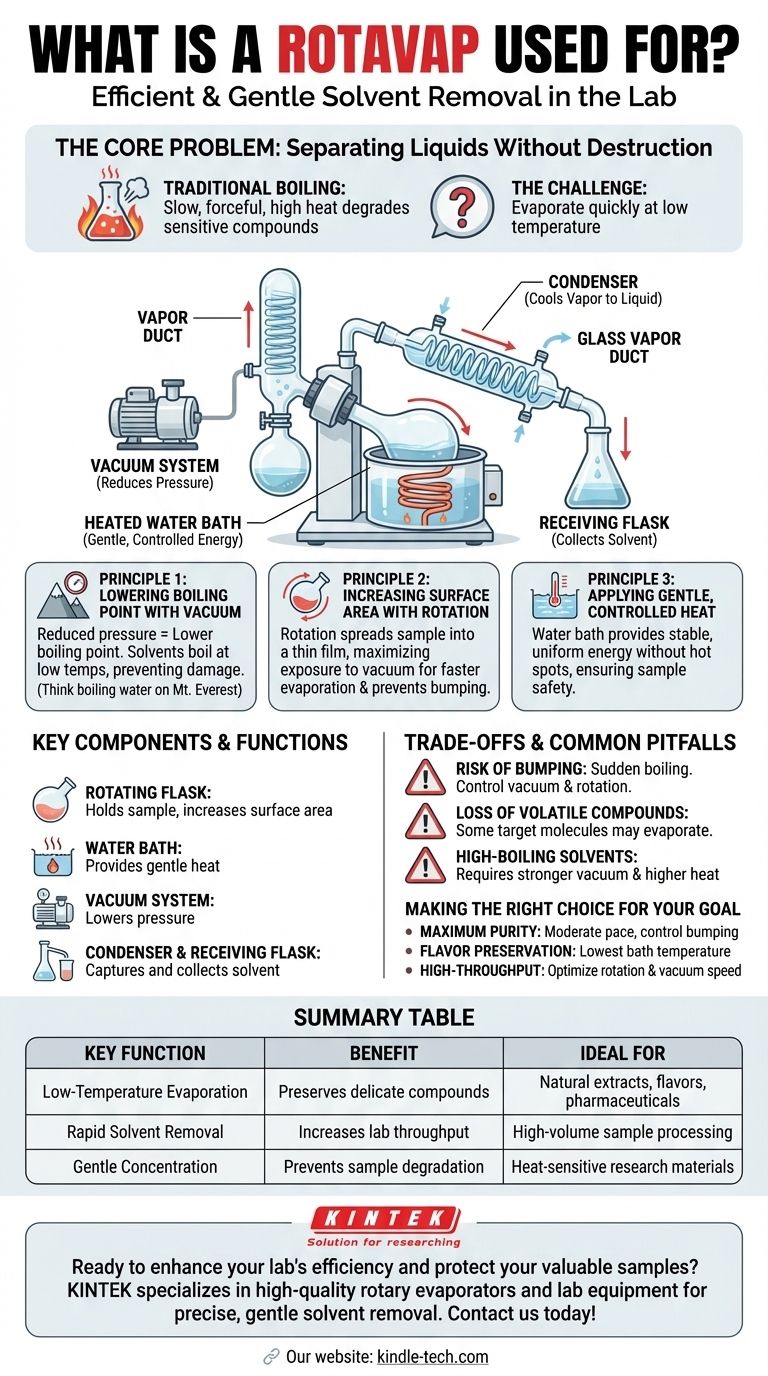
At its core, a rotary evaporator, or "rotavap," is a laboratory device designed for the efficient and gentle removal of solvents from a sample by evaporation. It achieves this by reducing the overall pressure to lower the solvent's boiling point while simultaneously rotating the sample to increase its surface area, dramatically speeding up the process without requiring high, potentially damaging temperatures.
A rotavap isn't just a tool for boiling off a liquid. It is a precision instrument for separating a volatile solvent from a non-volatile or less-volatile solute, solving the fundamental challenge of how to do so quickly without destroying the compound you want to keep.
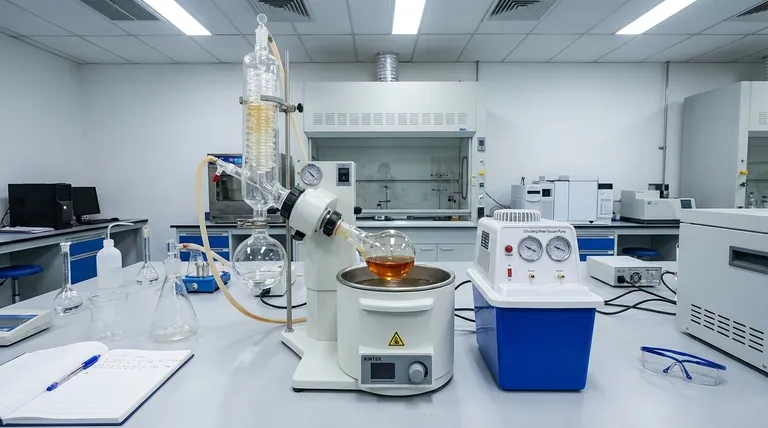

The Core Problem: Separating Liquids Without Destruction
To understand the value of a rotavap, you must first appreciate the limitations of traditional methods for removing a solvent.
