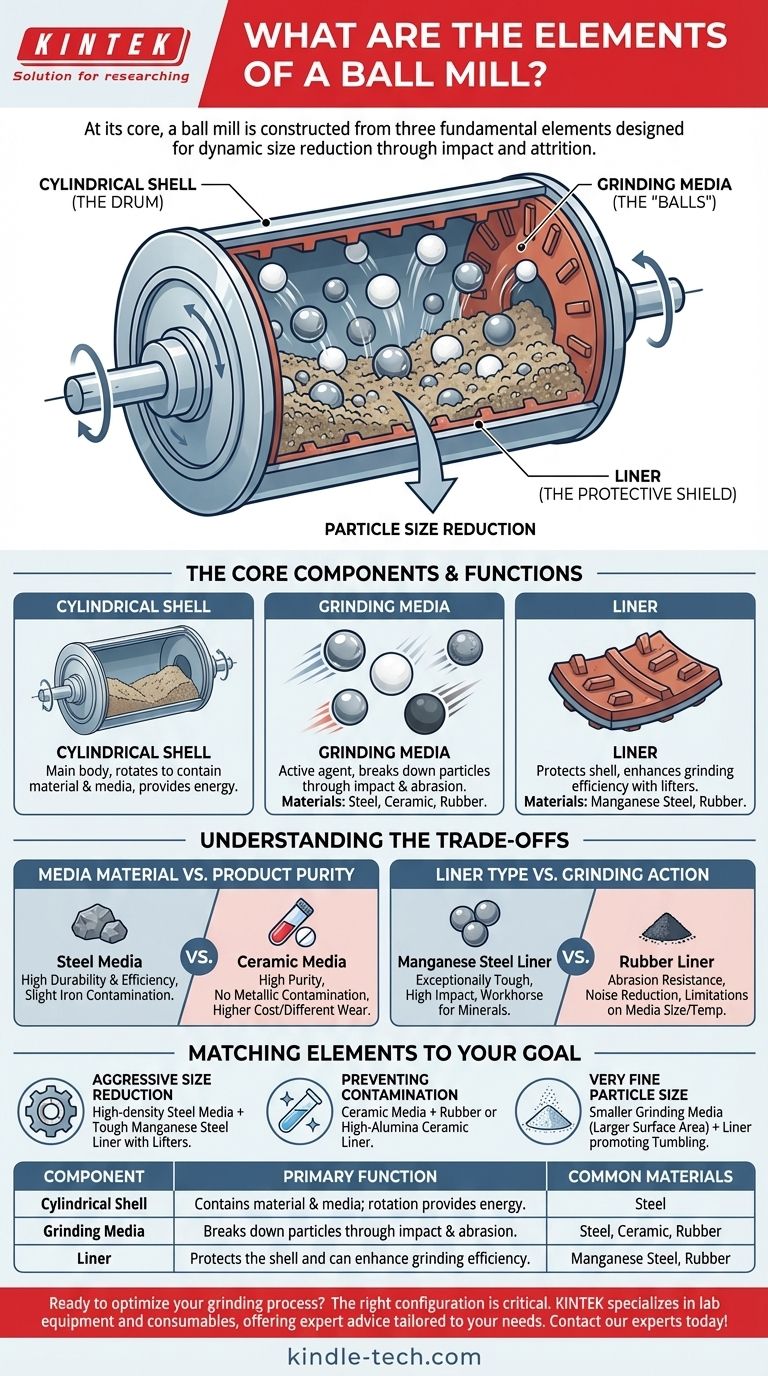
At its core, a ball mill is constructed from three fundamental elements. These are the rotating hollow cylindrical shell that contains the material, the grinding media (balls) placed inside the shell, and an abrasion-resistant liner that protects the shell's inner surface. Together, these components create a dynamic system for reducing the size of particles through impact and attrition.
The effectiveness of a ball mill does not lie in any single component, but in the precise interaction between the shell's rotation, the media's grinding action, and the liner's protective and lifting function. Understanding this interplay is key to controlling the final product.
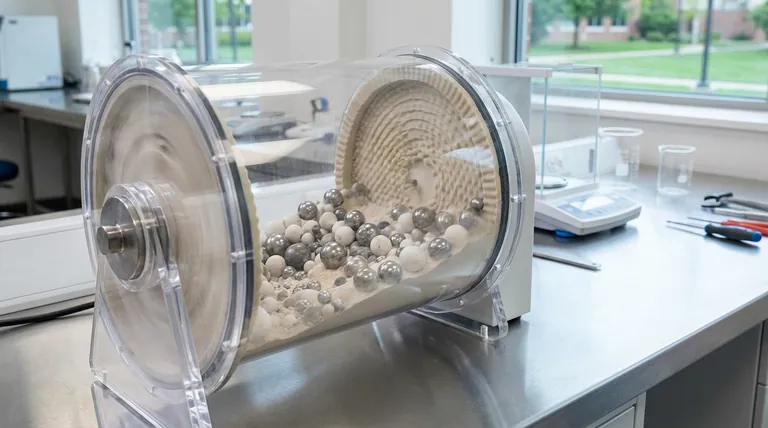

The Core Components and Their Functions
Each element of a ball mill has a distinct role. While the design appears simple, the function of each part is critical to achieving efficient and effective grinding.
