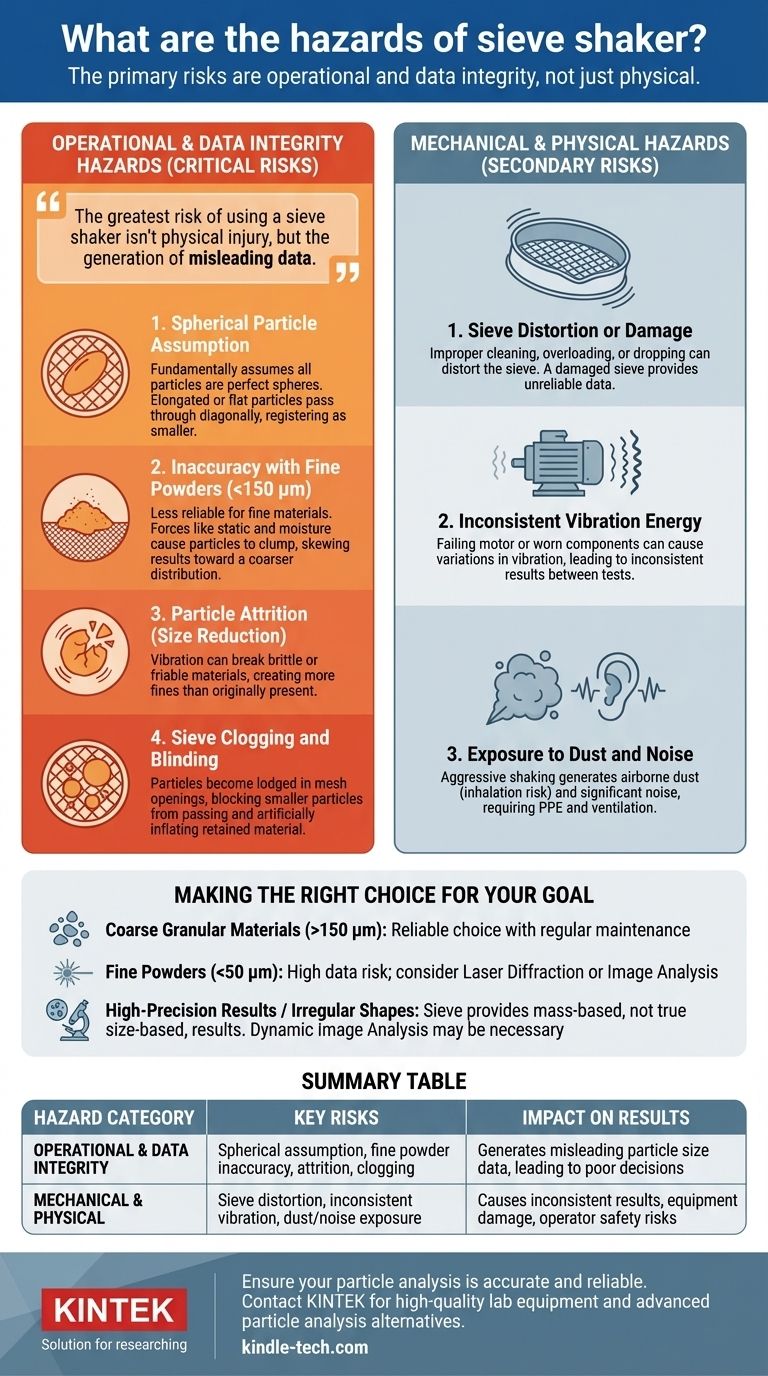
While generally safe with proper handling, the most significant hazards of a sieve shaker are not physical but operational. The primary risks involve the generation of inaccurate data due to inherent methodological flaws, such as the incorrect sizing of non-spherical particles, material degradation during testing, and sieve clogging. These issues can compromise the integrity of your results far more than any mechanical failure.
The greatest risk of using a sieve shaker isn't physical injury, but the generation of misleading data. This occurs when the method's limitations are not understood, leading to poor decisions based on flawed particle size analysis.

The Two Categories of Sieve Shaker Hazards
Sieve shaker hazards can be divided into two distinct groups. The most critical are the operational hazards that affect your data, while the secondary, more manageable risks are mechanical and physical.
