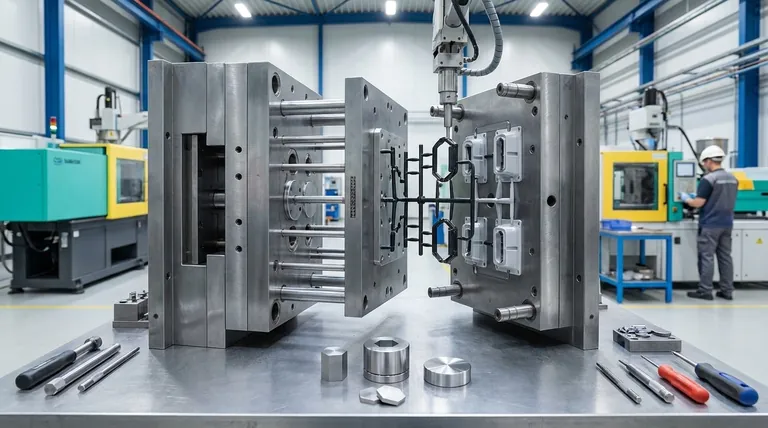
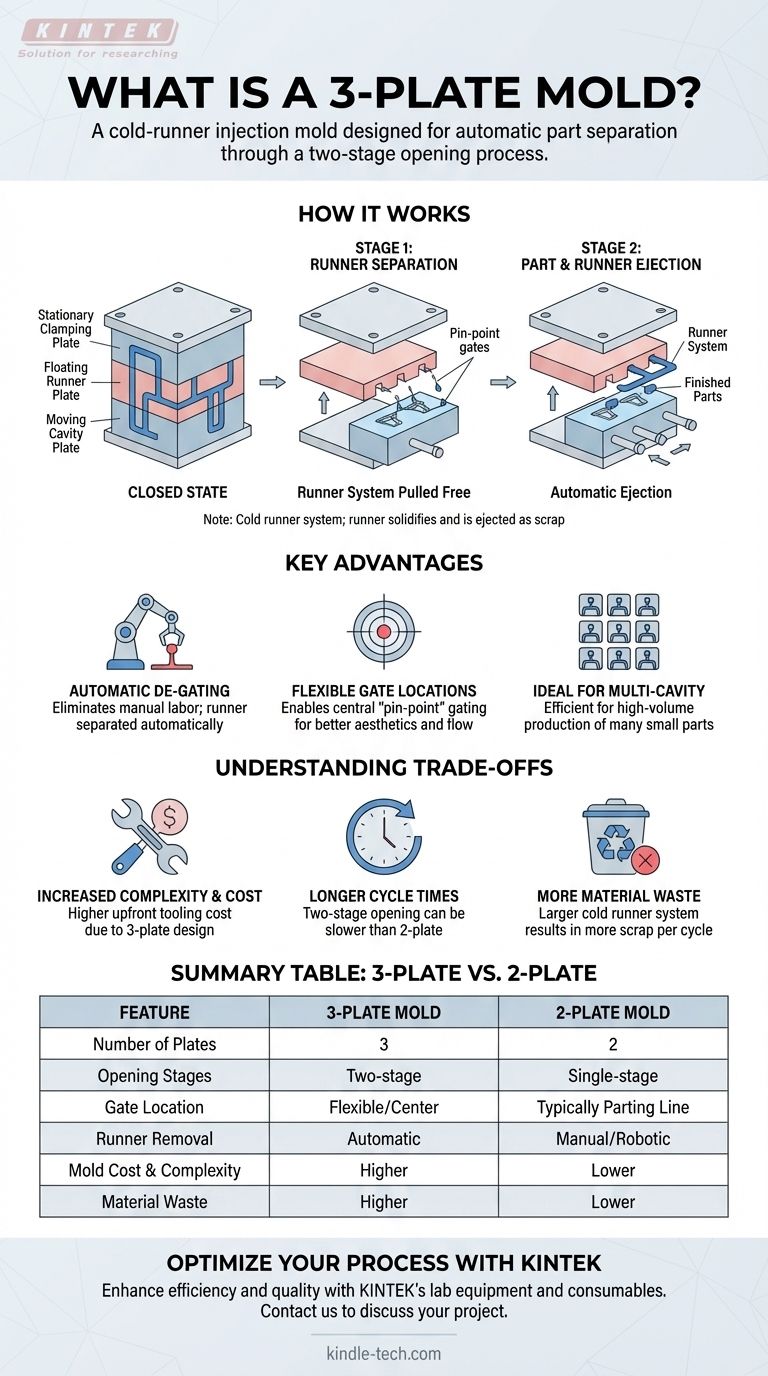
In essence, a 3-plate mold is a type of cold-runner injection mold designed to automatically separate the plastic part from its runner system during the ejection process. It achieves this by using three main plates that open in two distinct stages, allowing the runner to be removed in one gap and the finished part in another.