The Limits of Simple Boiling
The most basic way to remove a solvent like ethanol from a solution is to boil it. However, this method is slow and forceful.
Applying direct heat high enough to boil a solvent at atmospheric pressure (e.g., 78°C for ethanol) can easily "cook" or degrade heat-sensitive compounds, such as delicate flavor molecules, natural plant extracts, or complex synthetic chemicals.
The Need for a Gentler Method
The challenge, therefore, is to get the solvent to evaporate quickly but at a much lower temperature. This is precisely the problem the rotavap was engineered to solve. It manipulates the physical environment to make evaporation favorable without resorting to brute-force heat.
How a Rotary Evaporator Solves the Problem
A rotavap employs a three-pronged strategy to achieve fast, low-temperature evaporation. These principles work in concert to make the process highly efficient.
Principle 1: Lowering the Boiling Point with a Vacuum
The single most important principle is the relationship between pressure and boiling point. By attaching a vacuum pump, the rotavap reduces the pressure inside the system.
Think of boiling water: at sea level, it boils at 100°C (212°F). On top of Mount Everest, where the atmospheric pressure is much lower, water boils at only 71°C (160°F). A rotavap creates a "mountaintop in a bottle," lowering the pressure so significantly that solvents can boil at room temperature or with very mild heat.
Principle 2: Increasing Surface Area with Rotation
Evaporation only happens at the surface of a liquid. A stationary flask of liquid has a very small surface area relative to its total volume.
The rotation of the flask spreads the sample into a thin, continuously refreshed film on the interior wall. This dramatically increases the surface area exposed to the vacuum, leading to a much faster rate of evaporation. This rotation also provides gentle mixing, ensuring even heating and preventing violent boiling, known as bumping.
Principle 3: Applying Gentle, Controlled Heat
While the vacuum does most of the work, evaporation still requires energy (the latent heat of vaporization). The rotavap provides this energy in a highly controlled way.
The rotating flask is partially submerged in a heated water bath, which provides a stable, gentle, and uniform energy source. This prevents hot spots and ensures the sample is never exposed to a temperature higher than that of the bath itself.
A Look at the Key Components
Understanding the function of each part clarifies the entire process.
- The Rotating Flask and Drive: This holds your initial sample (solute + solvent). The motor rotates the flask, creating the thin film necessary for efficient evaporation.
- The Water Bath: This provides the gentle, controlled heat needed to fuel the evaporation process at the reduced pressure.
- The Vacuum System: A pump removes air from the glassware, lowering the internal pressure and thus the solvent's boiling point. A manometer is used to monitor and control this pressure.
- The Condenser and Receiving Flask: As the solvent evaporates into a gas, it travels into a chilled glass coil (the condenser). Here, it cools and turns back into a liquid, dripping down into a separate receiving flask for collection or disposal. This step ensures the solvent is captured and not released into the atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
While powerful, a rotavap is not without its challenges. Understanding them is key to successful operation.
Risk of Bumping and Foaming
If the vacuum is applied too quickly or the sample has a tendency to foam, it can violently boil and shoot up out of the rotating flask into the condenser. This contaminates the system and results in sample loss. The solution is to lower the pressure gradually and control the rotation speed.
Potential Loss of Volatile Compounds
The rotavap excels at separating non-volatile solutes (like salts or large molecules) from volatile solvents. However, if your target compound is also somewhat volatile, a portion of it may evaporate along with the solvent, reducing your final yield.
Limitations with High-Boiling Point Solvents
The device is most effective for solvents with low to moderate boiling points (e.g., acetone, hexane, ethanol). Removing high-boiling point solvents like water or DMSO requires a much stronger vacuum and higher bath temperatures, pushing the limits of standard lab equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational strategy should be dictated by your end goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity: Operate at a moderate pace, carefully controlling the vacuum to prevent any bumping that could contaminate your final, purified compound.
- If your primary focus is delicate flavor preservation: Use the lowest possible water bath temperature, even if it means running the process for longer. The goal is to remove the solvent without altering the fragile aromatic molecules.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production: Use the largest appropriate flask size and optimize the rotation speed and vacuum level to find the fastest rate of evaporation that does not cause bumping or foaming.
By understanding these principles, you move from simply operating a machine to truly mastering the art of separation.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Temperature Evaporation | Preserves delicate compounds | Natural extracts, flavors, pharmaceuticals |
| Rapid Solvent Removal | Increases lab throughput | High-volume sample processing |
| Gentle Concentration | Prevents sample degradation | Heat-sensitive research materials |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency and protect your valuable samples? KINTEK specializes in high-quality rotary evaporators and lab equipment designed for precise, gentle solvent removal. Whether you're concentrating delicate natural extracts or scaling up production, our solutions ensure optimal performance and sample integrity. Contact us today to find the perfect rotavap for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a water circulating vacuum pump? Superior Durability for Demanding Lab Environments
- What is the importance of a vacuum pump for Schottky hybrid interfaces? Achieve Atomic-Level Purity and Bonding
- What types of gases can a water circulating vacuum pump handle? Safely Manage Flammable, Condensable & Dirty Gases
- What determines the vacuum degree achievable by a water circulating vacuum pump? Unlock the Physics of Its Limits
- What can I use a vacuum pump for? Powering Industrial Processes from Packaging to Automation



















