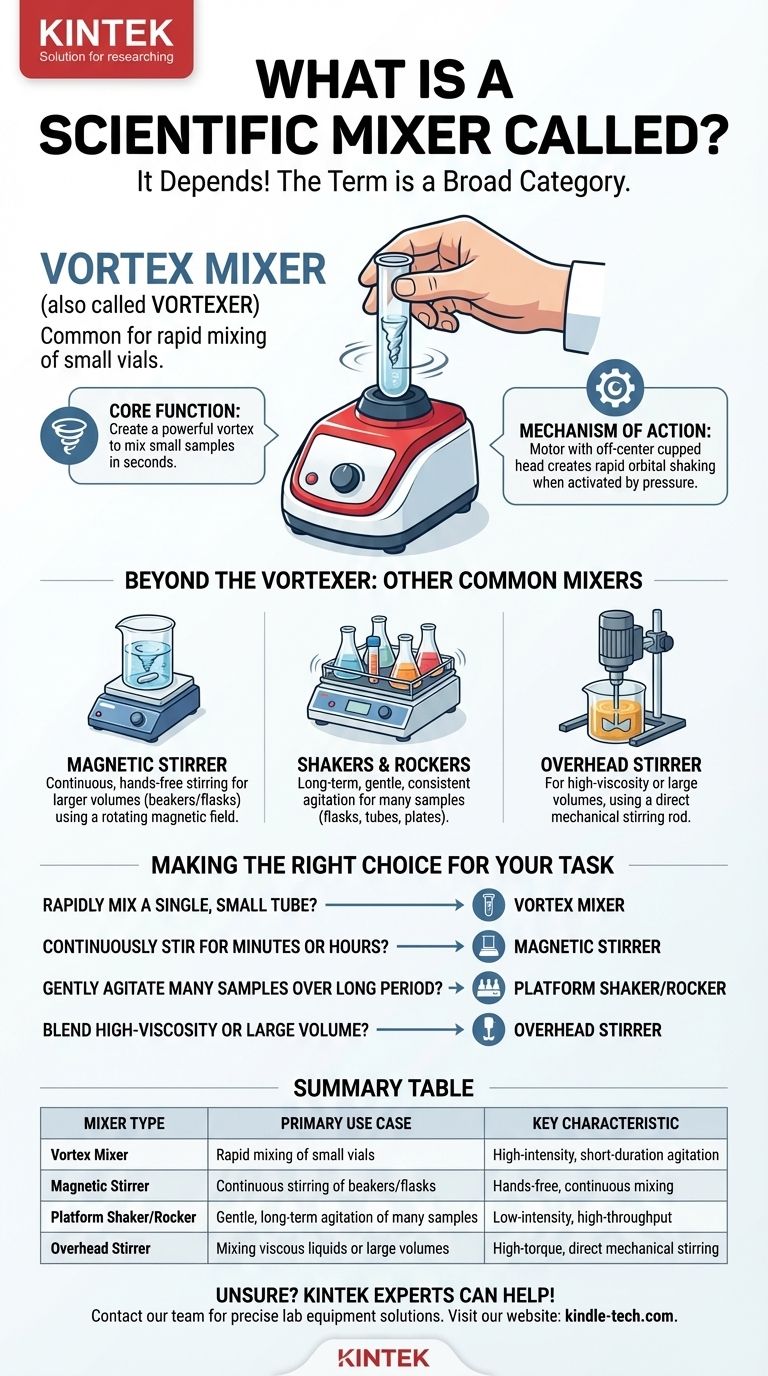
While there are many types of scientific mixers, a very common device used in laboratories for mixing small vials of liquid is called a vortex mixer, or simply a vortexer. It's designed for the rapid and energetic mixing of samples contained in test tubes or similar small vessels.
The term "scientific mixer" is a broad category, not a single device. The specific name, such as vortex mixer, magnetic stirrer, or shaker, depends entirely on the mechanism it uses and the task it is designed to perform.

What is a Vortex Mixer?
A vortex mixer is a foundational piece of equipment in almost any biology or chemistry lab. Its purpose is singular and effective: to create a powerful vortex within a small liquid sample, ensuring it becomes thoroughly mixed in seconds.
