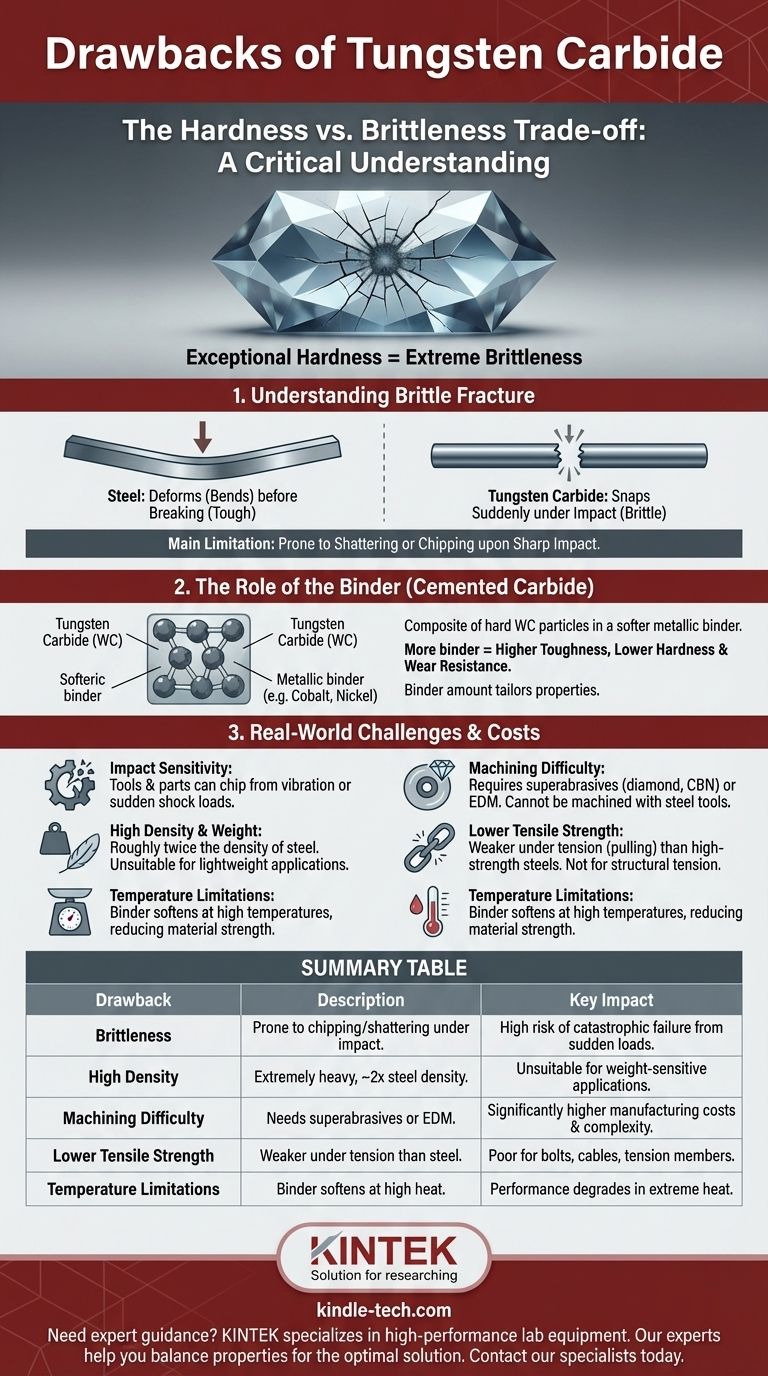
While exceptionally hard, the primary drawback of tungsten carbide is its brittleness. Unlike most metals which bend or deform under stress, tungsten carbide is prone to shattering or chipping upon sharp impact. This inherent lack of toughness, combined with its extreme density and the difficulty of machining it, defines its main limitations.
Users often mistake hardness for overall durability. The central takeaway is that tungsten carbide offers world-class scratch and wear resistance, but this comes at the direct expense of toughness, making it vulnerable to fracture from sudden impacts.

The Core Trade-off: Hardness vs. Brittleness
Tungsten carbide's greatest strength—its extreme hardness—is inextricably linked to its most significant weakness. Understanding this relationship is critical to using the material effectively.
Understanding Brittle Fracture
Tungsten carbide does not exhibit plastic deformation. When it reaches its breaking point, it fails suddenly and catastrophically.
