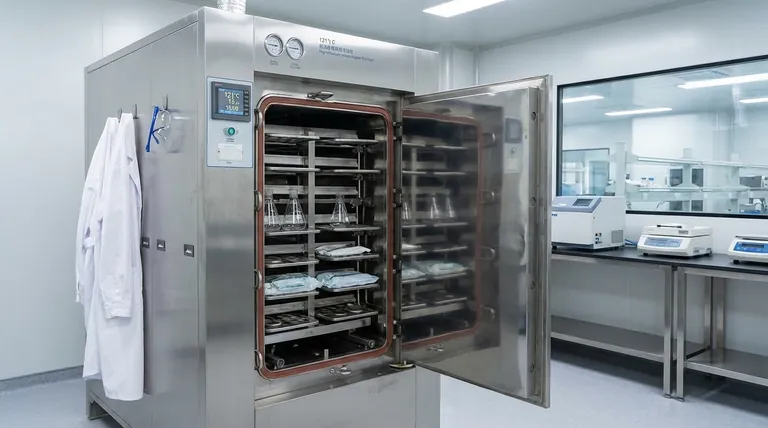
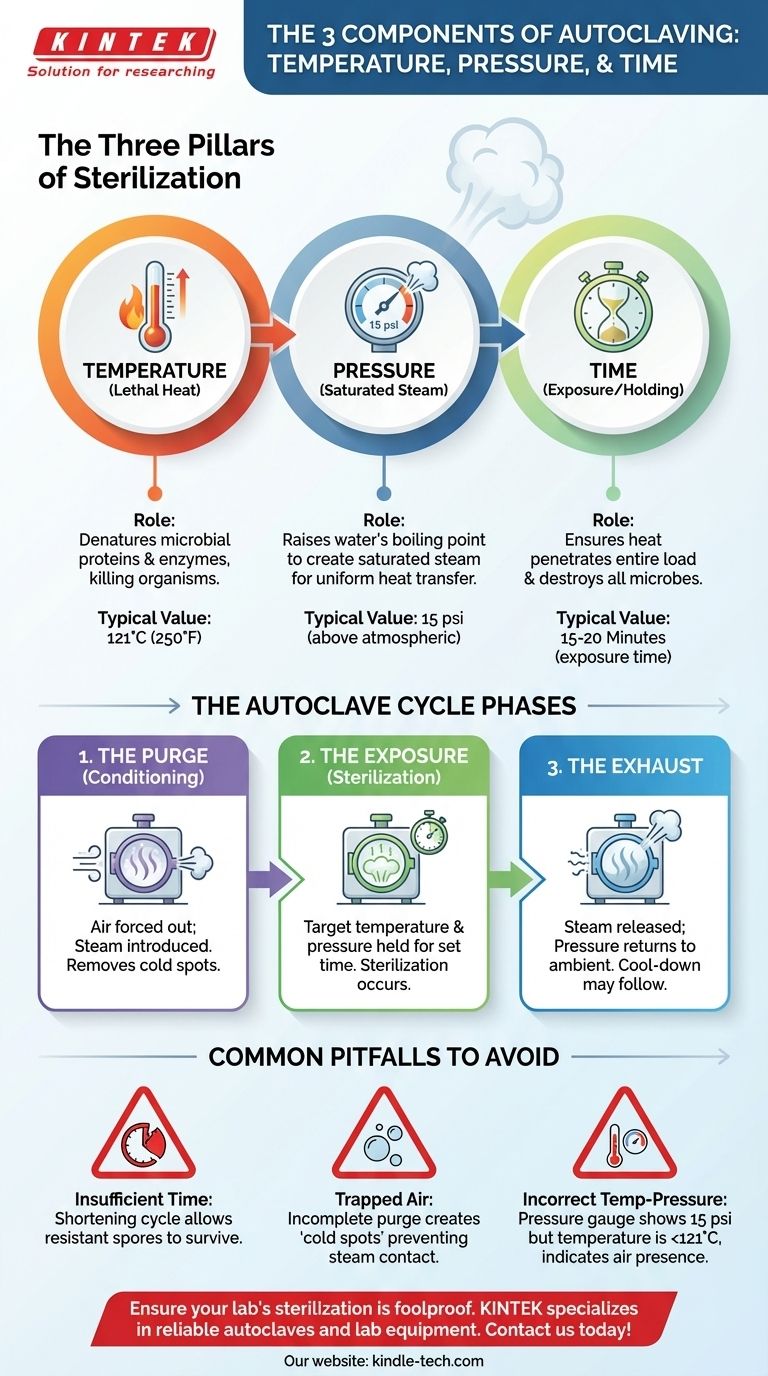
The three critical components of the autoclaving process are temperature, pressure, and time. While an autoclave machine has many physical parts, these three variables are the fundamental parameters that must be controlled to achieve successful sterilization. The entire process relies on using pressurized steam to reach and maintain a specific temperature for a set duration, ensuring the complete destruction of all microorganisms.
