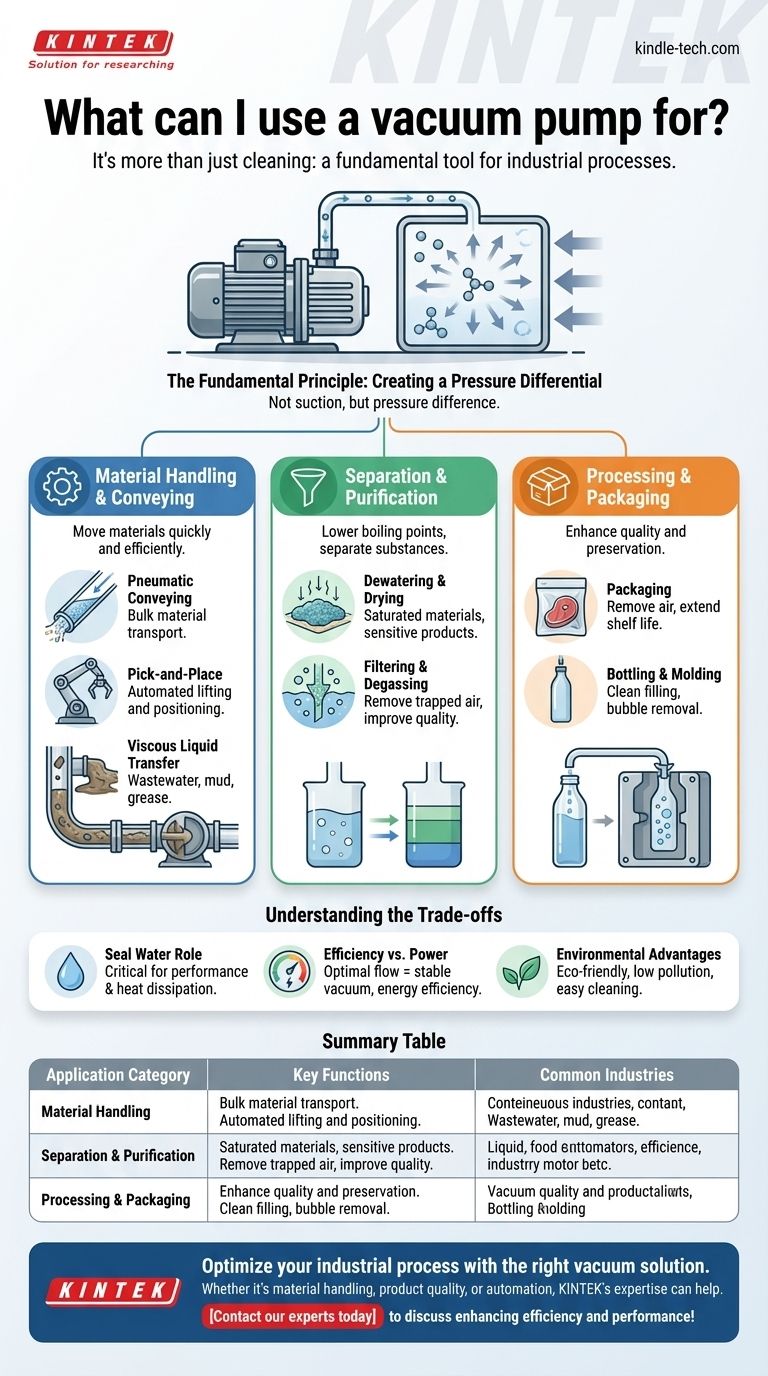
At its core, a vacuum pump is used for far more than just cleaning. This device is a fundamental tool in countless industrial processes, from food packaging and chemical manufacturing to wastewater treatment and automated assembly. Its primary function is to remove gas molecules from a sealed space, creating a pressure differential that can be harnessed to move materials, separate components, or improve product quality.
The crucial insight is that a vacuum pump doesn't "suck" material in. Instead, it creates a low-pressure zone, allowing the higher atmospheric pressure outside to do the actual work of pushing fluids, holding objects, or collapsing packaging.
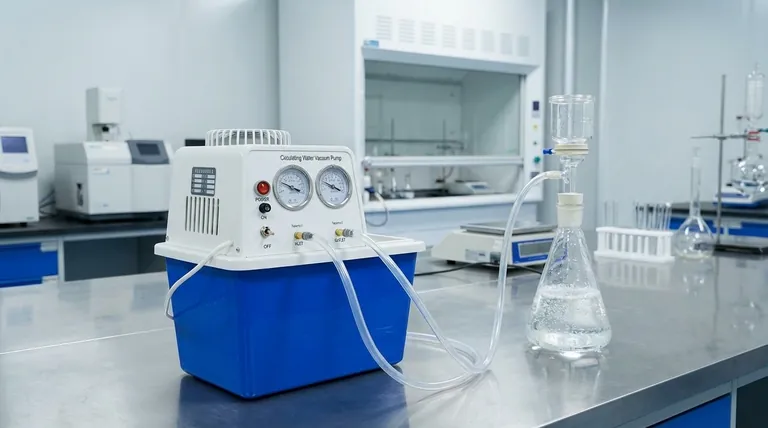

The Fundamental Principle: Creating a Pressure Differential
To understand the vast applications of a vacuum pump, you must first understand its core mechanism. It's not about suction; it's about pressure.
