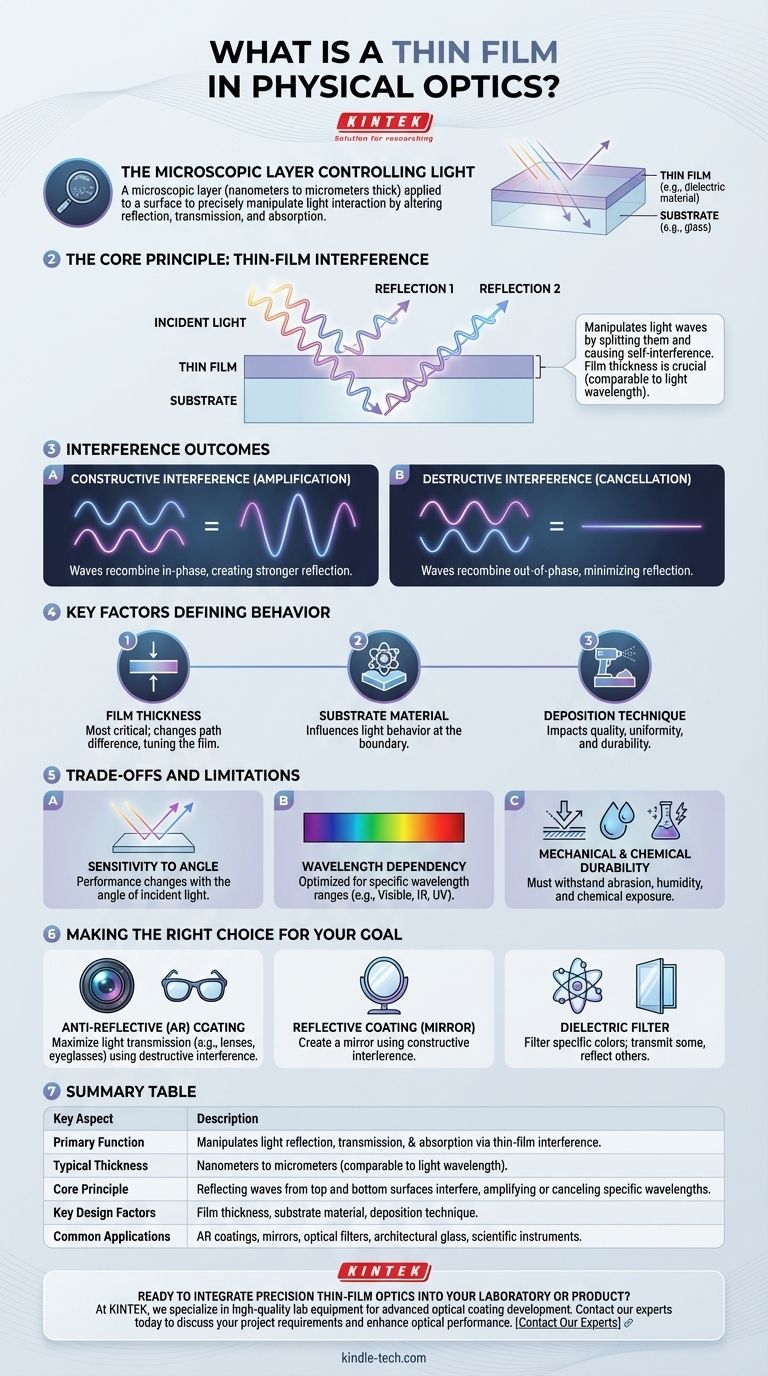
In the field of physical optics, a thin film is a microscopic layer of material, often just nanometers to micrometers thick, that is intentionally applied to a surface to precisely control how it interacts with light. These films work by altering the reflection, transmission, and absorption qualities of the underlying surface, known as the substrate.
The essential purpose of a thin film is to manipulate light waves through a phenomenon called thin-film interference. The film's carefully controlled thickness, which is often comparable to the wavelength of light itself, is the key variable that dictates its optical behavior.

The Core Principle: Manipulating Light Waves
To understand thin films, you must first understand that light behaves as a wave. A thin film's power comes from its ability to split a light wave and cause it to interfere with itself.
What Makes a Film "Thin"?
In optics, "thin" is a relative term. A film is considered thin when its thickness is on the same order of magnitude as the wavelength of light. For visible light, this means thicknesses ranging from a few nanometers to a few thousand nanometers.
The Role of Interference
When a light wave strikes a thin film, some of it reflects off the top surface, and some of it passes through to reflect off the bottom surface (at the film-substrate boundary). These two reflected waves then recombine.
Because the second wave traveled a longer path (down and back up through the film), it is now out of sync with the first wave. This difference can lead to two outcomes:
- Constructive Interference: If the waves recombine in-phase, they reinforce each other, creating a stronger reflection.
- Destructive Interference: If the waves recombine out-of-phase, they cancel each other out, minimizing or eliminating the reflection.
Controlling Reflection and Transmission
By precisely engineering the film's thickness and material, we can control whether the interference is constructive or destructive for specific wavelengths (colors) of light. This gives us direct control over what is reflected and what is transmitted through the surface.
Key Factors That Define a Film's Behavior
A thin film's performance is not accidental; it is the result of careful design based on several critical factors.
Film Thickness
This is the most critical variable. Changing the thickness directly changes the path difference between the two reflected light waves, allowing engineers to "tune" the film for specific wavelengths and effects.
The Substrate Material
The properties of the underlying material (like glass or plastic) influence how light behaves when it crosses the boundary into the film. This interaction is a key part of the design calculation.
Deposition Technique
How the film is applied—a process called deposition—has a significant impact on its quality, uniformity, and durability. These techniques determine the final optical characteristics of the coated surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, thin-film technology is not without its constraints. Understanding these is crucial for practical application.
Sensitivity to Angle
The performance of many thin-film coatings changes with the angle of incident light. A coating designed for light hitting straight-on (at 0 degrees) may not perform as well for light hitting at a 45-degree angle.
Wavelength Dependency
Thin films are almost always optimized for a specific range of wavelengths. An anti-reflective coating designed for visible light on a camera lens will not be effective for infrared or ultraviolet light.
Mechanical and Chemical Durability
Optical coatings can be delicate. They must often be designed not only for their optical properties but also to withstand environmental factors like abrasion, humidity, and chemical exposure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The design of a thin film is dictated entirely by its intended purpose.
- If your primary focus is maximizing light transmission (e.g., camera lenses, eyeglasses): Your goal is an anti-reflective (AR) coating designed for destructive interference across the visible spectrum.
- If your primary focus is creating a mirror: You need a highly reflective coating designed for constructive interference at the desired wavelengths.
- If your primary focus is filtering specific colors (e.g., scientific filters, architectural glass): You need a dielectric filter engineered to transmit some wavelengths while reflecting others.
Ultimately, a thin film transforms a simple piece of glass or plastic into a precision optical component.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Manipulates light reflection, transmission, and absorption via thin-film interference. |
| Typical Thickness | Nanometers to micrometers (comparable to the wavelength of light). |
| Core Principle | Light waves reflecting from the top and bottom surfaces interfere, amplifying or canceling specific wavelengths. |
| Key Design Factors | Film thickness, substrate material, and deposition technique. |
| Common Applications | Anti-reflective coatings, mirrors, optical filters, architectural glass, and scientific instruments. |
Ready to integrate precision thin-film optics into your laboratory or product?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced optical coating development and application. Whether you are researching new materials or scaling up production, our solutions help you achieve superior control over light interaction.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific project requirements and enhance your optical performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials



