The core principle of autoclaving is not just reaching a set temperature, but using pressurized steam to hold that lethal temperature for a sufficient length of time to guarantee sterilization. Each of the three components—temperature, pressure, and time—is indispensable.

The Three Pillars of Sterilization
To understand how an autoclave works, you must understand how these three variables interact. Missing or mismanaging any one of them will result in a failed sterilization cycle.
The Role of Temperature
The primary mechanism of sterilization in an autoclave is lethal heat.
High temperatures, typically 121°C (250°F) or higher, cause the essential proteins and enzymes within microorganisms, including resilient bacterial spores, to coagulate and denature, rendering them non-functional and killing the organism.
The Role of Saturated Steam (Pressure)
Pressure itself does not sterilize, but it is the critical component that allows water to achieve sterilizing temperatures.
At standard atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). By increasing the pressure inside the autoclave chamber (typically to 15 psi above atmospheric pressure), the boiling point of water is raised to 121°C.
This creates saturated steam, which is highly effective at transferring thermal energy to the items being sterilized, ensuring rapid and uniform heat penetration.
The Critical Factor of Time
Simply reaching the target temperature is not enough to ensure sterilization.
The items must be held at the target temperature and pressure for a specific duration, known as the exposure or holding time. This is typically 15-20 minutes for a 121°C cycle.
This holding time is necessary to ensure that the lethal heat has enough time to penetrate the entire load and destroy even the most heat-resistant bacterial spores.
How These Factors Work in a Sterilization Cycle
The interplay between temperature, pressure, and time is best understood by looking at the three phases of a typical autoclave cycle.
Phase 1: The Purge (Conditioning)
Steam is first introduced into the sealed chamber. This incoming steam forces the cooler, ambient air out through an exhaust port.
Removing air is absolutely critical because trapped air creates "cold spots" that prevent steam from making direct contact with surfaces, which would lead to sterilization failure. During this phase, pressure and temperature begin to rise.
Phase 2: The Exposure (Sterilization)
Once all the air is purged, the exhaust port closes. Steam continues to enter the chamber until the pre-set temperature and pressure (e.g., 121°C and 15 psi) are reached.
The cycle timer begins at this point. The system then holds these conditions constant for the entire specified exposure time, allowing lethal heat to destroy all microbes.
Phase 3: The Exhaust
After the exposure time is complete, the exhaust valve opens, releasing the steam and allowing the chamber pressure to return to ambient levels. The contents remain very hot and may require a cool-down period.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding the relationship between the three pillars helps in troubleshooting failed cycles.
Insufficient Time
This is a common error. Even if the correct temperature and pressure are reached, cutting the exposure time short may allow resistant spores to survive. The time required depends on the size and type of the load.
Trapped Air
If the purge phase is incomplete, pockets of air can prevent steam from reaching all surfaces. The autoclave's gauges might read the correct temperature and pressure, but the items will not be sterile due to these insulating cold spots.
Incorrect Temperature-Pressure Correlation
Temperature and pressure are directly linked in a saturated steam environment. If the pressure gauge shows 15 psi but the thermometer reads below 121°C, it often indicates the presence of residual air in the chamber, which means sterilization will fail.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying these principles correctly is the key to ensuring safe, sterile equipment every time.
- If your primary focus is routine lab sterilization: Always follow the validated cycle parameters for your specific materials, ensuring the correct temperature (121°C), pressure (15 psi), and time (15+ minutes) are used.
- If you are troubleshooting a failed cycle: First, check the cycle log to confirm all three parameters—temperature, pressure, and time—were met for the required duration, and then investigate for potential causes of trapped air.
- If you are sterilizing sensitive liquids or large loads: You may need to increase the cycle time to ensure the center of the load reaches the target temperature and is held there for the full exposure period.
Understanding that temperature, pressure, and time are an inseparable trio is the foundation for effective and reliable sterilization.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Sterilization | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Denatures microbial proteins | 121°C (250°F) |
| Pressure | Raises water's boiling point to create saturated steam | 15 psi above atmospheric |
| Time | Allows heat to penetrate and destroy all microbes | 15-20 minutes (exposure time) |
Ensure your lab's sterilization is foolproof. KINTEK specializes in reliable autoclaves and lab equipment designed to precisely control temperature, pressure, and time. Our expertise helps laboratories like yours achieve guaranteed sterility and compliance. Contact us today to find the perfect autoclave solution for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- Why is the prevention of air entrapment critical for the autoclave sterilization process? Ensure 100% Sterility Today
- Why is a 24-hour hydrothermal treatment in an autoclave necessary for BMO nanosheets? Unlock Superior Photocatalysis
- What is the primary purpose of an autoclave in the preparation of media for the biological leaching of uranium?
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization



















