ferrule into the tapered seat of the fitting body. This action compresses the ferrule onto the outer wall of the tube, creating a watertight and gas-tight seal through friction and deformation.
Common Applications
Because they are fast and easy to install without specialized tools (beyond wrenches), Type A fittings are ideal for accessible, low-risk systems. You will commonly find them in residential water supply lines (like under a sink), low-pressure pneumatic circuits, and instrumentation lines.
Type B: The "Manipulative" High-Integrity Fitting
Type B fittings demand an extra preparation step but create a mechanically superior connection. This makes them the required choice for systems where failure is not an option.
How It Works
Before installation, the end of the tube must be "manipulated" using a special flaring tool. This tool cold-forms the tube end into a 37° or 45° cone shape.
The fitting then seals by tightly pressing its own machined surface against this newly created flare on the tube. The nut's primary job is to hold these two metal surfaces together, creating a highly reliable metal-to-metal seal.
Common Applications
The strength and vibration resistance of the flared connection make Type B fittings essential for high-pressure or dynamic systems. This includes automotive brake lines, hydraulic systems, high-pressure gas lines (natural gas, propane), and HVAC refrigerant lines.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the correct fitting requires understanding the fundamental differences in their performance and installation requirements.
Installation Speed vs. Seal Integrity
Type A fittings are significantly faster to install and are more forgiving for a novice.
Type B fittings require more time, skill, and a specific tool to create the flare. However, this process yields a far more reliable and leak-proof connection suitable for critical systems.
Vibration and Pressure Resistance
This is the most critical distinction. A Type B flared connection provides a positive mechanical lock, making it extremely resistant to loosening from vibration or being forced apart by high pressure.
A Type A fitting relies purely on the compressive force of the ferrule. In high-vibration environments, this can slowly loosen over time, and extreme pressure spikes can potentially cause the tube to pull out of the fitting.
Reusability and Repair
Type A fittings can sometimes be disassembled and reassembled, but it is best practice to replace the ferrule each time, as it becomes permanently deformed during the initial installation.
Type B fittings are highly reusable. Since the flare is an integral part of the tube, the connection can be taken apart and put back together repeatedly without degrading the seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your system's operating conditions should be the sole factor in your decision.
- If your primary focus is speed and simplicity for a non-critical system: Choose a Type A (non-manipulative) fitting for tasks like household water lines or low-pressure air.
- If your primary focus is absolute reliability in a high-pressure or high-vibration environment: You must use a Type B (manipulative) fitting, as its mechanical lock is essential for safety and performance.
Understanding this fundamental distinction empowers you to select a fitting not just for convenience, but for long-term safety and system integrity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Type A (Non-Manipulative) | Type B (Manipulative) |
|---|---|---|
| Tube Preparation | None required | Tube end must be flared |
| Installation Speed | Fast and simple | Slower, requires a flaring tool |
| Seal Integrity | Good for low-pressure | Superior, metal-to-metal seal |
| Vibration Resistance | Lower | Excellent |
| Reusability | Low (ferrule replacement recommended) | High |
| Common Applications | Residential plumbing, low-pressure air | Hydraulic systems, brake lines, gas lines |
Need reliable fluid or gas connections for your laboratory or process system? The right compression fitting is critical for safety and performance. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including the right fittings for your specific pressure, temperature, and chemical compatibility requirements. Contact our experts today to ensure your system's integrity and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- How does a Hot Isostatic Press (HIP) machine improve AlFeTiCrZnCu alloys? Achieving 10 GPa Hardness and Maximum Density
- What are the factors affecting molding? Master the 4 Keys to Perfect Plastic Parts
- What is mould in manufacturing? Unlock Mass Production with Precision Tooling
- How does a Hot Isostatic Press (HIP) improve W-Cu densification? Achieve Near-Theoretical Density with High Pressure
- What is the function of high-strength pressure molds for nanostructured copper powders? Achieve High Purity Densification