The Cylindrical Shell (The Drum)
The shell is the main body of the machine. It is a hollow cylinder, typically made of steel, that rotates on a horizontal or slightly inclined axis.
Its primary purpose is to contain both the material to be ground and the grinding media. As the shell rotates, it continuously lifts the media and material, creating the energy needed for size reduction.
The Grinding Media (The "Balls")
This is the active agent of the grinding process. The shell is partially filled with balls, which are responsible for breaking down the particles of the target material.
The media can be made from various materials, including high-carbon steel, stainless steel, ceramic, or even rubber, depending on the application's demands for hardness and purity. As the shell turns, the media is lifted and then tumbles or cascades down, crushing and grinding the material through impact and abrasion.
The Liner (The Protective Shield)
The liner is a crucial wear part fitted to the inner surface of the cylindrical shell. Its most basic function is to protect the shell itself from the intense abrasive and impact forces generated by the grinding media.
Liners are commonly made from highly durable materials like manganese steel or specialized rubber compounds. Beyond protection, many liners incorporate "lifters"—raised bars that help grip and lift the grinding media higher, increasing the grinding efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs in Component Selection
The choice of material for each component directly impacts the mill's performance, maintenance costs, and the purity of the final product. There is no single "best" configuration; it is always a matter of balancing priorities.
Media Material vs. Product Purity
The most common trade-off involves the grinding media. Steel balls offer excellent durability and high grinding efficiency due to their density, making them ideal for ores and hard minerals. However, they inevitably introduce slight iron contamination into the product.
For applications where purity is paramount, such as in pharmaceuticals or high-quality ceramics, ceramic media is the standard choice. This eliminates metallic contamination but may come at a higher cost or with different wear characteristics.
Liner Type vs. Grinding Action
The liner material also presents a choice. Manganese steel liners are exceptionally tough and well-suited for high-impact applications with large, heavy steel balls. They are the workhorse for mineral processing.
Rubber liners, on the other hand, excel in resisting abrasion from finer materials and significantly reduce the noise level of the operation. However, they may have limitations regarding the maximum size of grinding media they can handle and the operating temperature.
Matching the Elements to Your Grinding Goal
The optimal setup for a ball mill is entirely dependent on the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is aggressive size reduction of hard materials: Use high-density steel media combined with a tough manganese steel liner designed with prominent lifters.
- If your primary focus is preventing product contamination: Opt for ceramic media and pair it with either a rubber liner or a high-alumina ceramic liner.
- If your primary focus is achieving a very fine final particle size: Consider using a larger volume of smaller grinding media, which increases the surface area for attrition, paired with a liner that promotes tumbling over high impact.
By understanding how these fundamental elements interact, you can effectively configure a ball mill to achieve virtually any particle size reduction goal.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical Shell | Contains material and media; rotation provides energy for grinding. | Steel |
| Grinding Media | Breaks down particles through impact and abrasion. | Steel, Ceramic, Rubber |
| Liner | Protects the shell and can enhance grinding efficiency. | Manganese Steel, Rubber |
Ready to optimize your grinding process? The right ball mill configuration is critical for achieving your target particle size and product purity. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering expert advice and solutions tailored to your specific laboratory needs. Contact our experts today to discuss the ideal ball mill setup for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What kind of material is a hammer mill used for? Process Brittle, Dry, and Crystalline Materials Efficiently
- What are the advantages of using an agate mortar for manual mixing? Protect Particle Integrity in Solid-State Batteries
- What are the advantages of a colloid mill? Achieve Superior Particle Size Reduction and Stable Emulsions
- What is the specific purpose of the fine grinding-light burning-fine grinding process in MgO? Maximize Sintered Density
- What is the importance of speed of rotation of a ball mill cylinder? Unlock Maximum Grinding Efficiency
- What is an example of pulverized? From Crushing Rocks to Winning Debates
- Why is mechanical alloying equipment used for nickel-based alloys? Enhance Powder Activity & Precision
- What is the function of a 3D motion mixer with WC balls for high-entropy alloys? Ensure Perfect Powder Homogeneity



















