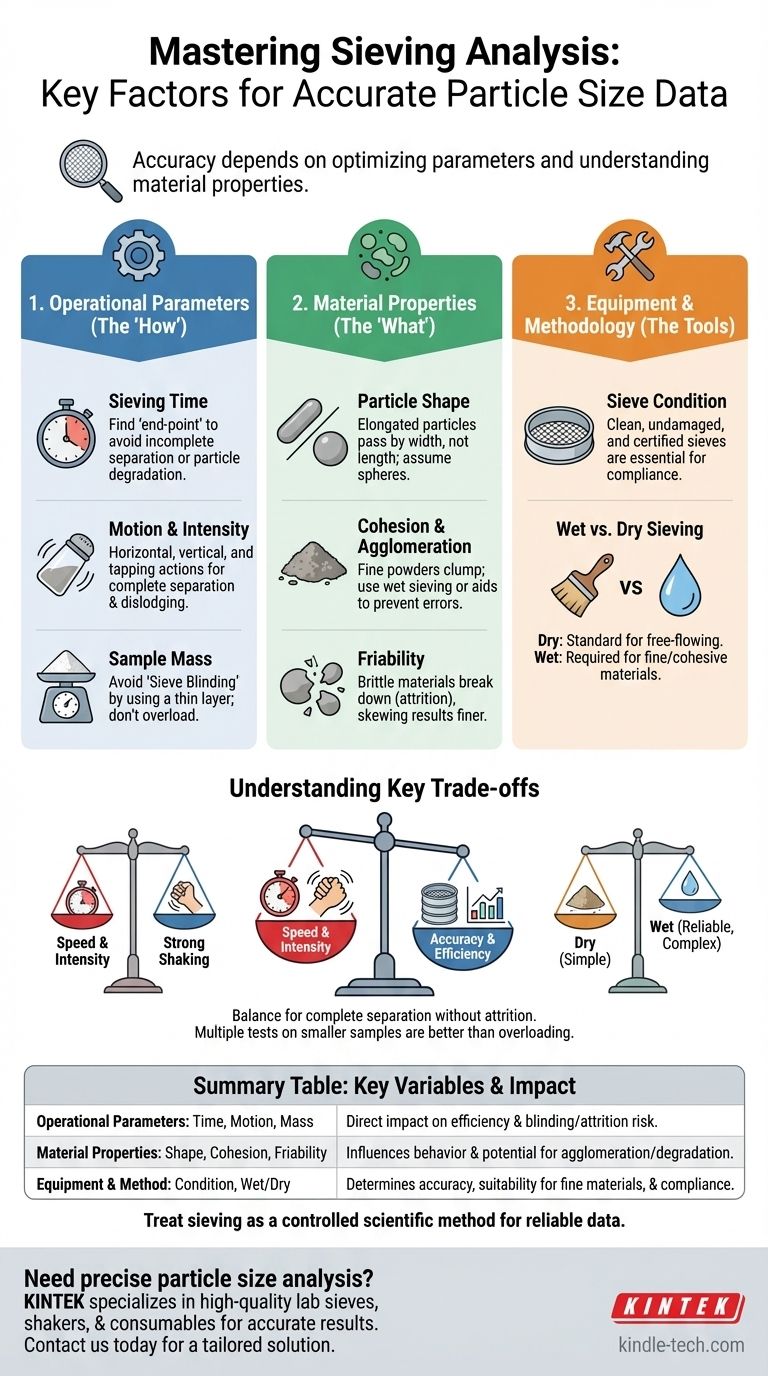
Ultimately, the accuracy of particle size analysis by sieving depends on a combination of controllable operational parameters and the inherent properties of the material being tested. Key factors include the duration and intensity of the sieving motion and the amount of sample loaded onto the sieves. These must be carefully optimized to ensure that every particle is given a sufficient opportunity to pass through the appropriate apertures.
Achieving reliable and repeatable sieving results is not just about shaking a sample. It is a controlled process of managing variables to ensure that the separation is both complete and does not alter the physical nature of the particles themselves.
1. Operational Parameters: The "How" of Sieving
The parameters you control directly during the analysis have the most immediate impact on the quality of your results.
Sieving Time
The duration of sieving must be long enough to achieve a complete separation. However, an excessively long time offers no benefit and can even cause problems.
An insufficient sieving time is a common error, leaving coarser particles on a finer sieve and skewing the distribution towards the coarse end.
The ideal time is often determined by finding the "sieving end-point"—the point at which the mass of material on each sieve no longer changes significantly (e.g., less than 0.1% change per minute).
Shaking Motion and Intensity
The movement of the sieve shaker is critical for particle separation. The goal is to both spread the material across the mesh and encourage particles to pass through.
A horizontal, circular motion helps distribute particles over the entire sieve surface, increasing the chance of them finding an aperture. A vertical tapping or vibrating motion helps dislodge near-size particles and clear blocked openings.