Operational & Data Integrity Hazards
This is the most significant category of risk. An unaddressed operational hazard invalidates your results, wasting time and resources and potentially leading to incorrect conclusions in research or production.
Mechanical & Physical Hazards
These risks relate to the machine's physical operation and its interaction with the environment. They are typically managed with standard laboratory safety protocols and proper equipment maintenance.
Understanding the Operational Hazards (Risks to Your Data)
The core purpose of a sieve shaker is to produce accurate particle size data. The following hazards directly threaten that outcome.
The Spherical Particle Assumption
Sieve analysis fundamentally assumes all particles are perfect spheres. In reality, this is almost never true.
Elongated or flat particles can pass through a mesh opening diagonally, meaning they are registered as being smaller than they actually are. This is a foundational, unavoidable limitation of the method.
Inaccuracy with Fine Powders
Sieve shakers become progressively less reliable for materials finer than 100 mesh (approximately 150 µm) and are generally considered unsuitable for particles smaller than 50 µm.
Forces like static electricity and moisture cause fine particles to clump together (agglomerate), preventing them from passing through the sieve mesh and skewing the distribution toward a coarser result.
Particle Attrition (Size Reduction)
The very vibration that drives the separation process can also be a source of error. The constant movement can cause brittle materials to break apart or friable particles to wear down.
This "size reduction" creates more fine particles than were in the original sample, leading to an inaccurate reading that shows the material is finer than it truly is.
Sieve Clogging and Blinding
"Blinding" occurs when particles become lodged in the mesh openings, effectively reducing the open area of the sieve.
This prevents other, smaller particles from passing through, creating a bottleneck that artificially inflates the amount of material retained on the clogged sieve.
Common Pitfalls and Mechanical Failures
While less critical than data integrity risks, mechanical failures can lead to inconsistent results and equipment damage.
Sieve Distortion or Damage
Improper cleaning, overloading the sieve with too much sample, or dropping a sieve can bend the frame or distort the mesh.
A damaged sieve is no longer a calibrated measuring instrument. Its use will produce entirely unreliable data and must be taken out of service immediately.
Inconsistent Vibration Energy
Sieve shakers rely on a consistent, repeatable vibrating motion. A failing motor or worn-out drive components can cause variations in vibrational energy between tests.
This inconsistency means that two tests run on the exact same sample could produce different results, destroying the repeatability that is a key advantage of the method.
Exposure to Dust and Noise
The aggressive shaking motion can generate significant airborne dust, which poses an inhalation risk, especially with hazardous materials.
Sieve shakers also produce considerable noise, requiring hearing protection for operators during prolonged use. Proper ventilation and personal protective equipment (PPE) are essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To mitigate these hazards, you must align your particle analysis method with your material's characteristics and your data quality requirements.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective analysis of coarse, granular materials (>150 µm): A sieve shaker is a reliable and straightforward choice, provided you perform regular maintenance and sieve inspection.
- If your primary focus is analyzing fine powders or materials smaller than 50 µm: The risk of inaccurate data is high; consider alternative methods like laser diffraction or image analysis that are designed for this range.
- If your primary focus is high-precision results for irregularly shaped particles: Recognize that a sieve shaker will always produce a mass-based, not a true size-based, result. More advanced methods like dynamic image analysis may be necessary.
Understanding these limitations is the first step toward generating particle size data you can truly trust.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Category | Key Risks | Impact on Results |
|---|---|---|
| Operational & Data Integrity | Spherical particle assumption, inaccuracy with fine powders (<150 µm), particle attrition, sieve clogging | Generates misleading particle size data, leading to poor decisions |
| Mechanical & Physical | Sieve distortion, inconsistent vibration, dust exposure, noise | Causes inconsistent results, equipment damage, and operator safety risks |
Ensure your particle analysis is accurate and reliable. The right equipment is critical for trustworthy data. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including robust sieve shakers and advanced particle analysis alternatives. Our experts can help you select the perfect solution for your specific materials and precision needs. Contact us today to optimize your laboratory processes and protect your results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- What is the primary purpose of using standard sieves? Master Particle Uniformity for High-Quality Catalyst Preparation
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials
- What are the factors affecting sieving performance and efficiency? Optimize Your Particle Separation Process



















