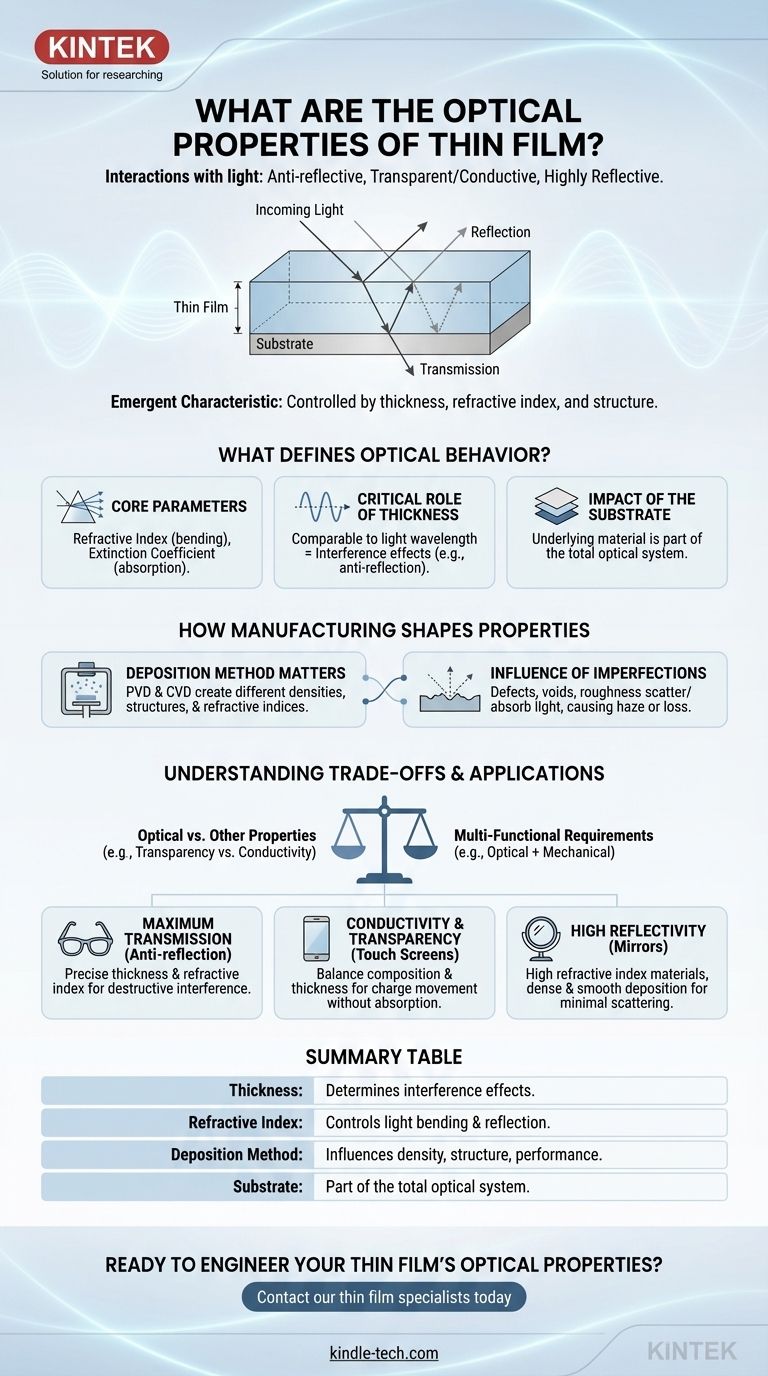
At their core, the optical properties of a thin film describe how it interacts with light, allowing it to be anti-reflective, transparent yet conductive, or highly reflective. These behaviors are not inherent to the film's material alone but are precisely controlled by its thickness, refractive index, and the presence of microscopic structural features.
The crucial takeaway is that a thin film's optical properties are an emergent characteristic, arising from a complex interplay between the chosen material, its thickness (often on the scale of light's wavelength), the underlying substrate, and the specific manufacturing process used to create it.