The intensity (amplitude) must be high enough to keep the particle bed moving but not so high that it causes particles to bounce without ever being properly tested against the mesh.
Sample Mass (Sieve Load)
Loading too much material onto a sieve is a primary source of inaccurate results. This condition, known as sieve blinding, overloads the mesh and prevents particles from reaching the apertures.
As a rule, no more than a thin layer of particles should cover the mesh at any point. This ensures each particle has a statistical chance to pass through. Standards like ASTM provide guidelines for maximum sample load based on sieve diameter and material density.
2. Material Properties: The "What" You Are Sieving
The physical characteristics of your sample dictate which operational challenges you are most likely to face.
Particle Shape
Sieve analysis assumes particles are perfect spheres. In reality, elongated or flaky particles pass through an aperture based on their second-smallest dimension.
This means that a long, thin particle will be classified by its width, not its length. This discrepancy is a fundamental limitation of the technique that you must be aware of when interpreting results.
Cohesion and Agglomeration
Fine powders, especially those under 75 microns, have a tendency to clump together due to moisture or electrostatic forces.
These agglomerates behave like larger particles and will not pass through the correct, finer mesh. This leads to an incorrectly coarse particle size distribution. Using sieving aids or switching to a wet sieving method can mitigate this issue.
Friability (Particle Brittleness)
If the material is brittle, the mechanical action of sieving can break the particles down. This process, known as attrition, creates more fine particles than were present in the original sample.
This skews the results toward the finer end of the distribution. For friable materials, it is critical to use the minimum sieving time and intensity necessary to achieve separation.
3. Equipment and Methodology: The Tools of the Trade
The state of your equipment and the chosen method are the final pieces of the puzzle.
Sieve Condition
Sieves must be clean, dry, and undamaged. Blocked or damaged apertures will retain particles that should have passed through, invalidating the test.
Regular inspection and proper cleaning are mandatory. For regulated environments, using certified and periodically recalibrated sieves is essential for data traceability and compliance.
Wet vs. Dry Sieving
Dry sieving is the standard and is suitable for most free-flowing materials.
Wet sieving is the required method for materials that agglomerate, are sticky, or contain very high amounts of fine particles (e.g., below 45 µm). In this process, a liquid (usually water with a wetting agent) is used to wash the particles through the sieve stack, breaking up clumps and eliminating static.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Making an informed decision requires balancing competing factors.
Accuracy vs. Speed
Increasing sieving time and intensity may seem to speed up the analysis, but it raises the risk of particle degradation (friability). The true goal is achieving a complete separation efficiently, not just finishing quickly. The most accurate result comes from the gentlest, shortest process that achieves a stable end-point.
Representativeness vs. Sieve Blinding
Using a larger sample mass can provide a more statistically representative analysis of the bulk material. However, this directly conflicts with the need to avoid overloading the sieves. It is better to perform multiple tests on smaller, representative samples than one test on an overloaded sample.
Dry vs. Wet Sieving
Dry sieving is faster, simpler, and requires less cleanup. However, for cohesive or very fine materials, the results will be inaccurate. Wet sieving provides far more reliable data for these difficult samples but adds complexity, including the need to dry and weigh each fraction afterward.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective should guide your protocol.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control: Standardize every parameter (time, amplitude, sample mass) based on an established internal or industry standard for maximum repeatability between tests.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a new or friable material: Determine the sieving end-point experimentally with minimal intensity, and check for particle damage under a microscope to ensure the method isn't altering the sample.
- If your primary focus is high accuracy for fine or cohesive powders: Default to wet sieving to eliminate errors from agglomeration and static, ensuring the most trustworthy distribution.
By treating sieving as a controlled scientific method rather than a simple mechanical process, you ensure your results are not just numbers, but reliable data you can trust.

Summary Table:
| Factor Category | Key Variables | Impact on Results |
|---|---|---|
| Operational Parameters | Sieving Time, Motion/Intensity, Sample Mass | Directly affects separation efficiency and risk of blinding/attrition |
| Material Properties | Particle Shape, Cohesion, Friability | Influences particle behavior and potential for agglomeration or degradation |
| Equipment & Method | Sieve Condition, Wet vs. Dry Sieving | Determines accuracy, suitability for fine/sticky materials, and compliance |
Need precise particle size analysis for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab sieves, shakers, and consumables designed for accuracy and repeatability. Whether you're handling fine powders, friable materials, or require wet sieving setups, our equipment ensures reliable data for quality control and R&D. Contact us today to discuss your specific application and get a tailored solution. Reach out to our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
People Also Ask
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- What are the factors affecting sieving performance and efficiency? Optimize Your Particle Separation Process
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide



















