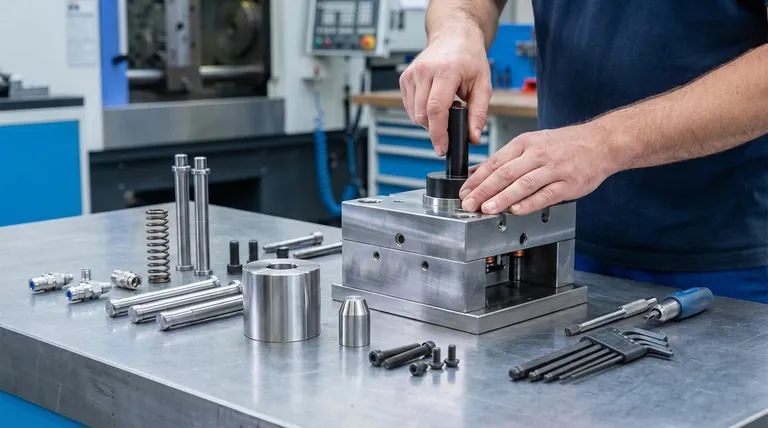
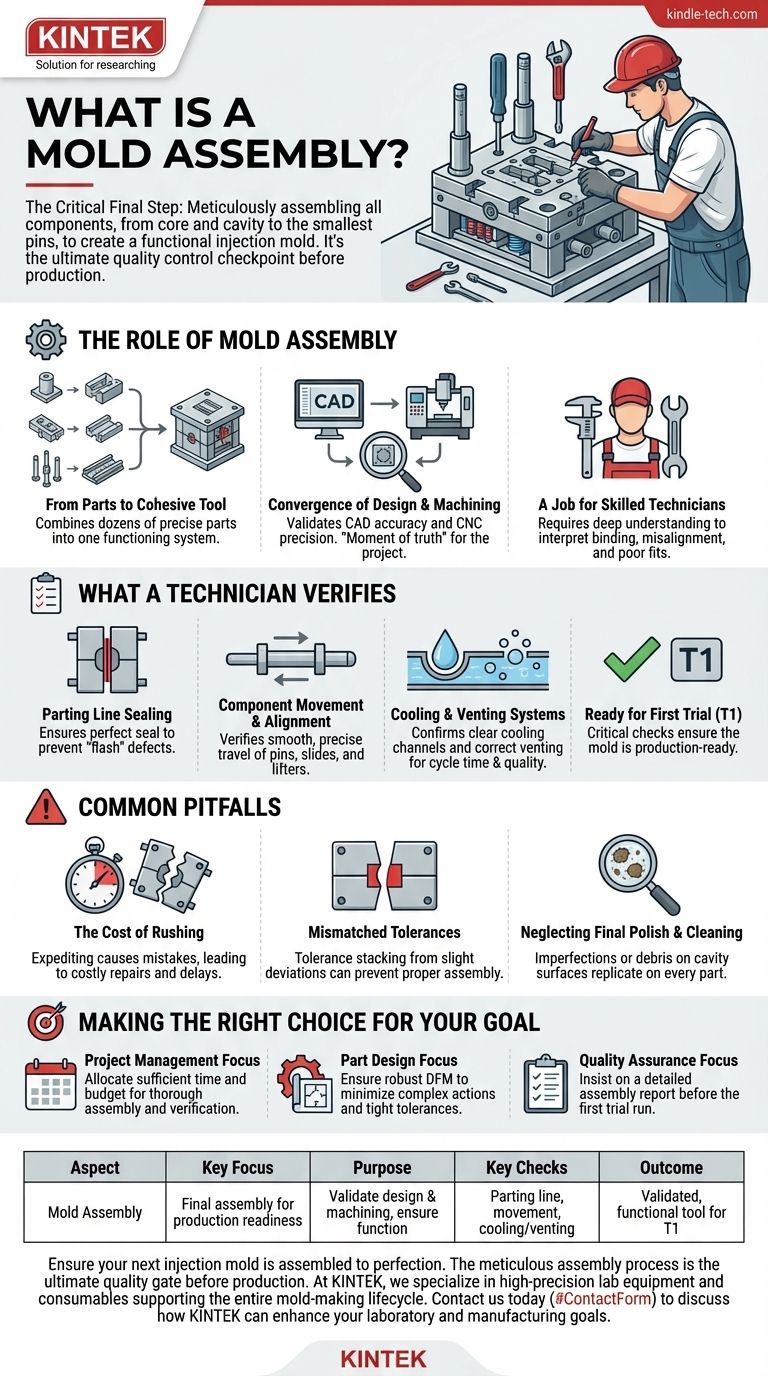
In short, a mold assembly is the critical final step in the mold-making process. During this stage, all the individually machined or purchased components—from the core and cavity halves to the smallest pins and screws—are meticulously put together to create the complete, functional injection mold. It is the moment where theory and individual parts converge into a working tool.