How a Vacuum Pump Works
A vacuum pump is a mechanical or chemical device designed to remove gas molecules—like air—from a sealed container or system.
This action lowers the pressure inside the container relative to the pressure outside of it.
The Result: A Powerful Force
This difference in pressure, known as a pressure differential, is the source of the pump's power. Nature seeks equilibrium, so the higher-pressure air outside the system constantly tries to push its way into the low-pressure zone created by the pump.
This powerful and predictable force can be precisely controlled and applied to perform a wide range of industrial tasks.
Key Industrial Applications
By manipulating pressure, vacuum pumps become essential components for enhancing efficiency, quality, and automation across numerous industries.
Material Handling and Conveying
Vacuum is used to move materials, both solid and liquid, quickly and efficiently.
Applications include pneumatic conveying, where bulk materials are moved through tubes, and pick-and-place operations in manufacturing, where vacuum grippers lift and position items. It is also highly effective for moving viscous liquids like mud, wastewater, and waste trap grease.
Separation and Purification
Creating a vacuum can lower the boiling point of liquids or help separate different substances.
This principle is used for dewatering saturated materials, evaporative drying of sensitive products, and filtering liquids from slurries. It is also critical for degassing liquids to remove trapped air, improving the quality and integrity of the final product.
Processing and Packaging
In food processing and manufacturing, vacuum pumps are essential for quality and preservation.
They are used for packaging to remove air and seal products, extending shelf life. They also play a role in bottling by ensuring clean and efficient filling, and in various molding processes where vacuum removes air bubbles from materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, the effective use of a vacuum pump requires understanding its operational needs and limitations, particularly in systems that use a liquid sealant.
The Critical Role of Seal Water
Many industrial vacuum pumps use a flow of seal water to create the vacuum and dissipate heat. The amount of this water is critical for stable performance.
Efficiency vs. Power Consumption
Using too little seal water will cause the vacuum level to fluctuate, reducing performance. Using too much water, however, provides no additional vacuum and simply wastes energy and resources.
The optimal flow is the minimum amount required to achieve a stable, maximum vacuum level.
Environmental Advantages
Despite the need for seal water in some designs, vacuum pumps are often considered environmentally friendly. They do not typically cause air pollution and are known for their ease of use and cleaning.
Matching the Pump to Your Goal
The right application depends entirely on the problem you need to solve. By understanding the core principle of pressure differential, you can determine how a vacuum pump can serve your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is moving heavy or viscous materials: Use a vacuum pump to create the pressure needed to efficiently transfer slurries, mud, or waste without direct mechanical contact.
- If your primary focus is improving product quality: Apply a vacuum for degassing to remove imperfections, for evaporative drying to protect sensitive goods, or for packaging to extend shelf life.
- If your primary focus is automation and assembly: Leverage vacuum for pick-and-place systems, allowing robots to reliably grip, lift, and move components on an assembly line.
Ultimately, a vacuum pump is a tool for harnessing atmospheric pressure to achieve a specific industrial goal with precision and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Functions | Common Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Material Handling | Pneumatic conveying, pick-and-place automation, moving viscous liquids | Manufacturing, Wastewater, Food Processing |
| Separation & Purification | Degassing, dewatering, evaporative drying, filtering | Chemical, Pharmaceutical, Environmental |
| Processing & Packaging | Removing air for packaging, bottling, molding processes | Food & Beverage, Plastics, Consumer Goods |
Optimize your industrial process with the right vacuum solution. Whether your goal is efficient material handling, superior product quality, or advanced automation, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and industrial consumables can help you select the perfect vacuum pump for your specific needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Variable Speed Peristaltic Pump
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the use of a vacuum evaporator? Transform Waste into Value and Achieve ZLD
- What core role do high-precision vacuum pumps play in PCL-TPE polycondensation? Master Molecular Growth Control
- Why are Viton O-rings utilized for sealing in carbochlorination experimental setups? Ensure Safety and Seal Integrity
- What are the temperature and pressure limitations for using the sample holder? Essential Guide for Lab Safety
- What functions do high-temperature stainless steel fixtures perform in TLP bonding? Ensure Joint Integrity
- How does graphite paper function as a consumable in hot pressing? Essential Tooling Protection for EHEA Composites
- How do thermocouples and their controllers ensure the scientific accuracy of a wet oxidation reaction process?
- What roles do graphite foil and boron nitride plates play in LLZO ultra-fast sintering? Optimize Solid-State Electrolytes



