What Defines a Thin Film's Optical Behavior?
A thin film is a layer of material ranging from a few nanometers to several micrometers thick. When its thickness approaches the wavelength of light, its interaction with that light becomes fundamentally different from that of a bulk material.
Core Optical Parameters
The primary optical properties of any material are defined by two key parameters: refractive index and extinction coefficient. The refractive index determines how much light bends when entering the material, while the extinction coefficient measures how much light is absorbed. In thin films, these values are heavily influenced by the film's density and microstructure.
The Critical Role of Thickness
Thickness is arguably the most important factor in a thin film's optical performance. When a film's thickness is comparable to or less than the wavelength of light, interference effects between light waves reflecting from the top and bottom surfaces become dominant. This is the principle behind anti-reflection coatings on eyeglasses.
The Impact of the Substrate
A thin film is always deposited onto a substrate, and the optical properties of this underlying material are part of the total system. The difference in refractive index between the substrate, the thin film, and the surrounding air dictates how light reflects and transmits at each interface.
How Manufacturing Shapes Optical Properties
The method used to create a thin film has a profound and direct impact on its final optical characteristics. The same material can yield vastly different results depending on how it is deposited.
The Deposition Method Matters
Techniques like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) create films with different densities, crystal structures, and internal stresses. These microscopic variations directly alter the film's refractive index and its ability to absorb light.
The Influence of Imperfections
Real-world thin films are not perfect. Structural defects, voids, localized impurities, and surface roughness all affect optical properties. These imperfections can scatter light, leading to haze, or absorb light, reducing transmission and increasing energy loss. Roughness, in particular, has a strong effect on reflection and transmission coefficients.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Thin films are rarely designed for a single purpose. Optimizing for one property often requires a compromise in another, and understanding these balances is key to successful application.
Balancing Optical and Other Properties
A classic example is a transparent conductive oxide (TCO) used in touch screens. The film must be optically transparent to see the display, but also electrically conductive to register a touch. Increasing conductivity often involves making the film thicker or doping it more heavily, which can reduce its transparency.
Multi-Functional Requirements
Many applications demand films that meet photonic, mechanical, and chemical requirements simultaneously. A coating on a camera lens, for example, must not only be anti-reflective (optical) but also durable and scratch-resistant (mechanical).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" optical properties are entirely dependent on the intended application. By understanding the core principles, you can engineer a film to manipulate light for a specific outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum transmission (e.g., anti-reflection coatings): Your goal is to precisely control the film's thickness and refractive index to cause destructive interference for specific wavelengths of light.
- If your primary focus is conductivity with transparency (e.g., touch screens, solar cells): You must carefully balance material composition and thickness to allow sufficient charge carrier movement without significantly absorbing visible light.
- If your primary focus is high reflectivity (e.g., mirrors): You will choose materials with a high refractive index and deposit them with a process that yields a dense, smooth film to minimize scattering and absorption.
Ultimately, engineering a thin film's optical properties is about controlling matter at the nanoscale to precisely dictate its interaction with light.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Optical Properties |
|---|---|
| Thickness | Determines light interference effects (e.g., anti-reflection). |
| Refractive Index | Controls how much light bends and reflects at interfaces. |
| Deposition Method (PVD/CVD) | Influences film density, structure, and final performance. |
| Substrate | The underlying material is part of the total optical system. |
Ready to Engineer Your Thin Film's Optical Properties?
The precise optical behavior of a thin film—whether for anti-reflection, transparent conductivity, or high reflectivity—is dictated by its material, thickness, and the deposition process. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to achieve exacting optical specifications for your research and production.
Let our expertise help you control light at the nanoscale. Contact our thin film specialists today to discuss your project requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the disadvantages of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Managing the Trade-offs of Low-Temperature Deposition
- What is the speed of PECVD? Achieve High-Speed, Low-Temperature Deposition for Your Lab
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
