Mold assembly is far more than simple mechanical construction. It is the ultimate quality control checkpoint that validates every preceding design and machining decision, ensuring the tool will function correctly before it is ever used in a production environment.

The Role of Mold Assembly in Manufacturing
Mold assembly is the bridge between the precision machining of individual components and the mass production of finished plastic parts. It is where the digital design becomes a physical, functional asset.
From Individual Parts to a Cohesive Tool
An injection mold is not a single block of steel. It is a complex machine composed of dozens, sometimes hundreds, of highly precise parts: the core and cavity, ejector pins, cooling channels, slides, lifters, and the mold base. The assembly process is the first time these separate elements are brought together to work as a single, cohesive system.
The Convergence of Design and Machining
This stage serves as the moment of truth for the entire tool-making project. It physically validates the accuracy of the CAD design and the precision of the CNC machining. If there are any errors in tolerance, dimension, or design, they will become apparent during assembly.
A Job for Skilled Technicians
Assembling a mold is not a routine task. It requires technicians with a comprehensive understanding of both mold structures and the injection molding process itself. They must be able to interpret subtle signs of binding, misalignment, or poor fits that could lead to catastrophic failure during production.
What a Technician Verifies During Assembly
A meticulous assembly process involves far more than just tightening bolts. Technicians perform a series of critical checks to ensure the mold is ready for its first trial run (T1).
Parting Line Sealing
The technician ensures that the two halves of the mold (the core and cavity) meet perfectly along the parting line. Any gap, however small, can allow molten plastic to escape, creating a defect known as flash on the finished parts.
Component Movement and Alignment
All moving components, such as ejector pins, slides, and lifters, must travel smoothly and precisely within their intended range. Any binding or misalignment can cause severe damage to the mold once it is under the immense pressure of an injection molding machine.
Cooling and Venting Systems
The technician verifies that all cooling channels are clear and properly connected to allow for efficient temperature control, which is critical for cycle time and part quality. They also confirm that tiny vents have been correctly machined to allow trapped air to escape the cavity as it fills with plastic.
Understanding the Common Pitfalls
The pressure to get a mold into production can lead to mistakes during assembly. Understanding these risks is key to preventing costly delays and tool damage.
The Cost of Rushing
Expediting the assembly process is a false economy. A missed check or a misaligned component can cause the mold to damage itself during the first trial. Repairing a complex, multi-ton steel tool is exponentially more expensive and time-consuming than getting the assembly right the first time.
Mismatched Tolerances
Even with advanced CNC machining, slight deviations can occur. The assembly process is the final defense against tolerance stacking, where the accumulation of small, acceptable deviations in individual parts results in a final assembly that doesn't fit together correctly.
Neglecting Final Polish and Cleaning
The final surface finish of the mold cavity dictates the finish of every part it produces. During assembly, technicians must ensure the cavity surfaces are flawlessly polished and absolutely free of any oil, dust, or debris. Any imperfection will be replicated on every single product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
A well-executed assembly is not an expense; it is an investment in the quality and reliability of your entire production run.
- If your primary focus is project management: Allocate sufficient time and budget for a thorough assembly and verification process; it is not a step to be expedited.
- If your primary focus is part design: Ensure your design for manufacturability (DFM) analysis is robust to minimize complex actions or tight tolerances that complicate assembly.
- If your primary focus is quality assurance: Insist on a detailed assembly report from your mold maker, including checks for alignment, movement, and sealing before the first trial run.
Ultimately, a precise and professional mold assembly is the foundation for high-quality, high-volume manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Focus |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Final assembly of all mold components for production readiness. |
| Key Checks | Parting line sealing, component movement, cooling/venting systems. |
| Outcome | A validated, functional tool ready for the first trial run (T1). |
Ensure your next injection mold is assembled to perfection. The meticulous assembly process is the ultimate quality gate before production. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-precision lab equipment and consumables that support the entire mold-making and manufacturing lifecycle. From design validation to final quality checks, our tools help you achieve flawless results. Contact us today (#ContactForm) to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and support your manufacturing goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Button Battery Tablet Press Sealing Mold for Lab Use
- Assemble Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
- High Shear Homogenizer for Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
People Also Ask
- What are the specific functions of a nylon die during battery mold assembly? Ensure Accurate Solid-State Battery Testing
- What is the function of two plate Mould? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Injection Molding
- What is a pellet die? A Guide to Creating Uniform Solid Samples from Powder
- What is the difference between two-plate and three-plate injection molds? Choose the Right Tool for Your Plastic Part
- What is the purpose of using high-precision battery testing systems and electrochemical workstations? | Unlock Battery Insights