The critical takeaway is that a 3-plate mold introduces mechanical complexity for a specific purpose: to enable flexible gate locations and automate the removal of the runner, which eliminates a manual post-processing step. This is a deliberate trade-off between higher tool cost and lower operational labor.

How a 3-Plate Mold Works
The name "3-plate" directly refers to its core construction, which dictates its unique opening sequence. Understanding this mechanical action is key to grasping its purpose.
The Core Components
A 3-plate mold is constructed from a stack of plates: a stationary clamping plate, a floating runner plate, and the moving cavity plate. The runner system, which channels the molten plastic, is machined across two of these plates, existing on two separate planes.
The Two-Stage Opening Sequence
When the molding cycle is complete, the mold doesn't just open once.
- First, a gap opens between the stationary plate and the floating runner plate. This action pulls the small, solidified "pin-point" gates away from the part, effectively cutting the runner free.
- Second, another gap opens between the floating runner plate and the moving cavity plate. This allows the now-separated runner system to be ejected, followed by the ejection of the finished parts from the cavity.
The Role of the Cold Runner
It is important to remember that this is a cold runner system. The plastic in the runner channels solidifies with the part in every cycle. This solidified runner is then ejected as scrap material, which can be reground and reused in some cases.
The Key Advantage: Automatic De-gating
The entire purpose of the complex two-stage opening is to achieve automatic de-gating. This provides several significant process and design advantages over a simpler 2-plate mold.
Eliminating Manual Labor
The primary benefit is the elimination of a secondary operation. With a 2-plate mold, an operator (or a robot) must manually trim the runner from each part. The 3-plate mold performs this task automatically within the mold, saving significant time and labor costs.
Enabling Flexible Gate Locations
This design uniquely allows for pin-point gating directly onto the top cosmetic surface of a part. This is ideal for filling round or conical parts evenly from the center, minimizing cosmetic gate blemishes and improving the part's structural integrity. A standard 2-plate mold can typically only gate along the part's outer edge (the parting line).
Ideal for Multi-Cavity Molds
When producing many small parts in a single shot, the ability to automatically separate each part from the complex runner system is highly efficient. It streamlines the manufacturing process for high-volume production runs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The benefits of a 3-plate mold do not come for free. The design introduces specific complexities and costs that must be considered.
Increased Mold Complexity and Cost
The addition of a third plate and the mechanisms required for the two-stage opening sequence make the mold more complex to design, machine, and maintain. This results in a significantly higher upfront tooling cost compared to a 2-plate mold.
Potentially Longer Cycle Times
The two separate opening and closing motions take more time than the single motion of a 2-plate mold. This can lead to a longer overall cycle time, which may impact part output on very high-volume projects.
More Material Waste
The runner system in a 3-plate mold is often larger and more complex than in a 2-plate mold. Since this is a cold runner that is ejected as scrap in every cycle, it results in more wasted material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right mold type requires balancing design requirements, production volume, and budget.
- If your primary focus is design flexibility and cosmetic finish: The 3-plate mold is an excellent choice when you need a central gate on a part surface for optimal flow and appearance.
- If your primary focus is reducing labor in high-volume production: The automatic de-gating feature makes the 3-plate mold highly effective for multi-cavity tools where manual trimming would be a bottleneck.
- If your primary focus is minimizing tool cost and material waste: A simpler 2-plate mold is almost always the more economical and efficient choice.
Ultimately, choosing a 3-plate mold is an informed engineering decision that prioritizes automation and design freedom over initial tool cost and cycle speed.
Summary Table:
| Feature | 3-Plate Mold | 2-Plate Mold |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Plates | 3 | 2 |
| Opening Stages | Two-stage | Single-stage |
| Gate Location | Flexible (e.g., center of part) | Typically parting line only |
| Runner Removal | Automatic (de-gating) | Manual or robotic trimming |
| Mold Cost & Complexity | Higher | Lower |
| Material Waste | Higher (larger runner) | Lower |
Optimize Your Injection Molding Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right mold design is critical for the efficiency and quality of your production. Whether you need the automated de-gating and design flexibility of a 3-plate mold or the cost-effectiveness of a 2-plate solution, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables can help you achieve your goals.
We provide the equipment and support to enhance your laboratory's capabilities and streamline your manufacturing workflow. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific project needs and bring value to your operation.
Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Ball Press Mold for Lab
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Cylindrical Press Mold with Scale for Lab
- Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- What are the primary functions of graphite molds in NiCr powder metallurgy? Optimize Your Composite Material Density
- Why are custom pressure molds used during the hot pressing process for solid polymer electrolytes?
- What is the physical role of graphite molds in vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Cu-Al2O3 Composite Densification
- Is it fitting the mould or mold? A Guide to Correct Spelling by Region

