The Core Function
The primary job of a vortexer is to agitate small vials of liquid. This is essential for tasks like resuspending pellets of cells, dissolving reagents into a solvent, or ensuring a reaction mixture is uniform before an experiment.
The Mechanism of Action
The device is quite simple. It contains an electric motor connected to a drive shaft. At the top of this shaft is a small, cupped rubber piece that is mounted slightly off-center.
When an operator presses a test tube onto the rubber cup, it activates the motor. The off-center rotation creates a rapid, orbital shaking motion that is transferred to the liquid, forming a strong vortex and mixing the contents.
Beyond the Vortexer: Other Common Mixers
The vortexer is ideal for small, quick tasks, but different scientific applications require different mixing technologies.
Magnetic Stirrers
For larger volumes of liquid in a beaker or flask, a magnetic stirrer is used. This device uses a rotating magnetic field to spin a coated magnet (a "stir bar") placed inside the liquid, providing continuous and hands-free stirring.
Shakers and Rockers
When samples require long-term, gentle, but consistent agitation, a platform shaker or rocker is the tool of choice. These devices move an entire platform—holding flasks, tubes, or plates—in a specific orbital or seesaw motion to keep solutions in constant, gentle suspension.
Overhead Stirrers
For very viscous (thick) liquids or much larger volumes that a magnetic stir bar cannot handle, an overhead stirrer is necessary. It works like a high-tech kitchen mixer, using a motor to drive a stirring rod with paddles directly into the substance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong mixer can ruin an experiment. The key differences lie in the volume of the sample and the type of agitation required.
Intensity vs. Gentleness
A vortex mixer provides extremely high-intensity, vigorous mixing for a few seconds. In contrast, a rocker provides very low-intensity, gentle agitation that can be sustained for hours without damaging sensitive samples like living cells.
Sample Volume and Throughput
A vortexer handles one tube at a time. A magnetic stirrer is for a single, larger container. A platform shaker, however, can agitate dozens or even hundreds of tubes or plates simultaneously, making it ideal for high-throughput work.
Viscosity and Consistency
A magnetic stir bar will be ineffective in thick or semi-solid substances. An overhead stirrer is the only option that has the mechanical power to mix high-viscosity materials like gels, creams, or polymer solutions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Task
Your specific goal determines the correct tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is to rapidly mix a single, small tube of liquid: A vortex mixer is the correct and most efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is to continuously stir a solution in a beaker for minutes or hours: A magnetic stirrer and stir bar are what you need.
- If your primary focus is to gently agitate many samples at once over a long period: You should use a platform shaker or rocker.
- If your primary focus is to blend a high-viscosity or very large volume solution: An overhead stirrer is the only suitable option.
Ultimately, selecting the right scientific mixer is about matching the device's specific action to your experimental needs.
Summary Table:
| Mixer Type | Primary Use Case | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Vortex Mixer | Rapid mixing of small vials | High-intensity, short-duration agitation |
| Magnetic Stirrer | Continuous stirring of beakers/flasks | Hands-free, continuous mixing |
| Platform Shaker/Rocker | Gentle, long-term agitation of many samples | Low-intensity, high-throughput |
| Overhead Stirrer | Mixing viscous liquids or large volumes | High-torque, direct mechanical stirring |
Unsure which scientific mixer is right for your application? The experts at KINTEK can help! We specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables your laboratory needs. Whether you require a vortex mixer for quick sample prep or an overhead stirrer for high-viscosity materials, we have the solution to ensure your experiments are a success. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and enhance your lab's efficiency and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Grinding Mill Single Tank Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- Why is a rotary mechanical homogenizer used for extended periods for forsterite-spinel? Achieve Peak Ceramic Uniformity
- How does a constant temperature rotary shaker contribute to evaluating iron nanoparticles? Optimize Dye Degradation
- What is a laboratory mixer? A Guide to Achieving Perfect Sample Homogeneity
- What is the difference between mixer and disperser? Choose the Right Tool for Your Process
- What are laboratory mixers used for? Achieve Perfect Sample Homogeneity and Reliable Results



