Think of the difference between a steel bar and a glass rod. You can bend the steel bar, and it will deform before it breaks. The glass rod, however, will snap cleanly with no bending. Tungsten carbide behaves much more like the glass rod in this scenario.
The Role of the Binder
Most commercial tungsten carbide is actually a composite material called cemented carbide. It consists of hard tungsten carbide (WC) particles held together in a softer, tougher metallic binder, typically cobalt or nickel.
The amount and type of binder dictate the material's final properties. A higher percentage of binder increases toughness and impact resistance but reduces hardness and wear resistance. This allows manufacturers to tailor grades for specific applications.
Impact on Practical Use
This brittleness has clear real-world consequences. A tungsten carbide wedding band, while nearly impossible to scratch, can crack or shatter if dropped on a hard surface like concrete.
Similarly, in industrial settings, a cutting tool made of tungsten carbide can chip or fracture if it experiences excessive vibration ("chatter") or a sudden shock load.
Manufacturing and Machining Challenges
The same hardness that makes tungsten carbide so desirable for wear resistance also makes it exceptionally difficult and expensive to process.
The Need for Superabrasives
Tungsten carbide is so hard that it cannot be effectively machined using conventional steel tools.
It can only be shaped and finished through grinding or electrical discharge machining (EDM). Final polishing requires superabrasives of superior hardness, such as diamond or cubic boron nitride (CBN) compounds.
High Cost and Complexity
This specialized processing requirement translates directly into higher manufacturing costs. Creating complex geometries is far more challenging and expensive with tungsten carbide than with steel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing tungsten carbide means accepting a specific set of compromises compared to other engineering materials.
High Density and Weight
Tungsten is one of the densest elements, and tungsten carbide is correspondingly very heavy. Its density is roughly twice that of steel.
This makes it unsuitable for applications where light weight is a primary design goal, such as in the aerospace industry.
Lower Tensile Strength
While tungsten carbide has incredibly high compressive strength (resistance to being squeezed), its tensile strength (resistance to being pulled apart) is generally lower than that of high-strength steels.
It is not the ideal choice for parts that will be under significant tension, such as bolts or structural cables.
Binder-Limited Temperature Resistance
Although tungsten carbide has good heat resistance, its performance at very high temperatures is often limited by its metallic binder. The cobalt or nickel binder will begin to soften at temperatures well below the melting point of the tungsten carbide particles themselves, causing the material to lose strength.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires a clear understanding of your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is extreme wear and scratch resistance: Tungsten carbide is an excellent choice for components like cutting tools, abrasive nozzles, or jewelry where abrasion is the main enemy.
- If your primary focus is impact resistance and toughness: You should consider materials like tool steels or other alloys, as tungsten carbide can fracture under sudden, sharp loads.
- If your primary focus is low cost or complex shapes: The high cost and difficulty of machining tungsten carbide may make materials like hardened steel a more practical alternative.
By understanding this fundamental balance between hardness and brittleness, you can confidently select the right material for your specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Drawback | Description | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Brittleness | Prone to chipping/shattering under impact, lacks plastic deformation. | High risk of catastrophic failure from sudden loads. |
| High Density | Extremely heavy, roughly twice the density of steel. | Unsuitable for weight-sensitive applications (e.g., aerospace). |
| Machining Difficulty | Can only be shaped with superabrasives (diamond, CBN) or EDM. | Significantly higher manufacturing costs and complexity. |
| Lower Tensile Strength | High compressive strength but weaker under tension than steel. | Poor choice for bolts, cables, or structural tension members. |
| Temperature Limitations | Binder (cobalt/nickel) softens at high temperatures, reducing strength. | Performance degrades in extreme heat environments. |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right material for your laboratory equipment?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables. Our experts understand the critical balance between material properties like hardness, toughness, and cost. We can help you choose the optimal solution for your specific application, ensuring durability, efficiency, and value.
Contact our specialists today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Iridium Dioxide IrO2 for Water Electrolysis
People Also Ask
- What is the role of the hydraulic system in hot pressing? Achieve Maximum Material Density and Strength
- How mechanical properties are affected by sintering? Master the Trade-offs for Stronger Materials
- How does a sputtering machine work? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials













